Schizophrenia Management
Schizophrenia Management. Mobile Phone Number 01987073965, 01797522136. Schizophrenia is managed with a combined approach of antipsychotic medications, psychological therapies (like CBT and family therapy), social skills training, and support from a community mental health team (CMHT). Treatment is tailored to the individual’s needs, focusing on symptom control, improving daily functioning, and addressing physical health concerns and substance use.

Key Components of Schizophrenia Management
- Antipsychotic Medications: These are a cornerstone of treatment, helping to control symptoms like hallucinations and delusions. Some are available as long-acting injections.
- Psychological Therapies:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Helps individuals challenge and cope with delusions and distressing feelings.
- Psychoeducation: Teaches individuals and their families about the illness and how to manage it effectively.
- Family Therapy: Helps loved ones understand schizophrenia and provide supportive care.
- Community Mental Health Teams (CMHTs): A multidisciplinary team provides day-to-day support, including nurses, social workers, occupational therapists, psychologists, and psychiatrists. They help with care plans and ensure as much independence as possible.
- Occupational and Vocational Support: Therapies that help people return to work or study are also an important part of treatment.
- Physical Health Monitoring: Regular check-ups for physical conditions, as people with schizophrenia are at higher risk for issues like cardiovascular problems and diabetes, are essential.
- Substance Use Management: Individuals with schizophrenia have a higher risk of substance misuse, so addressing this is a vital part of the treatment plan.
- Individualized Care Plans: Patients work with their healthcare team to develop a personalized plan that addresses their specific needs and goals.
Treatment-Resistant Schizophrenia
- For individuals who do not respond well to standard antipsychotic medications, clozapine may be recommended.
- It is also a treatment option for those with persistent risks of suicide or aggression despite other treatments.
Patient Involvement
- Active participation from the person with schizophrenia is crucial for successful treatment. This includes being prepared to take an active role in decision-making about their care plan.
সিজোফ্রেনিয়া অ্যান্টিসাইকোটিক ওষুধ, মনস্তাত্ত্বিক থেরাপি (যেমন সিবিটি এবং পারিবারিক থেরাপি), সামাজিক দক্ষতা প্রশিক্ষণ এবং একটি কমিউনিটি মানসিক স্বাস্থ্য দলের (সিএমএইচটি) সহায়তার সম্মিলিত পদ্ধতিরমাধ্যমে পরিচালিত হয় । চিকিৎসা ব্যক্তির চাহিদা অনুযায়ী তৈরি করা হয়, লক্ষণ নিয়ন্ত্রণ, দৈনন্দিন কার্যকারিতা উন্নত করা এবং শারীরিক স্বাস্থ্য সংক্রান্ত উদ্বেগ এবং মাদক ব্যবহারের সমাধানের উপর দৃষ্টি নিবদ্ধ করে।
সিজোফ্রেনিয়া ব্যবস্থাপনার মূল উপাদানগুলি
- অ্যান্টিসাইকোটিক ওষুধ: এগুলো চিকিৎসার মূল ভিত্তি, যা হ্যালুসিনেশন এবং বিভ্রমের মতো লক্ষণগুলি নিয়ন্ত্রণে সাহায্য করে। কিছু দীর্ঘ-কার্যকরী ইনজেকশন হিসাবে পাওয়া যায়।
- মনস্তাত্ত্বিক থেরাপি:
- জ্ঞানীয় আচরণগত থেরাপি (CBT): ব্যক্তিদের বিভ্রান্তি এবং কষ্টদায়ক অনুভূতির চ্যালেঞ্জ মোকাবেলা করতে এবং মোকাবেলা করতে সহায়তা করে।
- মনোশিক্ষা: ব্যক্তি এবং তাদের পরিবারকে অসুস্থতা এবং এটি কার্যকরভাবে পরিচালনা করার পদ্ধতি সম্পর্কে শেখায়।
- পারিবারিক থেরাপি: প্রিয়জনদের সিজোফ্রেনিয়া বুঝতে এবং সহায়ক যত্ন প্রদান করতে সাহায্য করে।
- কমিউনিটি মানসিক স্বাস্থ্য দল (CMHTs): একটি বহুমুখী দল প্রতিদিনের সহায়তা প্রদান করে, যার মধ্যে রয়েছে নার্স, সমাজকর্মী, পেশাগত থেরাপিস্ট, মনোবিজ্ঞানী এবং মনোরোগ বিশেষজ্ঞ। তারা যত্ন পরিকল্পনায় সাহায্য করে এবং যতটা সম্ভব স্বাধীনতা নিশ্চিত করে।
- পেশাগত এবং বৃত্তিমূলক সহায়তা: যেসব থেরাপি মানুষকে কাজে বা পড়াশোনায় ফিরে যেতে সাহায্য করে, সেগুলোও চিকিৎসার একটি গুরুত্বপূর্ণ অংশ।
- শারীরিক স্বাস্থ্য পর্যবেক্ষণ: সিজোফ্রেনিয়ায় আক্রান্ত ব্যক্তিদের হৃদরোগ এবং ডায়াবেটিসের মতো সমস্যা হওয়ার ঝুঁকি বেশি থাকে, তাই নিয়মিত শারীরিক পরীক্ষা করা অপরিহার্য।
- পদার্থ ব্যবহার ব্যবস্থাপনা: সিজোফ্রেনিয়ায় আক্রান্ত ব্যক্তিদের পদার্থের অপব্যবহারের ঝুঁকি বেশি থাকে, তাই এটি মোকাবেলা করা চিকিৎসা পরিকল্পনার একটি গুরুত্বপূর্ণ অংশ।
- ব্যক্তিগতকৃত যত্ন পরিকল্পনা: রোগীরা তাদের স্বাস্থ্যসেবা দলের সাথে কাজ করে একটি ব্যক্তিগতকৃত পরিকল্পনা তৈরি করে যা তাদের নির্দিষ্ট চাহিদা এবং লক্ষ্য পূরণ করে।
সিজোফ্রেনিয়ার চিকিৎসা-প্রতিরোধী
- যারা স্ট্যান্ডার্ড অ্যান্টিসাইকোটিক ওষুধের প্রতি ভালো সাড়া দেয় না, তাদের জন্য ক্লোজাপাইন সুপারিশ করা যেতে পারে।
- অন্যান্য চিকিৎসা সত্ত্বেও আত্মহত্যা বা আগ্রাসনের ঝুঁকি যাদের রয়েছে তাদের জন্যও এটি একটি চিকিৎসার বিকল্প।
রোগীর সম্পৃক্ততা
- সফল চিকিৎসার জন্য সিজোফ্রেনিয়া আক্রান্ত ব্যক্তির সক্রিয় অংশগ্রহণ অত্যন্ত গুরুত্বপূর্ণ। এর মধ্যে রয়েছে তাদের যত্ন পরিকল্পনা সম্পর্কে সিদ্ধান্ত গ্রহণে সক্রিয় ভূমিকা নেওয়ার জন্য প্রস্তুত থাকা।
Why is it called Schizophrenia?
The term “schizophrenia” comes from the Greek words “schizo” (split) and “phrene” (mind). It was coined in 1911 by Swiss psychiatrist Eugen Bleuler to describe the “split” or fragmented nature of thinking, feeling, and behaving that he observed in his patients, rather than a split in personality or identity. The name was intended to capture the separation between cognitive functions like perception, memory, and thinking that occurs in the illness.
Key Aspects of the Term’s Meaning:
- Fragmented Thinking: The “split” refers to a disruption in the normal connections between different parts of the mind, leading to muddled or disorganized thoughts.
- Separation of Function: Bleuler used the term to highlight how functions like personality, memory, and perception become disconnected from one another in people with the illness.
- Misconception: Despite its origin, the term has mistakenly led to the popular myth that schizophrenia involves a “split personality” or multiple distinct personalities, which is not accurate.
Ongoing Debate:
- Due to the enduring misconception that it refers to a split personality, and its potential for stigma, there is ongoing discussion about changing the name.
- Some have suggested alternative names, such as “psychosis spectrum syndrome” or “integration disorder”, to more accurately and less stigmatizingly describe the condition.
“সিজোফ্রেনিয়া” শব্দটি গ্রীক শব্দ “সিজো” (বিভক্ত) এবং “ফ্রেন” (মন) থেকে এসেছে। ১৯১১ সালে সুইস মনোরোগ বিশেষজ্ঞ ইউজেন ব্লিউলার এটি তৈরি করেছিলেন , ব্যক্তিত্ব বা পরিচয়ের বিভাজনের পরিবর্তে, তার রোগীদের মধ্যে চিন্তাভাবনা, অনুভূতি এবং আচরণের “বিভক্ত” বা খণ্ডিত প্রকৃতি বর্ণনা করার জন্য। এই নামটি রোগের সময় ঘটে যাওয়া জ্ঞানীয় কার্যাবলী যেমন উপলব্ধি, স্মৃতি এবং চিন্তাভাবনার মধ্যে বিচ্ছেদকে তুলে ধরার উদ্দেশ্যে তৈরি করা হয়েছিল।
শব্দটির অর্থের মূল দিকগুলি:
- খণ্ডিত চিন্তাভাবনা: “বিভক্ত” বলতে মনের বিভিন্ন অংশের মধ্যে স্বাভাবিক সংযোগের ব্যাঘাতকে বোঝায়, যার ফলে চিন্তাভাবনা এলোমেলো বা অসংগঠিত হয়।
- ফাংশনের পৃথকীকরণ: ব্লিউলার এই শব্দটি ব্যবহার করে রোগে আক্রান্ত ব্যক্তিদের ব্যক্তিত্ব, স্মৃতি এবং উপলব্ধির মতো কার্যাবলী কীভাবে একে অপরের থেকে বিচ্ছিন্ন হয়ে পড়ে তা তুলে ধরেন।
- ভুল ধারণা: এর উৎপত্তি সত্ত্বেও, এই শব্দটি ভুল করে জনপ্রিয় মিথের জন্ম দিয়েছে যে সিজোফ্রেনিয়ায় “বিভক্ত ব্যক্তিত্ব” বা একাধিক স্বতন্ত্র ব্যক্তিত্ব জড়িত, যা সঠিক নয়।
চলমান বিতর্ক:
- এটি একটি বিভক্ত ব্যক্তিত্বকে বোঝায় এবং এর কলঙ্কের সম্ভাবনার কারণে, নাম পরিবর্তনের বিষয়ে চলমান আলোচনা চলছে।
- কেউ কেউ এই অবস্থাটিকে আরও সঠিকভাবে এবং কম কলঙ্কজনকভাবে বর্ণনা করার জন্য”সাইকোসিস স্পেকট্রাম সিনড্রোম” বা “ইন্টিগ্রেশন ডিসঅর্ডার”এর মতো বিকল্প নামগুলির পরামর্শ দিয়েছেন ।
Clinical Features of Schizophrenia
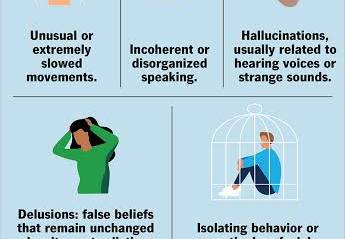
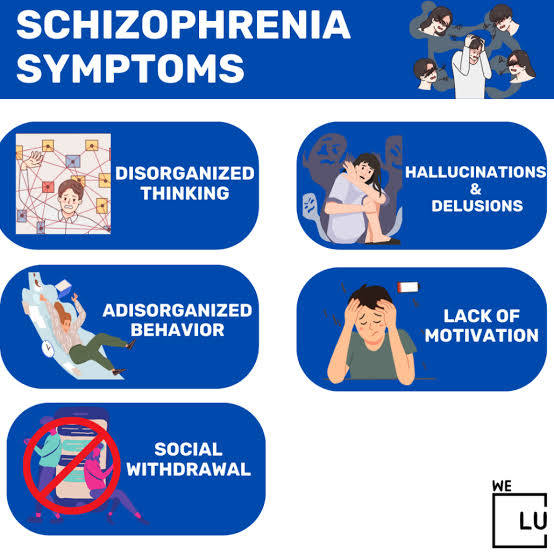
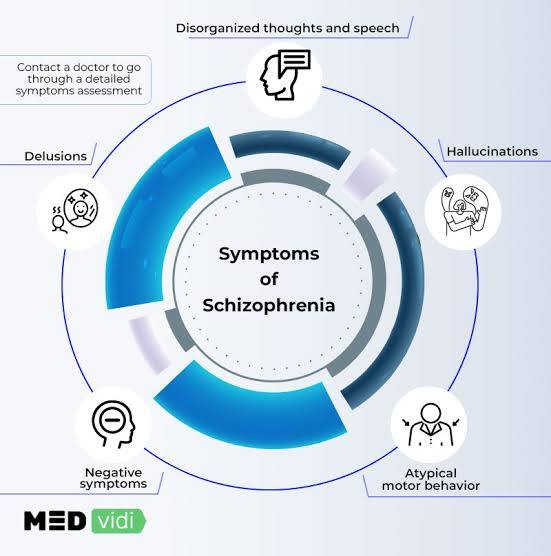
The clinical features of schizophrenia include positive symptoms like hallucinations (sensory experiences that aren’t real) and delusions (fixed false beliefs), negative symptoms such as a reduced range of emotions, loss of motivation, and social withdrawal, and cognitive impairments like difficulties with memory and executive function. Disorganized speech and behavior, including unusual movements, are also common. The symptoms can vary widely and often lead to social, occupational, and self-care difficulties.
Positive Symptoms
These are experiences that represent a break from reality.
- Hallucinations: Perceiving things that aren’t there, most commonly hearing voices, but also visual, tactile, or other sensory experiences.
- Delusions: Fixed, false beliefs that are not based in reality and are not explained by a person’s cultural background. Examples include the belief that one is being followed, has special powers, or that their thoughts are being controlled by others.
- Disorganized Speech and Thinking: Difficulty concentrating, jumping from one idea to another, and incoherent or muddled speech.
- Disorganized or Abnormal Behavior: Actions that appear bizarre, purposeless, or are inappropriate for the situation. This can include extreme agitation or catatonic behaviors, such as maintaining unusual postures or resisting movement.
Negative Symptoms
These involve a reduction or absence of normal emotional and motivational processes.
- Apathy and Lack of Motivation: Tremendous inertia, difficulty starting or completing tasks, and loss of interest or drive.
- Reduced Emotional Expression: A “flat affect,” where a person shows little emotion, or inappropriate emotional responses.
- Social Withdrawal: Avoiding friends and family and withdrawing from social activities.
- Poverty of Speech (Alogia): A lack of content in speech.
Cognitive Symptoms
These are impairments in various mental processes.
- Executive Function Deficits: Difficulty with planning, organizing, and abstract thinking.
- Memory Problems: Difficulties with working memory.
- Reduced Mental Processing Speed: Slower thought processes.
Diagnosis
A clinical diagnosis of schizophrenia is made after a thorough psychiatric history and mental status examination. It requires the presence of at least two symptoms, including delusions, hallucinations, disorganized speech, or disorganization behavior, lasting for at least one month. Other medical or psychiatric conditions that could cause these symptoms must be ruled out.
সিজোফ্রেনিয়ার ক্লিনিকাল বৈশিষ্ট্যগুলির মধ্যে রয়েছে ইতিবাচক লক্ষণ যেমন হ্যালুসিনেশন (ইন্দ্রিয়গত অভিজ্ঞতা যা বাস্তব নয়) এবং বিভ্রম (স্থির মিথ্যা বিশ্বাস), নেতিবাচক লক্ষণ যেমন আবেগের পরিসর হ্রাস, প্রেরণা হ্রাস এবং সামাজিকভাবে প্রত্যাহার, এবং স্মৃতিশক্তি এবং কার্যনির্বাহী কার্যকারিতায় অসুবিধার মতো জ্ঞানীয় দুর্বলতা। অস্বাভাবিক নড়াচড়া সহ বিশৃঙ্খল কথাবার্তা এবং আচরণও সাধারণ। লক্ষণগুলি ব্যাপকভাবে পরিবর্তিত হতে পারে এবং প্রায়শই সামাজিক, পেশাগত এবং স্ব-যত্নের অসুবিধার দিকে পরিচালিত করে।
ইতিবাচক লক্ষণ
এগুলো এমন অভিজ্ঞতা যা বাস্তবতা থেকে বিরতির প্রতিনিধিত্ব করে।
- হ্যালুসিনেশন: এমন জিনিসগুলি উপলব্ধি করা যা সেখানে নেই, সাধারণত কণ্ঠস্বর শোনা যায়, তবে দৃশ্য, স্পর্শকাতর বা অন্যান্য সংবেদনশীল অভিজ্ঞতাও।
- বিভ্রান্তি: স্থির, মিথ্যা বিশ্বাস যা বাস্তবতার উপর ভিত্তি করে নয় এবং কোনও ব্যক্তির সাংস্কৃতিক পটভূমি দ্বারা ব্যাখ্যা করা হয় না। উদাহরণ হিসেবে বলা যায়, একজনকে অনুসরণ করা হচ্ছে, তার বিশেষ ক্ষমতা আছে, অথবা তার চিন্তাভাবনা অন্যদের দ্বারা নিয়ন্ত্রিত হচ্ছে বলে বিশ্বাস করা যেতে পারে।
- অসংগঠিত কথাবার্তা এবং চিন্তাভাবনা: মনোযোগ দিতে অসুবিধা, এক ধারণা থেকে অন্য ধারণায় লাফিয়ে লাফিয়ে যাওয়া, এবং অসংলগ্ন বা অস্পষ্ট কথা বলা।
- অসংগঠিত বা অস্বাভাবিক আচরণ: এমন কাজ যা অদ্ভুত, উদ্দেশ্যহীন বলে মনে হয়, অথবা পরিস্থিতির জন্য অনুপযুক্ত। এর মধ্যে চরম উত্তেজনা বা ক্যাটাটোনিক আচরণ অন্তর্ভুক্ত থাকতে পারে, যেমন অস্বাভাবিক ভঙ্গি বজায় রাখা বা নড়াচড়া প্রতিরোধ করা।
নেতিবাচক লক্ষণ
এর মধ্যে স্বাভাবিক মানসিক এবং প্রেরণামূলক প্রক্রিয়াগুলির হ্রাস বা অনুপস্থিতি জড়িত।
- উদাসীনতা এবং প্রেরণার অভাব: প্রচণ্ড জড়তা, কাজ শুরু করতে বা সম্পন্ন করতে অসুবিধা, এবং আগ্রহ বা উদ্যম হ্রাস।
- আবেগের প্রকাশ কমে যাওয়া: একটি “সমতল প্রভাব”, যেখানে একজন ব্যক্তি খুব কম আবেগ, অথবা অনুপযুক্ত মানসিক প্রতিক্রিয়া দেখায়।
- সামাজিক প্রত্যাহার: বন্ধুবান্ধব এবং পরিবারকে এড়িয়ে চলা এবং সামাজিক কার্যকলাপ থেকে নিজেকে সরিয়ে নেওয়া।
- বাকশক্তির দারিদ্র্য (আলোজিয়া): বক্তৃতায় বিষয়বস্তুর অভাব।
জ্ঞানীয় লক্ষণ
এগুলো বিভিন্ন মানসিক প্রক্রিয়ার ব্যাঘাত।
- নির্বাহী কার্য ঘাটতি: পরিকল্পনা, সংগঠন এবং বিমূর্ত চিন্তাভাবনায় অসুবিধা।
- স্মৃতি সমস্যা: স্মৃতিশক্তির কার্যকারিতায় অসুবিধা।
- মানসিক প্রক্রিয়াকরণের গতি হ্রাস: ধীর চিন্তা প্রক্রিয়া।
রোগ নির্ণয়
সিজোফ্রেনিয়ার একটি ক্লিনিকাল রোগ নির্ণয় করা হয় পুঙ্খানুপুঙ্খ মানসিক ইতিহাস এবং মানসিক অবস্থা পরীক্ষার পরে। এর জন্য কমপক্ষে এক মাস স্থায়ী বিভ্রম, হ্যালুসিনেশন, অসংগঠিত কথাবার্তা, অথবা অসংগঠিত আচরণ সহ কমপক্ষে দুটি লক্ষণের উপস্থিতি প্রয়োজন। এই লক্ষণগুলির কারণ হতে পারে এমন অন্যান্য চিকিৎসা বা মানসিক অবস্থা বাদ দিতে হবে।
Causes of Schizophrenia
View all
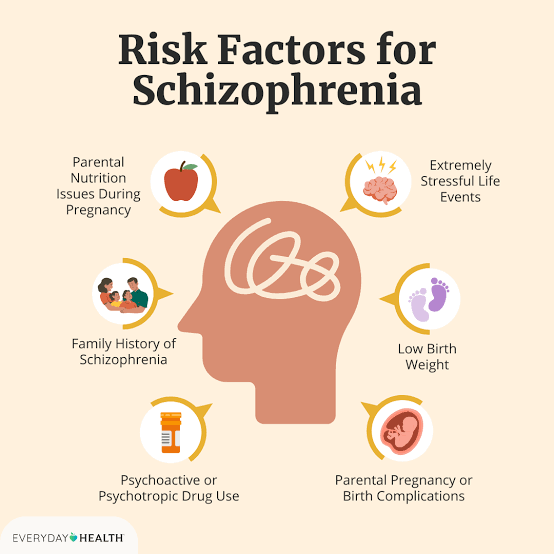
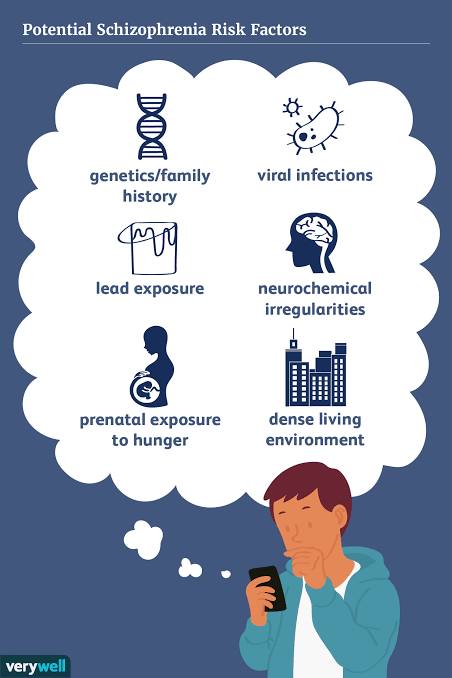
Schizophrenia doesn’t have one single cause but results from a complex interaction of genetic, brain development, and environmental factors. Key risk factors include a genetic predisposition, certain pregnancy and birth complications, childhood adversities like trauma, and the use of psychoactive substances, particularly cannabis during adolescence. These factors can interact, affecting brain structure, neurotransmitter function (like dopamine), and increasing vulnerability to the illness.
Genetic Factors
- Family History: Schizophrenia often runs in families, suggesting a genetic component, though no single gene is responsible.
- Rare Mutations: Rare genetic mutations, such as a deletion in chromosome 22q11, can significantly increase the risk of developing the disorder.
- Polygenic Risk: Schizophrenia is a polygenic disorder, meaning it’s influenced by the combined effects of many different genes spread across the genome.
Environmental Factors
- Pregnancy and Birth Complications: Factors during prenatal development, such as malnutrition or complications during birth, can increase risk.
- Adverse Childhood Experiences: Traumatic events, including physical, sexual, or emotional abuse during childhood, can increase vulnerability.
- Stressful Life Events: While not the sole cause, significant stressors like bereavement, job loss, or major life changes can trigger a psychotic episode in vulnerable individuals.
- Substance Use: Using certain drugs, especially cannabis during the teen and young adult years, is linked to an elevated risk of developing schizophrenia.
- Urban Environments: Growing up in an urban setting has been identified as a risk factor.
Brain and Neurotransmitter Factors
- Brain Differences: Studies show subtle differences in brain structure and connections in people with schizophrenia compared to healthy individuals.
- Neurotransmitter Imbalance: Alterations in brain chemicals, particularly neurotransmitters like dopamine and glutamate, are believed to play a role in the development of symptoms.
Viral Infections
- Infections Before Birth: Exposure to certain viruses, such as those in the Herpesviridae family, during the prenatal period is considered a contributing factor.
In essence, schizophrenia arises from a complex interplay between an individual’s genetic makeup, brain development, and exposure to various environmental challenges.
সিজোফ্রেনিয়ার কোনও একক কারণ নেই, তবে এটি জেনেটিক, মস্তিষ্কের বিকাশ এবং পরিবেশগত কারণগুলির জটিল মিথস্ক্রিয়ার ফলে ঘটে। প্রধান ঝুঁকির কারণগুলির মধ্যে রয়েছে জিনগত প্রবণতা, নির্দিষ্ট গর্ভাবস্থা এবং জন্মগত জটিলতা, শৈশবের প্রতিকূলতা যেমন আঘাত, এবং সাইকোঅ্যাকটিভ পদার্থের ব্যবহার, বিশেষ করে বয়ঃসন্ধিকালে গাঁজার ব্যবহার। এই কারণগুলি মিথস্ক্রিয়া করতে পারে, মস্তিষ্কের গঠন, নিউরোট্রান্সমিটারের কার্যকারিতা (যেমন ডোপামিন)প্রভাবিত করে এবং অসুস্থতার ঝুঁকি বাড়ায়।
জেনেটিক ফ্যাক্টর
- পারিবারিক ইতিহাস: সিজোফ্রেনিয়া প্রায়শই পরিবারগুলিতে ঘটে, যা একটি জেনেটিক উপাদান নির্দেশ করে, যদিও কোনও একক জিন এর জন্য দায়ী নয়।
- বিরল মিউটেশন: বিরল জেনেটিক মিউটেশন, যেমন ক্রোমোজোম 22q11-এ মুছে ফেলা, এই ব্যাধি হওয়ার ঝুঁকি উল্লেখযোগ্যভাবে বাড়িয়ে দিতে পারে।
- পলিজেনিক ঝুঁকি: সিজোফ্রেনিয়া একটি পলিজেনিক ব্যাধি, যার অর্থ এটি জিনোমে ছড়িয়ে থাকা বিভিন্ন জিনের সম্মিলিত প্রভাব দ্বারা প্রভাবিত হয়।
পরিবেশগত কারণ
- গর্ভাবস্থা এবং প্রসবের জটিলতা: প্রসবপূর্ব বিকাশের সময়কার কারণগুলি, যেমন অপুষ্টি বা জন্মের সময় জটিলতা, ঝুঁকি বাড়াতে পারে।
- শৈশবের প্রতিকূল অভিজ্ঞতা: শৈশবে শারীরিক, যৌন বা মানসিক নির্যাতন সহ আঘাতজনিত ঘটনাগুলি দুর্বলতা বৃদ্ধি করতে পারে।
- জীবনের চাপপূর্ণ ঘটনা: যদিও একমাত্র কারণ নয়, তবুও শোক, চাকরি হারানো, অথবা জীবনের বড় পরিবর্তনের মতো উল্লেখযোগ্য চাপগুলি দুর্বল ব্যক্তিদের মধ্যে একটি মানসিক রোগের সূচনা করতে পারে।
- পদার্থের ব্যবহার: কিশোর এবং তরুণ বয়সে কিছু নির্দিষ্ট ওষুধ, বিশেষ করে গাঁজা সেবন, সিজোফ্রেনিয়া হওয়ার ঝুঁকি বাড়ায়।
- নগর পরিবেশ: শহুরে পরিবেশে বেড়ে ওঠাকে ঝুঁকির কারণ হিসেবে চিহ্নিত করা হয়েছে।
মস্তিষ্ক এবং নিউরোট্রান্সমিটারের কারণগুলি
- মস্তিষ্কের পার্থক্য: গবেষণায় দেখা গেছে যে সুস্থ ব্যক্তিদের তুলনায় সিজোফ্রেনিয়া আক্রান্ত ব্যক্তিদের মস্তিষ্কের গঠন এবং সংযোগের মধ্যে সূক্ষ্ম পার্থক্য রয়েছে।
- নিউরোট্রান্সমিটার ভারসাম্যহীনতা: মস্তিষ্কের রাসায়নিক পদার্থের পরিবর্তন, বিশেষ করে ডোপামিন এবং গ্লুটামেটের মতো নিউরোট্রান্সমিটার, লক্ষণগুলির বিকাশে ভূমিকা পালন করে বলে মনে করা হয়।
ভাইরাল সংক্রমণ
- জন্মের আগে সংক্রমণ: প্রসবপূর্ব সময়কালেকিছু নির্দিষ্ট ভাইরাসের সংস্পর্শে আসা, যেমন হার্পিসভিরিডি পরিবারেরভাইরাস , একটি অবদানকারী কারণ হিসাবে বিবেচিত হয়।
মূলত, একজন ব্যক্তির জিনগত গঠন, মস্তিষ্কের বিকাশ এবং বিভিন্ন পরিবেশগত চ্যালেঞ্জের সংস্পর্শের মধ্যে জটিল পারস্পরিক ক্রিয়া থেকে স্কিজোফ্রেনিয়ার উদ্ভব হয়।
Diagnosis of Schizophrenia
A diagnosis of schizophrenia requires a mental health professional to conduct a comprehensive assessment, including evaluating specific symptoms like delusions, hallucinations, disorganized speech, or negative symptoms, and ensuring these have significantly impaired functioning for at least six months. Medical tests, such as blood and imaging scans, are used to rule out other medical or psychiatric conditions (e.g., substance use, tumors, or mood disorders) that could cause similar symptoms.
Key Diagnostic Criteria
According to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th Edition, Text Revision (DSM-5-TR), a diagnosis of schizophrenia involves the presence of two or more symptoms for a significant portion of time, including at least one of the following:
- Delusions: Fixed, false beliefs that are not changed even when presented with new facts.
- Hallucinations: Sensory experiences that aren’t real, such as hearing voices or seeing things others can’t perceive.
- Disorganized Speech: Incoherent or irrelevant speech.
- Grossly Disorganized or Catatonic Behavior: Erratic and inappropriate behaviors, or a significant decrease in movement and responsiveness.
- Negative Symptoms: A reduction in normal functions, such as a lack of emotional expression, decreased motivation, or withdrawal from social activities.
Ruling Out Other Causes
Before diagnosing schizophrenia, a healthcare provider must rule out other potential causes for the symptoms:
- Other Mental Health Disorders: Conditions like bipolar disorder, major depressive disorder with psychotic features, or schizoaffective disorder can present with psychotic symptoms.
- Substance Use: Use of illicit drugs or certain prescribed medications can cause temporary psychosis.
- Medical Conditions: Brain tumors, strokes, or other neurological conditions can manifest with similar symptoms.
How a Diagnosis is Made
- Medical Evaluation: A primary care physician or psychiatrist performs a thorough medical and psychological exam.
- Symptom Assessment: The healthcare professional will ask about symptoms and their duration and impact on daily life.
- Medical Tests: Blood tests and imaging scans like CT or MRI may be ordered to rule out other medical conditions.
- Referral: If symptoms persist and other causes are ruled out, the patient is referred to a community mental health team for further assessment by a psychiatrist.
A diagnosis of schizophrenia is made only after a comprehensive evaluation confirms the specific pattern of symptoms, rules out other disorders and medical causes, and identifies that the symptoms have significantly impacted the person’s ability to work, study, or perform daily tasks.
সিজোফ্রেনিয়া রোগ নির্ণয়ের জন্য একজন মানসিক স্বাস্থ্য পেশাদারকে একটি বিস্তৃত মূল্যায়ন পরিচালনা করতে হবে, যার মধ্যে রয়েছে বিভ্রম, হ্যালুসিনেশন, অসংলগ্ন বক্তৃতা বা নেতিবাচক লক্ষণগুলির মতো নির্দিষ্ট লক্ষণগুলির মূল্যায়ন করা এবং কমপক্ষে ছয় মাস ধরে এই লক্ষণগুলির কার্যকারিতা উল্লেখযোগ্যভাবে ব্যাহত হয়েছে তা নিশ্চিত করা। রক্ত এবং ইমেজিং স্ক্যানের মতো চিকিৎসা পরীক্ষাগুলি অন্যান্য চিকিৎসা বা মানসিক অবস্থা (যেমন, পদার্থের ব্যবহার, টিউমার, বা মেজাজের ব্যাধি) বাতিল করার জন্য ব্যবহৃত হয় যা একই রকম লক্ষণ সৃষ্টি করতে পারে।
মূল ডায়াগনস্টিক মানদণ্ড
ডায়াগনস্টিক অ্যান্ড স্ট্যাটিস্টিক্যাল ম্যানুয়াল অফ মেন্টাল ডিসঅর্ডারস, ৫ম সংস্করণ, টেক্সট রিভিশন (DSM-5-TR) অনুসারে, সিজোফ্রেনিয়া রোগ নির্ণয়ের ক্ষেত্রে উল্লেখযোগ্য সময়ের জন্য দুটি বা ততোধিক লক্ষণের উপস্থিতি জড়িত থাকে, যার মধ্যে কমপক্ষে নিম্নলিখিতগুলির মধ্যে একটি অন্তর্ভুক্ত থাকে:
- বিভ্রান্তি: স্থির, মিথ্যা বিশ্বাস যা নতুন তথ্য উপস্থাপন করার পরেও পরিবর্তিত হয় না।
- হ্যালুসিনেশন: সংবেদনশীল অভিজ্ঞতা যা বাস্তব নয়, যেমন কণ্ঠস্বর শোনা বা এমন কিছু দেখা যা অন্যরা বুঝতে পারে না।
- অসংগঠিত বক্তৃতা: অসংলগ্ন বা অপ্রাসঙ্গিক বক্তৃতা।
- চরমভাবে বিশৃঙ্খল বা ক্যাটাটোনিক আচরণ: অনিয়মিত এবং অনুপযুক্ত আচরণ, অথবা নড়াচড়া এবং প্রতিক্রিয়াশীলতায় উল্লেখযোগ্য হ্রাস।
- নেতিবাচক লক্ষণ: স্বাভাবিক ক্রিয়াকলাপ হ্রাস, যেমন আবেগের প্রকাশের অভাব, প্রেরণা হ্রাস, অথবা সামাজিক কার্যকলাপ থেকে সরে আসা।
অন্যান্য কারণ বাদ দেওয়া
সিজোফ্রেনিয়া নির্ণয়ের আগে, একজন স্বাস্থ্যসেবা প্রদানকারীকে লক্ষণগুলির অন্যান্য সম্ভাব্য কারণগুলি বাতিল করতে হবে:
- অন্যান্য মানসিক স্বাস্থ্য ব্যাধি: বাইপোলার ডিসঅর্ডার, মানসিক বৈশিষ্ট্য সহ প্রধান বিষণ্ণতাজনিত ব্যাধি, অথবা সিজোএফেক্টিভ ডিসঅর্ডারের মতো অবস্থাগুলি মানসিক লক্ষণগুলির সাথে উপস্থিত হতে পারে।
- পদার্থের ব্যবহার: অবৈধ ওষুধ বা নির্দিষ্ট কিছু নির্ধারিত ওষুধের ব্যবহার অস্থায়ী মনোবিকারের কারণ হতে পারে।
- চিকিৎসাগত অবস্থা: মস্তিষ্কের টিউমার, স্ট্রোক, বা অন্যান্য স্নায়বিক অবস্থার ক্ষেত্রেও একই রকম লক্ষণ দেখা দিতে পারে।
কিভাবে রোগ নির্ণয় করা হয়
- চিকিৎসা মূল্যায়ন: একজন প্রাথমিক চিকিৎসা চিকিৎসক বা মনোরোগ বিশেষজ্ঞ একটি পুঙ্খানুপুঙ্খ চিকিৎসা এবং মানসিক পরীক্ষা করেন।
- লক্ষণ মূল্যায়ন: স্বাস্থ্যসেবা পেশাদার লক্ষণগুলি, তাদের সময়কাল এবং দৈনন্দিন জীবনের উপর প্রভাব সম্পর্কে জিজ্ঞাসা করবেন।
- মেডিকেল পরীক্ষা: অন্যান্য চিকিৎসাগত অবস্থা বাতিল করার জন্য রক্ত পরীক্ষা এবং সিটি বা এমআরআই-এর মতো ইমেজিং স্ক্যানের নির্দেশ দেওয়া যেতে পারে।
- রেফারেল: যদি লক্ষণগুলি অব্যাহত থাকে এবং অন্যান্য কারণগুলি বাতিল করা হয়, তাহলে রোগীকে একজন মনোরোগ বিশেষজ্ঞের দ্বারা আরও মূল্যায়নের জন্য একটি কমিউনিটি মানসিক স্বাস্থ্য দলের কাছে পাঠানো হয়।
সিজোফ্রেনিয়া রোগ নির্ণয় তখনই করা হয় যখন একটি বিস্তৃত মূল্যায়ন লক্ষণগুলির নির্দিষ্ট ধরণ নিশ্চিত করে, অন্যান্য ব্যাধি এবং চিকিৎসা কারণগুলিকে বাতিল করে দেয় এবং সনাক্ত করে যে লক্ষণগুলি ব্যক্তির কাজ, পড়াশোনা বা দৈনন্দিন কাজ সম্পাদনের ক্ষমতাকে উল্লেখযোগ্যভাবে প্রভাবিত করেছে।
Investigations for Schizophrenia
Investigations for schizophrenia primarily involve a thorough clinical assessment by a mental health professional, rather than specific diagnostic tests, but may include blood tests and imaging to rule out other conditions. Common blood tests look for underlying medical issues, infections, or substance use, while brain imaging like MRI or CT scans can identify structural issues or tumors. An EEG may be used to rule out seizure disorders.
Clinical Assessment
- Detailed Evaluation: A mental health professional will conduct a comprehensive assessment of your symptoms, including delusions, hallucinations, disorganized thinking, and changes in emotions and behavior.
- History: Information about your personal, family, and social history is gathered to understand the context of your symptoms.
- Involving Others: Family members or friends can provide valuable insights into your experiences and behavior, especially since your own perception may be affected.
Tests to Rule Out Other Conditions
- Blood Tests: These can check for infections, anemia, or chemical imbalances that might mimic psychiatric symptoms. Specific tests may include:
- Complete Blood Count (CBC)
- Liver and kidney function tests
- Thyroid function tests
- Drug toxicology screen: to detect substance use
- Imaging Tests:
- MRI or CT Scan: Brain scans can help rule out tumors, strokes, or structural changes that might cause psychotic symptoms.
- Electroencephalogram (EEG): This test can help rule out seizure disorders or other abnormalities in brain activity.
Diagnostic Criteria
- While there are no specific tests for schizophrenia, diagnosis relies on meeting the criteria outlined in diagnostic manuals like the DSM-5.
- This involves the presence of specific symptoms, such as hallucinations and delusions, along with significant disruptions in social or occupational functioning, persisting for a defined period.
- The symptoms must also not be better explained by another medical condition, substance use, or a different mental health disorder.
সিজোফ্রেনিয়ার তদন্তে প্রাথমিকভাবে নির্দিষ্ট রোগ নির্ণয়ের পরীক্ষার পরিবর্তে একজন মানসিক স্বাস্থ্য পেশাদারের দ্বারা একটি পুঙ্খানুপুঙ্খ ক্লিনিকাল মূল্যায়ন জড়িত থাকে, তবে অন্যান্য অবস্থা বাতিল করার জন্য রক্ত পরীক্ষা এবং ইমেজিং অন্তর্ভুক্ত থাকতে পারে। সাধারণ রক্ত পরীক্ষায় অন্তর্নিহিত চিকিৎসা সমস্যা, সংক্রমণ বা পদার্থের ব্যবহার সনাক্ত করা যায়, অন্যদিকে এমআরআই বা সিটি স্ক্যানের মতো মস্তিষ্কের ইমেজিং কাঠামোগত সমস্যা বা টিউমার সনাক্ত করতে পারে। খিঁচুনির ব্যাধি বাদ দেওয়ার জন্য একটি EEG ব্যবহার করা যেতে পারে।
ক্লিনিক্যাল মূল্যায়ন
- বিস্তারিত মূল্যায়ন: একজন মানসিক স্বাস্থ্য পেশাদার আপনার লক্ষণগুলির একটি বিস্তৃত মূল্যায়ন পরিচালনা করবেন, যার মধ্যে রয়েছে বিভ্রম, হ্যালুসিনেশন, অসংগঠিত চিন্তাভাবনা এবং আবেগ ও আচরণের পরিবর্তন।
- ইতিহাস: আপনার লক্ষণগুলির প্রেক্ষাপট বোঝার জন্য আপনার ব্যক্তিগত, পারিবারিক এবং সামাজিক ইতিহাস সম্পর্কে তথ্য সংগ্রহ করা হয়।
- অন্যদের সম্পৃক্ত করা: পরিবারের সদস্যরা বা বন্ধুরা আপনার অভিজ্ঞতা এবং আচরণ সম্পর্কে মূল্যবান অন্তর্দৃষ্টি প্রদান করতে পারে, বিশেষ করে যেহেতু আপনার নিজস্ব ধারণা প্রভাবিত হতে পারে।
অন্যান্য অবস্থা বাতিল করার জন্য পরীক্ষা
- রক্ত পরীক্ষা: এগুলো সংক্রমণ, রক্তাল্পতা, অথবা রাসায়নিক ভারসাম্যহীনতা পরীক্ষা করতে পারে যা মানসিক লক্ষণগুলির অনুকরণ করতে পারে। নির্দিষ্ট পরীক্ষাগুলির মধ্যে অন্তর্ভুক্ত থাকতে পারে:
- সম্পূর্ণ রক্ত গণনা (সিবিসি)
- লিভার এবং কিডনির কার্যকারিতা পরীক্ষা
- থাইরয়েড ফাংশন পরীক্ষা
- ড্রাগ টক্সিকোলজি স্ক্রিন: পদার্থের ব্যবহার সনাক্ত করতে
- ইমেজিং পরীক্ষা:
- এমআরআই বা সিটি স্ক্যান: মস্তিষ্কের স্ক্যানগুলি টিউমার, স্ট্রোক, বা মানসিক লক্ষণগুলির কারণ হতে পারে এমন কাঠামোগত পরিবর্তনগুলি বাতিল করতে সাহায্য করতে পারে।
- ইলেক্ট্রোএনসেফালোগ্রাম (EEG): এই পরীক্ষাটি মস্তিষ্কের কার্যকলাপে খিঁচুনিজনিত ব্যাধি বা অন্যান্য অস্বাভাবিকতা বাতিল করতে সাহায্য করতে পারে।
ডায়াগনস্টিক মানদণ্ড
- যদিও সিজোফ্রেনিয়ার জন্য কোন নির্দিষ্ট পরীক্ষা নেই, রোগ নির্ণয় নির্ভর করে DSM-5 এর মতো ডায়াগনস্টিক ম্যানুয়ালগুলিতে বর্ণিত মানদণ্ড পূরণের উপর।
- এর মধ্যে রয়েছে নির্দিষ্ট লক্ষণগুলির উপস্থিতি, যেমন হ্যালুসিনেশন এবং বিভ্রম, এবং সামাজিক বা পেশাগত কার্যকারিতায় উল্লেখযোগ্য ব্যাঘাত, যা একটি নির্দিষ্ট সময়ের জন্য স্থায়ী হয়।
- লক্ষণগুলি অন্য কোনও চিকিৎসা অবস্থা, মাদকাসক্তি, বা অন্য কোনও মানসিক স্বাস্থ্য ব্যাধি দ্বারা আরও ভালভাবে ব্যাখ্যা করা উচিত নয়।
When Schizophrenia Patient Become Angry?
A schizophrenia patient may become angry due to symptoms of psychosis, paranoia, delusions, or emotional distress. Aggression is a serious problem, but it is often a sign of untreated symptoms, substance abuse, or extreme stress rather than an intrinsic trait. To handle an aggressive patient, ensure everyone’s safety by removing yourself from immediate danger, calling for professional help (like a mental health crisis team or emergency services), and encouraging them to adhere to their prescribed treatment and medication to reduce the risk of future anger.
Why a Patient Might Become Angry
- Psychotic Symptoms: During psychotic episodes, changes in behavior are common, and a person may become upset, confused, suspicious, or angry.
- Delusions and Paranoia: Delusions and paranoia can lead to a sense of threat or hostility, potentially resulting in aggressive behavior.
- Emotional Distress: Anxiety, frustration, or other emotional states can trigger anger.
- Untreated Symptoms: Inadequate treatment for schizophrenia can increase the risk of aggression.
- Substance Abuse: Substance abuse can precipitate or worsen aggressive behavior.
- Environmental Stress: The patient’s environment, including social interactions and changes in surroundings, can play a role in aggression.
- Frustrating Events: Environmental triggers or frustrating events can cause impulsive aggressive outbursts.
What to Do When a Patient is Angry
- Prioritize Safety: If you feel you are in immediate danger, leave the situation or call for emergency help by dialing 911 or your local emergency services number.
- Call for Professional Help: Contact a local mental health crisis line or a mental health professional for assistance.
- Encourage Treatment Adherence: Help the patient understand the importance of their medication and treatment, as consistency can significantly reduce aggression.
- Work as a Team: Closely work with the patient, their family, and caregivers to create a supportive and individualized care plan.
- Be Aware of Triggers: Identify and address factors in the patient’s environment that may contribute to their anger.
- Seek Support for Caregivers: Caregivers of aggressive patients with schizophrenia face unique challenges and can benefit from support and resources.
Preventing Future Anger
- Medication: Ensure the patient takes prescribed antipsychotics, as they can help manage symptoms and reduce aggression.
- Individualized Care: Develop a treatment plan tailored to the patient’s specific needs and environment.
- Supportive Environment: Work to create a low-stress, supportive social environment for the patient.
একজন সিজোফ্রেনিয়া রোগী মনোরোগ, প্যারানয়া, বিভ্রম বা মানসিক যন্ত্রণার লক্ষণগুলির কারণে রেগে যেতে পারেন । আগ্রাসন একটি গুরুতর সমস্যা, তবে এটি প্রায়শই কোনও অন্তর্নিহিত বৈশিষ্ট্যের পরিবর্তে চিকিৎসা না করা লক্ষণ, মাদকদ্রব্যের অপব্যবহার বা চরম চাপের লক্ষণ। একজন আক্রমণাত্মক রোগীকে সামলাতে, তাৎক্ষণিক বিপদ থেকে নিজেকে সরিয়ে নিয়ে, পেশাদার সাহায্যের জন্য (যেমন মানসিক স্বাস্থ্য সংকট দল বা জরুরি পরিষেবা) ডাকা এবং ভবিষ্যতে রাগের ঝুঁকি কমাতে তাদের নির্ধারিত চিকিৎসা এবং ওষুধ মেনে চলতে উৎসাহিত করার মাধ্যমে সকলের নিরাপত্তা নিশ্চিত করুন।
কেন একজন রোগী রেগে যেতে পারেন
- মানসিক লক্ষণ: মানসিক রোগের সময়, আচরণে পরিবর্তন আসা খুবই সাধারণ এবং একজন ব্যক্তি বিরক্ত, বিভ্রান্ত, সন্দেহজনক বা রাগান্বিত হতে পারেন।
- বিভ্রান্তি এবং প্যারানোয়া: বিভ্রান্তি এবং প্যারানয়া হুমকি বা শত্রুতার অনুভূতির দিকে পরিচালিত করতে পারে, যার ফলে আক্রমণাত্মক আচরণের সম্ভাবনা থাকে।
- মানসিক যন্ত্রণা: উদ্বেগ, হতাশা, বা অন্যান্য মানসিক অবস্থা রাগের কারণ হতে পারে।
- চিকিৎসা না করা লক্ষণ: সিজোফ্রেনিয়ার অপর্যাপ্ত চিকিৎসা আগ্রাসনের ঝুঁকি বাড়িয়ে দিতে পারে।
- মাদকদ্রব্যের অপব্যবহার: মাদকদ্রব্যের অপব্যবহার আক্রমণাত্মক আচরণকে ত্বরান্বিত করতে পারে বা আরও খারাপ করতে পারে।
- পরিবেশগত চাপ: রোগীর পরিবেশ, যার মধ্যে সামাজিক মিথস্ক্রিয়া এবং পারিপার্শ্বিক পরিবর্তন অন্তর্ভুক্ত, আগ্রাসনে ভূমিকা পালন করতে পারে।
- হতাশাজনক ঘটনা: পরিবেশগত কারণ বা হতাশাজনক ঘটনাগুলি আবেগপ্রবণ আক্রমণাত্মক বিস্ফোরণের কারণ হতে পারে।
রোগী রেগে গেলে কী করবেন
- নিরাপত্তাকে অগ্রাধিকার দিন: যদি আপনার মনে হয় আপনি তাৎক্ষণিক বিপদের মধ্যে আছেন, তাহলে পরিস্থিতি ছেড়ে চলে যান অথবা 911 অথবা আপনার স্থানীয় জরুরি পরিষেবা নম্বরে ডায়াল করে জরুরি সাহায্যের জন্য কল করুন।
- পেশাদার সাহায্যের জন্য কল করুন: সহায়তার জন্য স্থানীয় মানসিক স্বাস্থ্য সংকট লাইন বা মানসিক স্বাস্থ্য পেশাদারের সাথে যোগাযোগ করুন।
- চিকিৎসা মেনে চলাকে উৎসাহিত করুন: রোগীকে তাদের ওষুধ এবং চিকিৎসার গুরুত্ব বুঝতে সাহায্য করুন, কারণ ধারাবাহিকতা আগ্রাসন উল্লেখযোগ্যভাবে কমাতে পারে।
- একটি দল হিসেবে কাজ করুন: রোগী, তাদের পরিবার এবং যত্নশীলদের সাথে ঘনিষ্ঠভাবে কাজ করে একটি সহায়ক এবং ব্যক্তিগতকৃত যত্ন পরিকল্পনা তৈরি করুন।
- ট্রিগার সম্পর্কে সচেতন থাকুন: রোগীর পরিবেশের এমন কিছু কারণ চিহ্নিত করুন এবং সমাধান করুন যা তাদের রাগের কারণ হতে পারে।
- যত্নশীলদের জন্য সহায়তা চাও: সিজোফ্রেনিয়ায় আক্রান্ত আক্রমণাত্মক রোগীদের যত্নশীলরা অনন্য চ্যালেঞ্জের মুখোমুখি হন এবং সহায়তা এবং সংস্থান থেকে উপকৃত হতে পারেন।
ভবিষ্যতের রাগ প্রতিরোধ করা
- ঔষধ: রোগীর নির্ধারিত অ্যান্টিসাইকোটিকস গ্রহণ নিশ্চিত করুন, কারণ তারা লক্ষণগুলি পরিচালনা করতে এবং আক্রমণাত্মকতা কমাতে সাহায্য করতে পারে।
- ব্যক্তিগতকৃত যত্ন: রোগীর নির্দিষ্ট চাহিদা এবং পরিবেশের সাথে মানানসই একটি চিকিৎসা পরিকল্পনা তৈরি করুন।
- সহায়ক পরিবেশ: রোগীর জন্য একটি কম চাপযুক্ত, সহায়ক সামাজিক পরিবেশ তৈরি করার জন্য কাজ করুন।
Complications of Schizophrenia
Complications of schizophrenia include increased risk of suicide, co-occurring mental health conditions like depression and substance use disorders, and negative effects on physical health, such as higher rates of obesity, heart disease, and diabetes. Individuals may also experience cognitive impairment, making it difficult to work or complete education, leading to homelessness and financial issues. Socially, stigma and negative symptoms can lead to social isolation and relationship problems, and there is a generally lower life expectancy for people with schizophrenia.
Mental and Emotional Complications
- Suicide and self-harm: The risk of suicide, suicide attempts, and self-harm is significantly elevated.
- Co-occurring disorders: Schizophrenia often co-occurs with other mental health conditions, including depression, anxiety, and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD).
- Substance misuse: There is a high rate of substance use, such as alcohol and drugs, with individuals often using them to self-medicate symptoms.
Social and Lifestyle Complications
- Social isolation: Symptoms like social withdrawal and lack of motivation can lead to long-term disconnection from others.
- Employment and education challenges: Cognitive difficulties, such as problems with attention and memory, can make it hard to maintain a job or pursue education.
- Homelessness and financial issues: Impaired work ability and other factors can contribute to financial problems and homelessness.
- Stigma and victimization: Societal stigma associated with the condition can negatively impact relationships and increase the risk of being victimized.
Physical Health Complications
- Cardiovascular and metabolic issues: Schizophrenia is linked to a higher risk of physical health problems like obesity, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes.
- Reduced life expectancy: On average, people with schizophrenia die significantly earlier than the general population due to a combination of these complications.
Cognitive Complications
- Cognitive decline: Difficulty with attention, memory, executive functions like planning, and problem-solving are common.
- Disorganized thinking and behavior: The ability to organize thoughts, speak coherently, and complete tasks can be impaired.
সিজোফ্রেনিয়ার জটিলতার মধ্যে রয়েছে আত্মহত্যার ঝুঁকি বৃদ্ধি, বিষণ্ণতা এবং মাদক ব্যবহারের ব্যাধির মতো সহ-ঘটমান মানসিক স্বাস্থ্যের অবস্থা এবং শারীরিক স্বাস্থ্যের উপর নেতিবাচক প্রভাব, যেমন স্থূলতা, হৃদরোগ এবং ডায়াবেটিসের উচ্চ হার। ব্যক্তিরা জ্ঞানীয় দুর্বলতাও অনুভব করতে পারে, যার ফলে কাজ করা বা শিক্ষা সম্পূর্ণ করা কঠিন হয়ে পড়ে, যার ফলে গৃহহীনতা এবং আর্থিক সমস্যা দেখা দেয়। সামাজিকভাবে, কলঙ্ক এবং নেতিবাচক লক্ষণগুলি সামাজিক বিচ্ছিন্নতা এবং সম্পর্কের সমস্যার দিকে পরিচালিত করতে পারে এবং সিজোফ্রেনিয়ায় আক্রান্ত ব্যক্তিদের আয়ু সাধারণত কম থাকে।
মানসিক এবং আবেগগত জটিলতা
- আত্মহত্যা এবং আত্ম-ক্ষতি: আত্মহত্যা, আত্মহত্যার প্রচেষ্টা এবং নিজের ক্ষতি করার ঝুঁকি উল্লেখযোগ্যভাবে বৃদ্ধি পায়।
- সহ-ঘটমান ব্যাধি: সিজোফ্রেনিয়া প্রায়শই অন্যান্য মানসিক স্বাস্থ্যের অবস্থার সাথে সহ-সমন্বিত হয়, যার মধ্যে রয়েছে বিষণ্নতা, উদ্বেগ এবং অবসেসিভ-বাধ্যতামূলক ব্যাধি (OCD)।
- পদার্থের অপব্যবহার: অ্যালকোহল এবং মাদকের মতো পদার্থ ব্যবহারের হার বেশি, যেখানে ব্যক্তিরা প্রায়শই লক্ষণগুলি স্ব-ঔষধের জন্য এগুলি ব্যবহার করে।
সামাজিক এবং জীবনযাত্রার জটিলতা
- সামাজিক আলাদা থাকা: সামাজিকভাবে দূরে থাকা এবং অনুপ্রেরণার অভাবের মতো লক্ষণগুলি অন্যদের থেকে দীর্ঘমেয়াদী বিচ্ছিন্নতার দিকে পরিচালিত করতে পারে।
- কর্মসংস্থান এবং শিক্ষার চ্যালেঞ্জ: মনোযোগ এবং স্মৃতিশক্তির সমস্যাগুলির মতো জ্ঞানীয় সমস্যাগুলি চাকরি বজায় রাখা বা পড়াশোনা করা কঠিন করে তুলতে পারে।
- গৃহহীনতা এবং আর্থিক সমস্যা: কর্মক্ষমতার অভাব এবং অন্যান্য কারণ আর্থিক সমস্যা এবং গৃহহীনতার কারণ হতে পারে।
- কলঙ্ক এবং নির্যাতন: এই অবস্থার সাথে সম্পর্কিত সামাজিক কলঙ্ক সম্পর্কের উপর নেতিবাচক প্রভাব ফেলতে পারে এবং শিকার হওয়ার ঝুঁকি বাড়াতে পারে।
শারীরিক স্বাস্থ্য জটিলতা
- হৃদরোগ এবং বিপাকীয় সমস্যা: সিজোফ্রেনিয়া স্থূলতা, হৃদরোগ এবং ডায়াবেটিসের মতো শারীরিক স্বাস্থ্য সমস্যার উচ্চ ঝুঁকির সাথে যুক্ত।
- আয়ু হ্রাস: গড়ে, এই জটিলতার সংমিশ্রণের কারণে সিজোফ্রেনিয়ায় আক্রান্ত ব্যক্তিরা সাধারণ জনগণের তুলনায় উল্লেখযোগ্যভাবে আগে মারা যান।
জ্ঞানীয় জটিলতা
- জ্ঞানীয় পতন: মনোযোগ, স্মৃতিশক্তি, পরিকল্পনার মতো কার্যনির্বাহী কার্যাবলী এবং সমস্যা সমাধানে অসুবিধা সাধারণ।
- অসংগঠিত চিন্তাভাবনা এবং আচরণ: চিন্তাভাবনা সংগঠিত করার, সুসংগতভাবে কথা বলার এবং কাজগুলি সম্পন্ন করার ক্ষমতা ব্যাহত হতে পারে।
Prevention of Schizophrenia
There is no guaranteed way to prevent schizophrenia, but you can reduce your risk by avoiding drug and alcohol abuse, especially during adolescence. Maintaining strong social connections, managing stress effectively, taking care of your physical health, and protecting yourself from head injuries are also recommended. For those with a family history or other risk factors, seeking therapy for trauma and getting mental health support early can help.
Lifestyle & Behavioral Factors
- Avoidance of Substance Use: Illicit drugs, particularly cannabis, cocaine, and methamphetamines, and heavy alcohol use are strongly linked to schizophrenia.
- Stress Management: Develop healthy coping strategies for stress and anxiety through therapy, social support, or other stress-reduction techniques.
- Social Engagement: Stay connected with friends and family to prevent loneliness and maintain self-esteem and a positive outlook.
- Trauma Therapy: Seek professional help for childhood traumas like brain injuries or abuse, as this can help prevent potential future disorders.
Physical & Environmental Factors
- Physical Fitness: Regular exercise and good nutrition contribute to overall physical and mental well-being.
- Head Injury Protection: Wear helmets during contact sports or while biking to prevent head injuries, which are a risk factor.
- Dietary Considerations: While not a direct prevention, some research suggests Omega-3 fatty acids may help, though more evidence is needed.
For High-Risk Individuals
- Early Mental Health Support: Accessing early support, even for other mental health conditions, can improve overall emotional and physical health.
- Family History Considerations: If schizophrenia runs in your family, be particularly vigilant about substance use and seek support for any traumatic experiences.
- Develop an Action Plan: Work with a doctor to create an emergency action plan that outlines known triggers, personal warning signs of psychosis, and emergency contacts.
সিজোফ্রেনিয়া প্রতিরোধের কোন নিশ্চিত উপায় নেই, তবে আপনি মাদক ও অ্যালকোহলের অপব্যবহার এড়িয়েআপনার ঝুঁকি কমাতে পারেন , বিশেষ করে বয়ঃসন্ধিকালে। শক্তিশালী সামাজিক সংযোগ বজায় রাখা, কার্যকরভাবে চাপ পরিচালনা করা, আপনার শারীরিক স্বাস্থ্যের যত্ন নেওয়া এবং মাথার আঘাত থেকে নিজেকে রক্ষা করার পরামর্শ দেওয়া হয়। যাদের পারিবারিক ইতিহাস বা অন্যান্য ঝুঁকির কারণ রয়েছে, তাদের জন্য মানসিক আঘাতের জন্য থেরাপি নেওয়া এবং প্রাথমিকভাবে মানসিক স্বাস্থ্য সহায়তা নেওয়া সাহায্য করতে পারে।
জীবনধারা এবং আচরণগত কারণগুলি
- পদার্থ ব্যবহার পরিহার: অবৈধ মাদক, বিশেষ করে গাঁজা, কোকেন এবং মেথামফেটামিনএবং অতিরিক্ত অ্যালকোহল সেবন সিজোফ্রেনিয়ার সাথে দৃঢ়ভাবে জড়িত।
- মানসিক চাপ ব্যবস্থাপনা: থেরাপি, সামাজিক সহায়তা, অথবা অন্যান্য চাপ-হ্রাস কৌশলের মাধ্যমে চাপ এবং উদ্বেগের জন্য স্বাস্থ্যকর মোকাবেলার কৌশল তৈরি করুন।
- সামাজিক সম্পৃক্ততা: একাকীত্ব এড়াতে এবং আত্মসম্মান এবং ইতিবাচক দৃষ্টিভঙ্গি বজায় রাখতে বন্ধুবান্ধব এবং পরিবারের সাথে যোগাযোগ রাখুন।
- ট্রমা থেরাপি: শৈশবের আঘাত যেমন মস্তিষ্কের আঘাত বা নির্যাতনের জন্য পেশাদার সাহায্য নিন, কারণ এটি ভবিষ্যতের সম্ভাব্য ব্যাধি প্রতিরোধ করতে সাহায্য করতে পারে।
ভৌত ও পরিবেশগত কারণসমূহ
- শারীরিক সুস্থতা: নিয়মিত ব্যায়াম এবং ভালো পুষ্টি সামগ্রিক শারীরিক ও মানসিক সুস্থতায় অবদান রাখে।
- মাথার আঘাতের সুরক্ষা: মাথার আঘাত এড়াতে, যা ঝুঁকিপূর্ণ, স্পর্শে খেলাধুলার সময় বা সাইকেল চালানোর সময় হেলমেট পরুন।
- খাদ্যতালিকাগত বিবেচ্য বিষয়গুলি: যদিও সরাসরি প্রতিরোধ নয়, কিছু গবেষণা পরামর্শ দেয় যে ওমেগা-৩ ফ্যাটি অ্যাসিড সাহায্য করতে পারে, যদিও আরও প্রমাণ প্রয়োজন।
উচ্চ ঝুঁকিপূর্ণ ব্যক্তিদের জন্য
- প্রাথমিক মানসিক স্বাস্থ্য সহায়তা: অন্যান্য মানসিক স্বাস্থ্যের অবস্থার জন্যও প্রাথমিক সহায়তা পাওয়া সামগ্রিক মানসিক এবং শারীরিক স্বাস্থ্যের উন্নতি করতে পারে।
- পারিবারিক ইতিহাস বিবেচনা: যদি আপনার পরিবারে সিজোফ্রেনিয়া থাকে, তাহলে মাদক সেবনের ব্যাপারে বিশেষভাবে সতর্ক থাকুন এবং যেকোনো আঘাতজনিত অভিজ্ঞতার জন্য সহায়তা নিন।
- একটি কর্ম পরিকল্পনা তৈরি করুন: একজন ডাক্তারের সাথে কাজ করে একটি জরুরি কর্ম পরিকল্পনা তৈরি করুন যাতে পরিচিত ট্রিগার, সাইকোসিসের ব্যক্তিগত সতর্কতা লক্ষণ এবং জরুরি যোগাযোগের রূপরেখা থাকে।
Prevention of Hallucinations
Prevention strategies for human hallucinations focus on addressing underlying causes like stress, sleep deprivation, substance use, and certain medical conditions through lifestyle changes, medication adjustments, and therapy. For AI, prevention involves grounding outputs in verifiable data using techniques like Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), providing clear prompts, and fine-tuning models on specific, curated content.
For Human Hallucinations
- Lifestyle and Environment:
- Improve Sleep Hygiene: Maintain a regular sleep schedule, get enough quality sleep, and avoid stimulants like caffeine or alcohol close to bedtime.
- Healthy Habits: Eat balanced meals and get regular physical activity to help manage symptoms.
- Manage Stress: Practice stress-reduction techniques and create a peaceful sleep environment to alleviate stress and anxiety.
- Adjust Environment: Reduce triggering sights and objects by improving lighting, covering mirrors, or removing objects that cause visual disturbances.
- Medication and Treatment:
- Address Substance Use: Avoid illicit drugs, excessive alcohol, and medications that cause hallucinations.
- Medication Adjustments: If medication is a cause, especially for conditions like Parkinson’s disease, the treating doctor may adjust or stop certain drugs, such as dopamine agonists or anticholinergics.
- Medical Treatment: Antipsychotic medications, given under medical supervision, may be used for severe hallucinations, though they should be reviewed regularly due to potential side effects.
- Psychosocial Strategies:
- Education and Counseling: Educate yourself and your family about hallucinations to help manage symptoms and understand the importance of adhering to treatments.
- Support: Seek support groups and counseling to help cope with the experience of hallucinations.
মানুষের হ্যালুসিনেশন প্রতিরোধের কৌশলগুলি জীবনধারা পরিবর্তন, ওষুধের সমন্বয় এবং থেরাপির মাধ্যমে মানসিক চাপ, ঘুমের অভাব, মাদকদ্রব্যের ব্যবহার এবং কিছু নির্দিষ্ট চিকিৎসা অবস্থার মতো অন্তর্নিহিত কারণগুলিকে মোকাবেলা করারউপর দৃষ্টি নিবদ্ধ করে । AI-এর ক্ষেত্রে, প্রতিরোধের মধ্যে রয়েছে Retrieval-Augmented Generation(RAG) এর মতো কৌশল ব্যবহার করে যাচাইযোগ্য ডেটার আউটপুটগুলিকে গ্রাউন্ডিং করা , স্পষ্ট প্রম্পট প্রদান করা এবং নির্দিষ্ট, কিউরেটেড কন্টেন্টের উপর মডেলগুলিকে সূক্ষ্ম-টিউনিং করা।
মানুষের হ্যালুসিনেশনের জন্য
- জীবনধারা এবং পরিবেশ:
- ঘুমের স্বাস্থ্যবিধি উন্নত করুন: নিয়মিত ঘুমের সময়সূচী বজায় রাখুন, পর্যাপ্ত মানসম্পন্ন ঘুম পান এবং ঘুমানোর আগে ক্যাফেইন বা অ্যালকোহলের মতো উত্তেজক পদার্থ এড়িয়ে চলুন।
- স্বাস্থ্যকর অভ্যাস: লক্ষণগুলি পরিচালনা করতে সুষম খাবার খান এবং নিয়মিত শারীরিক কার্যকলাপ করুন।
- মানসিক চাপ নিয়ন্ত্রণ করুন: মানসিক চাপ কমানোর কৌশল অনুশীলন করুন এবং মানসিক চাপ এবং উদ্বেগ কমাতে একটি শান্তিপূর্ণ ঘুমের পরিবেশ তৈরি করুন।
- পরিবেশ সামঞ্জস্য করুন: আলো উন্নত করে, আয়না ঢেকে দেয়, অথবা দৃষ্টিশক্তির ব্যাঘাত ঘটায় এমন বস্তু অপসারণ করে দৃশ্য এবং বস্তুর উদ্দীপনা কমাতে সাহায্য করুন।
- ঔষধ এবং চিকিৎসা:
- পদার্থ ব্যবহারের ঠিকানা: অবৈধ ওষুধ, অতিরিক্ত অ্যালকোহল এবং হ্যালুসিনেশন সৃষ্টিকারী ওষুধ এড়িয়ে চলুন।
- ওষুধের সমন্বয়: যদি ওষুধ একটি কারণ হয়, বিশেষ করে পার্কিনসন রোগের মতো অবস্থার জন্য, তাহলে চিকিৎসারত ডাক্তার কিছু ওষুধ, যেমন ডোপামিন অ্যাগোনিস্ট বা অ্যান্টিকোলিনার্জিক, সামঞ্জস্য করতে বা বন্ধ করতে পারেন।
- চিকিৎসা: চিকিৎসা তত্ত্বাবধানে প্রদত্ত অ্যান্টিসাইকোটিক ওষুধগুলি গুরুতর হ্যালুসিনেশনের জন্য ব্যবহার করা যেতে পারে, যদিও সম্ভাব্য পার্শ্বপ্রতিক্রিয়ার কারণে সেগুলি নিয়মিত পর্যালোচনা করা উচিত।
- মনোসামাজিক কৌশল:
- শিক্ষা এবং পরামর্শ: লক্ষণগুলি পরিচালনা করতে এবং চিকিৎসা মেনে চলার গুরুত্ব বুঝতে সাহায্য করার জন্য নিজেকে এবং আপনার পরিবারকে হ্যালুসিনেশন সম্পর্কে শিক্ষিত করুন।
- সমর্থন: হ্যালুসিনেশনের অভিজ্ঞতা মোকাবেলায় সহায়তা গোষ্ঠী এবং কাউন্সেলিং সন্ধান করুন।
 HRTD Medical Institute
HRTD Medical Institute




