Cardiac Arrhythmia & ECG Details
Cardiac Arrhythmia & ECG: Mobile Phone Number 01797522136, 01987073965. Abnormal Heart Rhythm is called Cardiac Arrhythmia or Heart Arrhythmia. Heart এর ছন্দ বৈষম্যকে Arrhythmia বলে। There are five types of Arrhythmia.
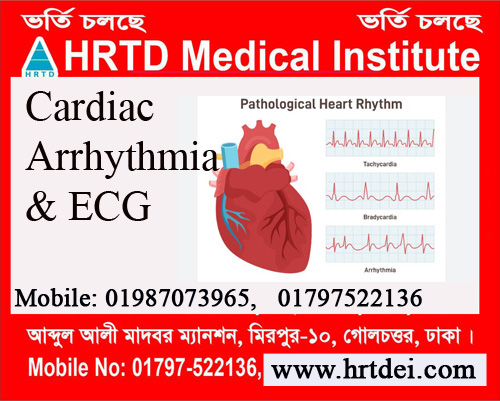
They are Tachycardia, Bradycardia, Atrial Arrhythmia, Ventricular Arrhythmia and Brady Arrhythmia. To know arrhythmia clearly there are some medical courses at HRTD Medical Institute. The courses are post-diploma training in cardiology. PDT Cardiology 3 Months, PDT Cardiology 6 Months, PDT Cardiology 1 Year, and PDT Cardiology 2 Years.
1. Cardiac Arrhythmia কাকে বলে? কত প্রকার ও কি কি?
Heart এর অস্বাভাবিক ছন্দকে Cardiac Arrhythmia বলে। অথবা, Heart এর ছন্দ বৈষম্যকে Cardiac Arrhythmia বলে।
Cardiac Arrhythmia 5 প্রকার।
- Tachycardia
- Brady cardia
- Supra ventricular arrhythmias (atrial arrhythmia)
- Ventricular arrhythmias
- Brady arrhythmias
2. Tachycardia এবং Bradycardia কাকে বলে?
Tachycardia:
Heart beat প্রতি মিনিটে ১০০ এর বেশি হলে তাকে Tachycardia বলে।
Brady Cardia:
Heart beat প্রতি মিনিটে ৬০ এর কম হলে তাকে Bradycardia বলে।
3. Supra ventricular arrhythmia কাকে বলে? উহা কত প্রকার ও কি কি?
Atria থেকে যে Arrhythmia শুরু হয় তাকে Supra ventricular Arrhythmia বলে। একে Atrial arrhythmiaও বলা হয়।
Supra ventricular Arrhythmia সাত প্রকার।
- Premature Atrial Contractions (PACs)
- Paroxysmal Supra ventricular Tachycardia (PSVT)
- Accessory Pathway Tachycardia (Bypass tract tachycardia)
- AV nodal Re-entrant Tachycardia (AVNRT)
- Atrial Tachycardia
- Atrial Fibrillation
- Atrial Flutter
4.Ventricular Arrhythmia কাকে বলে? Ventricular Arrhythmia কত প্রকার ও কি কি?
Ventricle chamber থেকে যে সকল Arrhythmia শুরু হয় তাদেরকে Ventricular Arrhythmia বলে।
Ventricular Arrhythmia তিন প্রকার।
- Premature Ventricular Contractions(PVCs)
- Ventricular Tachycardia(V-tach)
- Ventricular fibrillation (V-fib)
5. Brady arrhythmia কাকে বলে? এর common type গুলি কি কি?
Cardio conductive system এর রোগের কারনে heart rhythm slow হলে তাকে Brady arrhythmia বলে।
Brady arrhythmia এর common type গুলি হচ্ছে।
- Sinus Node Dysfunction
- Slow heart rhythm due to abnormal SA Node
- Heart block
6. Premature atrial contraction কি ধরনের রোগ?
In Cardiac Arrhythmia, Premature atrial contraction একটি supra ventricular arrhythmia
এই ধরনের arrhythmia তে নির্দিষ্ট সময়ের পূর্বেই atria থেকে heartbeat শুরু হয় ।
7. Paroxysmal Supra ventricular Tachycardia কি ধরনের রোগ?
Paroxysmal Supra ventricular Tachycardia হচ্ছে একটি Supra ventricular Arrhythmia. এই ধরনের Arrhythmia
তে heart rhythm থাকে দ্রুত,কিন্তু নিয়মিত(regular).
8. Accessory Pathway Tachycardia কি ধরনের রোগ?
Accessory Pathway Tachycardia হচ্ছে একটি Supra ventricular Arrhythmia. এই ধরনের Arrhythmia তে heart rhythm থাকে ( fast) দ্রুত.সাধারণত route এর পাশাপাশি abnormal electrical pathway এর মধ্যে দিয়ে চলে যায়। একই সাথে দুই ধরনের route কাজ করাতে heart beat দ্রুত হয়ে থাকে।
9. AV Nodal Re-entrant Tachycardia কি ধরনের রোগ?
AV Nodal Re-entrant Tachycardia হচ্ছে একটি Supra ventricular Arrhythmia .এই ধরনের Arrhythmia তে heart rhythm থাকে ( fast) দ্রুত। AV Node এ একাধিক থাকার কারণে দ্রুত হয়ে থাকে। AV Node এ একাধিক pathway থাকার কারণে heart rhythm দ্রুত হয়ে থাকে।
10. Atrial Tachycardia কি ধরনের রোগ?
Atrial Tachycardia হচ্ছে Supra ventricular Arrhythmia. এই রোগে heart rhythm থাকে দ্রুত।এই দ্রুত heart rhythm শুরু হয় Atria থেকে । এই heart rate থাকে প্রতি মিনিটে ১০০ এর বেশি।
11. Atrial fibrillation কি ধরনের রোগ?
In Cardiac Arrhythmia, Atrial fibrillation হচ্ছে এক ধরনের Supra ventricular Arrhythmia এবং খুবই common একটি Arrhythmia রোগ। এই Arrhythmia তে heart rhythm থাকে irregular. এই Arrhythmia তে Atria থেকে অনেকগুলি impulse শুরু হয় এবং ছড়িয়ে পরে। Impulse গুলি AV Node এর মধ্যে দিয়ে যাওয়ার জন্য প্রতিযোগিতা করে। এতে লব্ধ (resulting)rhythm থাকে disorganized, rapid এবং irregular.কারণ impulse গুলি Atria এর মধ্যে দিয়ে disorderly fashion এ গমন করে ফলে Atrial contraction এ কোন coordination থাকে না।
12. Atrial flutter কি ধরনের রোগ?
Atrial flutter হচ্ছে একটি Supra ventricular Arrhythmia বা Atrial Arrhythmia. এতে Atrium এ এক বা একাধিক rapid circuit থাকে। Atrial fibrillation এর চেয়ে Atrial flutter বেশী organized এবং regular.
13.Premature Ventricular Contractions কি ধরনের রোগ?
Premature Ventricular Contractions হচ্ছে এক ধরনের ventricular Arrhythmia। এই ধরনের Arrhythmia তে নির্দিষ্ট সময়ের পূর্বেই Ventricular থেকে heart beat শুরু হয়।এই ধরনের Arrhythmia খুবই common. Stress অতিরিক্ত কফি বা নিকোটিন অথবা exercise এর কারণে এই ধরনের Arrhythmia হয়ে থাকে। Heart disease এবং electrolyte imbalance এর কারণেও এই ধরনের Arrhythmia হয়ে থাকে।
14.Ventricular Tachycardia(V-tach) কি ধরনের রোগ?
Ventricular Tachycardia হচ্ছে একটি ventricular Arrhythmia এই Arrhythmia তে heart beat থাকে rapid এবং এটি ventricle থেকে শুরু হয়। rapid heart beat হওয়ার কারনে blood pump কমে যায় এবং blood supply কমে যায়। Ventricular Tachycardia খুব মারাত্মক হতে পারে বিশেষ করে যাদের heart disease থাকে। Ventricular Tachycardia এর symptom অন্যান্য Arrhythmia এর চেয়ে বেশি হয়ে থাকে।
15. Ventricular fibrillation (V-fib) কি ধরনের রোগ?
Ventricular fibrillation হচ্ছে একটি ventricular Arrhythmia . এতে ventricle থেকে impulse গুলির irregular and disorganized firing ঘটে । তাই ventricle কম্পিত হয়। কিন্তু effective contractionপরিচালনা করতে পারেনা। ফলে blood pump কমে যায় এবং দেহে blood supply ও কমে যায়। Ventricular fibrillation একটি medical emergency যা CPR এবংdefibrillation দ্বারা দ্রুত চিকিৎসা করা হয়।
16. Anti Arrhythmia Drug কাকে বলে? Common Anti Arrhythmia drug class গুলি কি কি?
যে সকল Drug Arrhythmia এর বিরুদ্ধে কাজ করে তাদেরকে Anti Arrhythmia Drug বলে।
Common Anti Arrhythmia drug class গুলি –
- Beta-blockers
- Calcium channel blockers
- Sodium channel blockers
- Potassium channel blockers
17. Common Beta blockers drug গুলি কি কি?
Common Beta blockers drug গুলি হচ্ছে –
- Atenolol
- Metoprolol
- Bisoprolol
18. Common Calcium Channel Blocker Drug গুলি কি কি?
Common Calcium Channel Blocker Drug গুলি হচ্ছে –
- Amlodipine
- Nifedipine
- Verapamil
19. Name common sodium channel blocker drugs used to treat cardiovascular disease.
common sodium channel blocker drugs used for the treatment of cardiovascular disease:
- Ranolazine
- Disopyramide
- Mexiletine
- Triamterine
- Amiloride
- Moricizine
- Quinidine
- Procainamide
- Tocainide
- Amiodarone
- Propafenone
- Flecainine
- Encainide
- Ajmaline
20. Mention the names of common sodium channel blocker drugs used to treat Seizures.
Common sodium channel blocker drugs used for the treatment of Seizures:
- Phenytoin
- Lamotrigine
- Oxcarbazepine
- Eslicarbazepine acetate
21. Name common sodium channel blocker drugs used to treat epilepsy.
- Oxcarbazepine
22. Mention the names of common sodium channel blocker anesthetics.
- Lidocaine
23. Causes of Atrial Fibrillation
Causes of Atrial Fibrillation in Cardiac Arrhythmia:
Problems with the heart’s structure are the most common cause of atrial fibrillation (AFib).
Heart diseases and health problems that can cause AFib include:
- A heart problem you’re born with is called a congenital heart defect.
- A problem with the heart’s natural pacemaker is called sick sinus syndrome.
- A sleep disorder called obstructive sleep apnea.
- Heart attack.
- Heart valve disease.
- High blood pressure.
- Lung diseases, including pneumonia.
- Narrowed or blocked arteries are called coronary artery disease.
- Thyroid disease such as an overactive thyroid.
- Infections from viruses.
Heart surgery or stress due to surgery or sickness may also cause AFib. Some people who have atrial fibrillation have no known heart disease or heart damage.
Lifestyle habits that can trigger an AFib episode may include:
- Drinking too much alcohol or caffeine.
- Illegal drug use.
- Smoking or using tobacco.
- Taking medicines that contain stimulants, including cold and allergy medicines without a prescription.
24. Risk factors of Atrial Fibrillation in Cardiac Arrhythmia
Things that can increase the risk of atrial fibrillation (AFib) include:
- Age. The risk of AFib increases as you grow older.
- Caffeine, nicotine, or illegal drug use. Caffeine, nicotine, and some illegal drugs — such as amphetamines and cocaine — can cause your heart to beat faster. Use of these substances may lead to the development of more serious arrhythmias.
- Drinking too much alcohol. Drinking too much alcohol can affect the electrical signals in the heart. This can increase the risk of atrial fibrillation.
- Changes in the level of body minerals. Minerals in the blood called electrolytes — such as potassium, sodium, calcium, and magnesium — help the heartbeat. If these substances are too low or too high, irregular heartbeats may occur.
- Family history. An increased risk of atrial fibrillation occurs in some families.
- Heart problems or heart surgery. Coronary artery disease, heart valve disease, and heart problems present at birth increase the risk of AFib. A history of heart attack or heart surgery also makes a person more likely to get the condition.
- High blood pressure. Having high blood pressure increases the risk of getting coronary artery disease. Over time, high blood pressure may cause part of the heart to become stiff and thick. This can change how heartbeat signals travel through the heart.
- Obesity. People who are obese are at higher risk of developing atrial fibrillation.
- Other long-term health conditions. You may be more likely to get AFib if you have diabetes, chronic kidney disease, lung disease, or sleep apnea.
- Some medicines and supplements. Some prescription medicines and certain cough and cold remedies bought without a prescription can cause irregular heartbeats.
- Thyroid disease. Having an overactive thyroid gland can raise the risk of irregular heartbeats.
25. Complications of Atrial Fibrillation in Cardiac Arrhythmia
Blood clots are a dangerous complication of atrial fibrillation (AFib). Blood clots can lead to stroke.
The risk of stroke from AFib increases as you grow older. Other health conditions also may increase the risk of a stroke due to AFib. These conditions include:
- High blood pressure.
- Diabetes.
- Heart failure.
- Some types of heart valve disease.
Blood thinners are commonly prescribed to prevent blood clots and strokes in people with atrial fibrillation.
26. Prevention of Atrial Fibrillation
Healthy lifestyle choices can reduce the risk of heart disease and may prevent atrial fibrillation (AFib). Here are some basic heart-healthy tips:
- Control high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes.
- Don’t smoke or use tobacco.
- Eat a diet that’s low in salt and saturated fat.
- Exercise at least 30 minutes a day on most days of the week unless your healthcare team says not to.
- Get good sleep. Adults should aim for 7 to 9 hours daily.
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Reduce and manage stress.
Special Notes on Supraventricular Cardiac Arrhythmias
This type of arrhythmia starts in the atria or the gateway to the lower chambers.
- Atrial fibrillation is the most common type of arrhythmia. More than 2.5 million people in the United States have atrial fibrillation. This condition causes your heart to beat more than 400 beats per minute. Also, your heart’s upper and lower chambers do not work together as they should. When this happens, the lower chambers do not fill completely or pump enough blood to your lungs and body.
- Atrial flutter can cause the upper chambers of your heart to beat 250 to 350 times per minute. The signal that tells the atria to beat may be blocked by damaged or scar tissue. This may cause the upper chambers and lower chambers to beat at different rates.
- Paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (PSVT) causes extra heartbeats because of a problem with the electrical signals that begin in the upper chambers and travel to the lower chambers. This type of arrhythmia begins and ends suddenly. It can happen during vigorous physical activity. It is usually not dangerous and often happens in young people.
Special Notes on Ventricular Cardiac Arrhythmias
Ventricular arrhythmias start in your heart’s lower chambers, called the ventricles. These arrhythmias can be very dangerous and usually require medical care right away.
- Ventricular tachycardia is a fast, regular beating of your ventricles that may last for only a few seconds or for much longer. A few beats of ventricular tachycardia often do not cause problems. However, if this lasts for more than a few seconds, it can lead to more serious arrhythmias, such as ventricular fibrillation (v-fib).
- Ventricular fibrillation occurs if electrical signals make the ventricles quiver instead of pumping normally. Without the ventricles pumping blood to the body, cardiac arrest and death can happen within a few minutes.
Symptoms of Ventricular Fibrillation
Just before v-fib, you may have these ventricular fibrillation symptoms:
- Chest pain (angina).
- Dizziness or lightheadedness.
- Nausea.
- Racing or erratic pulse (including other types of arrhythmia).
- Heart palpitations (where you become unpleasantly aware of your own heartbeat).
- Shortness of breath.
Someone who has this condition will collapse with little or no warning and won’t respond or react when you try to wake them. They’ll also gasp for breath or stop breathing.
Causes of Ventricular Fibrillation
- Heart attack or ischemia, which can feel like chest pain (angina).
- Heart conditions like cardiomyopathy that change the structure of your heart.
- Other arrhythmias (abnormal electrical rhythms) or arrhythmia-causing conditions.
- Congenital (present at birth) heart issues like Brugada syndrome.
- Heart surgery.
- Certain medications.
- Certain types of drug use including cocaine and methamphetamine.
- Electrolyte imbalances (too much or too little potassium or magnesium in your blood).
- Electrical shock.
- Commotio cordis (the result of getting hit in the chest with a small, fast-moving object like a baseball or hockey puck).
Risk Factors for Ventricular Fibrillation
In addition to existing heart conditions like coronary artery disease, the following raise your risk of v-fib:
- Hypoxemia (low oxygen in your blood).
- Electrolyte abnormalities.
- Acidosis (too much acid in your body).
Complications of Ventricular Fibrillation
It’s rare for people to make a complete recovery from v-fib. Contact your provider for help managing lingering issues after ventricular fibrillation.
Complications of ventricular fibrillation rhythm include:
- Sudden cardiac arrest and death.
- Coma.
- Brain damage.
- Heart muscle damage.
- Kidney failure.
- Liver failure.
Diagnosis and Tests for Ventricular Fibrillation
A provider can confirm a ventricular fibrillation rhythm with an electrocardiogram (EKG), especially after resuscitating you from cardiac arrest. They can also diagnose it during cardiac arrest if you have a cardiac monitor on or an implanted cardiac device.
They’ll also work to find out what causes ventricular fibrillation. A provider will collect your medical history and do a physical exam. They may order several other tests, like blood tests, an echocardiogram, a cardiac MRI (magnetic resonance imaging), or a coronary angiogram with a cardiac catheterization.
Management and Treatment of Ventricular Fibrillation
This condition is a life-threatening medical emergency. Every minute counts. Ventricular fibrillation treatment starts with calling your local emergency number. The following actions can help save the life of someone who’s in sudden cardiac arrest because of v-fib:
- Stay calm and call 911 or your local emergency number.
- Begin CPR: Chest compressions are an essential, lifesaving step, especially until someone finds and uses an automated external defibrillator (AED) or until first responders arrive (whichever happens first).
- Use an AED: Ventricular fibrillation is one of the “shockable” arrhythmias, meaning an AED can help return your heart’s rhythm to a normal one. When someone uses an AED in the first three minutes after a person collapses because of v-fib, the survival rate of ventricular fibrillation can be as high as 95%.
If you survive a ventricular fibrillation rhythm, you’re at a higher risk of it happening again. Your healthcare provider will run tests to find out what caused it and what follow-up options will work best to keep it from happening again. For example, if medications or an electrolyte imbalance caused your v-fib, a provider can stop the medicines or correct your electrolyte imbalance.
You also may need treatments like:
- Antiarrhythmic medications: These medications help keep your heart rhythm normal.
- Implanted device: Most people who survive ventricular fibrillation will need a provider to place an implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD). This device can detect arrhythmias and deliver an electric shock to restore your heart to a normal rhythm. These devices are almost always permanent.
A provider may suggest procedures like ablation or cardiac sympathetic denervation. These less common treatments destroy signal pathways.
Complications/side effects of the treatment
Like any medication, antiarrhythmics have side effects. Work with your provider to find the medicine that’s best for you.
When an ICD fires in response to v-fib, you may experience pain or shock.
Prevention of Fibrillation
Most cases of v-fib start out as another type of ventricular arrhythmia. If you show symptoms of an abnormal heart rhythm in your lower heart chambers, a provider can monitor your rhythms. Finding these issues early can help prevent you from developing ventricular fibrillation.
If someone in your family has a type of arrhythmia that families can pass down to each other, ask about genetic testing. Testing people who may be at risk can help them take steps to prevent dangerous heart rhythms.
Since heart attacks are the top cause of ventricular fibrillation, preventing a heart attack can prevent v-fib, as well. You can do this by making lifestyle changes like:
- Eating heart-healthy foods.
- Getting regular physical activity.
- Managing high blood pressure, high cholesterol and diabetes mellitus.
- Managing your stress.
- Staying at a weight that’s healthy for you.
 HRTD Medical Institute
HRTD Medical Institute




