Diploma in Physiotherapy Technology (DPTT) Course Fee:
Diploma in Physiotherapy Technology( DPTT 3 Years): Mobile No: 01987-073965. This is a long course of physiotherapy in Bangladesh. This diploma course of physiotherapy contains 24 subjects in 6 semesters. Admission Fee: 20,500/-, Monthly Fee (36 x 3000)= 108,000/-, Exam. Fee (2333×6)= 14,000/-, Total Course Fee= 142,500/-

Subjects of 1st Semester & 2nd Semester:
The first Semester contains 5 subjects and the subjects are Human Anatomy & Physiology, Chemistry & Pharmacology, First Aid & Treatment, Hematology & Pathology, and Study of OTC Drugs and Medicine. The second semester contains 5 subjects and the subjects are Orthopedic Anatomy & Physiology, Neuro Anatomy & Physiology, Cardiovascular Anatomy & Physiology, Electro Physics, and Study of TENS.

3rd Semester contains 4 subjects and 5th semester contains 4 subjects. 5th semester contains 3 subjects and 6th semester contains 3 subjects.
Total Subjects for Diploma in Physiotherapy Technology 3 Years Course
1st Year Subjects ( 1st Semester and 2nd Semester)
- Human Anatomy & Physiology
- Chemistry & Pharmacology-1
- First Aid & Treatment
- Hematology & Pathology
- Study of OTC Drugs
- Orthopedic Anatomy & Physiology
- Neuro Anatomy & Physiology
- Cardiovascular Anatomy & Physiology
- Electro Physics
- Study of TENS
2nd Year Subjects ( 3rd Semester & 4th Semester)
- Microbiology and Antimicrobial Drugs
- Bone Joints & Diseases
- Claytons Electrotherapy-1
- Therapeutic Exercise-1
- Community Medicine-1
- Electrotherapy & Hydrotherapy
- Claytons Electrotherapy-2
- Therapeutic Exercise-2
3rd Year Subjects ( 5th Semester & 6th Semester)
- Anatomy of Backbone
- Back Pain & Physiotherapy Treatment
- Skin Anatomy & Physiology
- Vertebral Muscles & Their Abnormalities
- Physiotherapy Equipment
- Neuromuscular Coordination
Course Fee Summary:
Course Duration: 3 Years, Total Subjects: 24, Total Marks: 2400, Total Classes (3 x 144): 432 Hours, Admission Fee: 20,500/-, Monthly Fee (36 x 3000): 108,000/-, Exam. Fee ( 6 ): 14,000/-, Total Course Fee: 142,500/-
Teachers for Diploma in Physiotherapy Technology Course
- Dr. Md. Sakulur Rahman, MBBS, CCD (BIRDEM), Course Director
- Dr. Sanjana Binte Ahmed, BDS, MPH, Assistant Course Director
- Dr. Tisha, MBBS, PGT Gyne, Assistant Course Director
- Dr. Suhana, MBBS, PGT Medicine
- Dr. Danial Hoque, MBBS, C-Card
- Dr. Tisha, MBBS
- Dr. Afrin Jahan, MBBS, PGT Medicine
- Dr. Ananna, MBBS
- Dr. Lamia Afroze, MBBS
- Dr. Amena Afroze Anu, MBBS, PGT Gyne, Assistant Course Director
- Dr. Farhana Antara, MBBS,
- Dr. Nazmun Nahar Juthi, BDS, PGT
- Dr. Farhana Sharna, MBBS
- Dr. Bushra, MBBS
- Dr. Turzo, MBBS
- Dr. Kamrunnahar Keya, BDS, PGT (Dhaka Dental College)
- Dr. Shamima, MBBS, PGT Gyne
- Dr. Alamin, MBBS
- Dr. Benzir Belal, MBBS
- Dr. Disha, MBBS
- Dr. Mahinul Islam, MBBS
- Dr. Tisha, MBBS, PGT Medicine
- Dr. Anika, MBBS, PGT
- Dr. Jannatul Ferdous, MBBS, PGT Gyne
- Dr. Jannatul Aman, MBBS, PGT
- Dr. Rayhan, BPT
- Dr. Abu Hurayra, BPT
- Dr. Sharmin Ankhi, MBBS, PGT Medicine
- Md. Monir Hossain, B Pharm, M Pharm
- Md. Monirul Islam, B Pharm, M Pharm
- Md. Feroj Ahmed, BSc Pathology, PDT Medicine
Location for Diploma in Physiotherapy Technology 3 Years Course
Location for Diploma in Physiotherapy Technology 3 Years Course: Mobile Phone Number 01797522136, 01987073965. HRTD Medical Institute, Abdul Ali Madbor Mansion, Section-6, Block-Kha, Road-1, Plot-11, Metro Rail Piller Number 249, Mirpur-10 Golchattar, Dhaka-1216. This Institute is situated just by the West Side of Agrani Bank and the South Side of Islami Bank and Janata Bank Limited.
Objectives of Physiotherapy Course/ Physiotherpay Diploma
একজন ফিজিওথেরাপিষ্ট এর পক্ষে একটি ফিজিওথেরাপী চেম্বার বা ফিজিওথেরাপী সেন্টার বা ফিজিওথেরাপী ক্লিনিক ম্যানেজ করা সম্ভব হয় না বা ম্যানেজ করা উচিৎ না । কারন সেখানে থাকে অনেক মেশিনারী এবং অনেক কাজ । যেমন মেশিনারী ম্যানেজমেন্ট, মার্কেটিং ম্যানেজমেন্ট, একাউন্টস ম্যানেজমেন্ট, ফিনেনশিয়াল ম্যানেজমেন্ট, রোগীদের ডেটা ম্যানেজমেন্ট, রোগীদের কাউন্সিলিং ইত্যাদি ।
ফিজিওথেরাপি ৩ বছর/ ৪ বছরের ডিপ্লোমা কোর্স সফলভাবে সমাপ্ত করার পরে, শিক্ষার্থীরা সক্ষম হবে:
(১) ফিজিওথেরাপি সম্পর্কিত অনেক জ্ঞান ও দক্ষতা অর্জন করতে পারবে ।
(২) বিভিন্ন ফিজিওথেরাপি সরঞ্জাম এবং আনুষাঙ্গিক পরিচালনা এবং রক্ষণাবেক্ষণের জ্ঞান ও দক্ষতা অর্জন করতে পারবে ।
(৩) ফিজিওথেরাপি সম্পর্কিত প্রয়োজনীয় ডকুমেন্টেশন বজায় রাখার জ্ঞান ও দক্ষতা অর্জন করতে পারবে ।
(৪) ফিজিওথেরাপি যন্ত্রগুলি পরিচালনার বিপদ এবং তাদের প্রতিরক্ষামূলক জ্ঞান ও দক্ষতা অর্জন করতে পারবে ।
(৫) ফিজিওথেরাপিউটিক কার্যক্রম তদারকি জ্ঞান ও দক্ষতা অর্জন করতে পারবে ।
(৬) ফিজিওথেরাপিউটিক কার্যক্রমের ভবিষ্যত উন্নয়ন ও পরিকল্পনায় অবদান রাখাতে পারবে।
Physiotherapy Chamber Starting & Establishment
After completing the Diploma in Physiotherapy Technology 3 Years Course you can start a Physiotherapy Chamber in any location in Bangladesh. You need to obtain The Registration and The License from the Respective Authority of the Government of the People’s Republic of Bangladesh. We only help our students obtain registration and licenses for the Starting & Establishment of Physiotherapy Chamber.
ডিপ্লোমা ইন ফিজিওথেরাপি টেকনোলজি 3 বছরের কোর্স সম্পন্ন করার পর আপনি বাংলাদেশের যেকোনো স্থানে একটি ফিজিওথেরাপি চেম্বার শুরু করতে পারেন। আপনাকে গণপ্রজাতন্ত্রী বাংলাদেশ সরকারের সংশ্লিষ্ট কর্তৃপক্ষের কাছ থেকে নিবন্ধন এবং লাইসেন্স পেতে হবে। আমরা শুধুমাত্র আমাদের ছাত্রদের ফিজিওথেরাপি চেম্বারের শুরু ও প্রতিষ্ঠার জন্য নিবন্ধন এবং লাইসেন্স পেতে সাহায্য করি।
ফিজিওথেরাপি ডিপ্লোমা বা ফিজিওথেরাপি কোর্স কেন করবেন?
ফিজিওথেরাপি ডিপ্লোমা বা ফিজিওথেরাপি কোর্স করে ফিজিওথেরাপি চ্যাম্বার, ফিজিওথেরাপি সেন্টার, ফিজিওথেরাপি ক্লিনিক, অথরা ফিজিওথেরাপি হাসপাতাল গড়ে তুলতে পারবেন। এটা নির্ভর করে আপনার অর্থনৈতিক অবস্থা এবং মেধার উপর । ফিজিওথেরাপি সেন্টারে চাকরি করতে পারবেন, বাসায় বাসায় অথবা হাসপাতালে হাসপাতালে গিয়ে থেরাপী দিতে পারবেন ।
| Course Title | Course Summery |
|---|---|
| Physiotherapy Training Course (PTTC) | Course Duration = 1 Year Total Subjects = 10 Total Marks = 1000 Total Classes (3 x 48) = 144 Hours Admission Fee = 10,500 Monthly Fee (12 x 3000) = 36,000 Exam. Fee ( 2 ) = 6,000 Total Course Fee = 52,500 |
| Diploma Physiotherapy Assistant (DPTA) | Course Duration = 2 Years Total Subjects = 18 Total Marks = 1800 Total Classes (3 x 96) = 288 Hours Admission Fee = 16,500 Monthly Fee (24 x 3000) = 72,000 Exam. Fee ( 4 ) = 4,000 Total Course Fee = 92,500 |
| Diploma in Physiotherapy Technology(DPTT) | Course Duration = 3 Years Total Subjects = 24 Total Marks = 2400 Total Classes (3 x 144) = 432 Hours Admission Fee = 20,500 Monthly Fee (36 x 3000) = 108,000 Exam. Fee ( 6 ) = 14,000 Total Course Fee = 142,500 |
| Diploma in Physiotherapy (DIPT) | Course Duration = 4 Years Total Subjects = 30 Total Marks = 3000 Total Classes (3 x 192) = 576 Hours Admission Fee = 30,500 Monthly Fee (48 x 3000) = 144,000 Exam. Fee ( 8 ) = 8,000 Total Course Fee = 182,500 |
Human Anatomy and Physiology for Diploma in Physiotherapy Technology Course 3 Years
The study of the Body Structure and its functions is Anatomy and Physiology. Here we discuss the systems of the Human Body and its Organs, Tissues, and Cells. The systems of the Human Body are the Digestive System, Respiratory System, Cardiovascular System, Skeletal System, Muscular System, Nervous System, Endocrine System, Immune System, Lymphatic System, Integumentary System, and Urinary System.
শারীরিক গঠন এবং এর কার্যাবলীর অধ্যয়ন হল অ্যানাটমি এবং ফিজিওলজি। এখানে আমরা মানবদেহের সিস্টেম এবং এর অঙ্গ, টিস্যু এবং কোষ নিয়ে আলোচনা করি। মানবদেহের সিস্টেমগুলি হ'ল হজম সিস্টেম, শ্বাসযন্ত্র, কার্ডিওভাসকুলার সিস্টেম, কঙ্কাল সিস্টেম, পেশীতন্ত্র, স্নায়ুতন্ত্র, এন্ডোক্রাইন সিস্টেম, ইমিউন সিস্টেম, লিম্ফ্যাটিক সিস্টেম, ইন্টিগুমেন্টারি সিস্টেম এবং ইউরিনারি সিস্টেম।
Pharmacology-1 for Diploma in Physiotherapy Technology Course 3 Years
The study of Drugs and Medicine is called Pharmacology. Here we discuss group-wise drugs and their medicines in Pharmacology-1. Common Groups of Drugs are Pain Killer Drugs, Anti Ulcer Drugs, Anti Vomiting Drugs, Laxative Drugs, Motility Drugs, Antimotility Drugs, Bronchodilator Drugs, Antibiotic Drugs, Anti Fungal Drugs, Anti Protozoal Drugs, Anti Viral Drugs, Anthelmintic Drugs, Anti Hypertensive Drugs, Beta Blocker Drugs, Calcium Channel Blocker Drugs, ACE Inhibitor Drugs, Hemostatic Drugs, Analgesic Drugs, Antipyretic Drugs, Anti Thrombotic Drugs, etc.
ওষুধ ও ওষুধের অধ্যয়নকে ফার্মাকোলজি বলা হয়। এখানে আমরা ফার্মাকোলজি-১ এ গ্রুপভিত্তিক ওষুধ ও তাদের ওষুধ নিয়ে আলোচনা করেছি। ওষুধের সাধারণ গ্রুপগুলি হল পেইন কিলার ড্রাগস, অ্যান্টি আলসার ড্রাগস, অ্যান্টি-ভোমিটিং ড্রাগস, ল্যাক্সেটিভ ড্রাগস, মোটিলিটি ড্রাগস, অ্যান্টিমোটিলিটি ড্রাগস, ব্রঙ্কোডাইলেটর ড্রাগস, অ্যান্টিবায়োটিক ড্রাগস, অ্যান্টি ফাংগাল ড্রাগস, অ্যান্টি প্রোটোজোয়াল ড্রাগস, অ্যান্টি ভাইরাল ড্রাগস, অ্যান্টি-ভাইরাল ড্রাগস, অ্যান্টি-অ্যান্টিভেনস ড্রাগস। , বিটা ব্লকার ওষুধ, ক্যালসিয়াম চ্যানেল ব্লকার ড্রাগস, এসিই ইনহিবিটর ড্রাগস, হেমোস্ট্যাটিক ড্রাগস, অ্যানালজেসিক ড্রাগস, অ্যান্টিপাইরেটিক ড্রাগস, অ্যান্টি থ্রম্বোটিক ড্রাগস ইত্যাদি।
First Aid for Diploma in Physiotherapy Technology Course 3 Years
First Aid is an important subject for Medical Courses including Diplomas in Medicine& Surgery Course, RMP Courses, LMAF Courses, Paramedical Courses, DMA Courses, DMS Courses, Nursing Courses, Dental Courses, Pathology Courses, Physiotherapy Courses, Caregiver Courses, etc. Here we discuss Shock, Classification Shock, Causes of Shock, Stages of Shock, Clinical Features of Shock, Hypovolemic Shock, Cardiogenic Shock, Neurogenic Shock, Traumatic Shock, Burn Shock, Electric Shock, Psychogenic Shock, Anaphylactic Shock, First Aid of Shock, First Aid of Cut, First of Snake Bite, First Aid of Accidental Injury, etc.
ফার্স্ট এইড মেডিসিন এবং সার্জারি কোর্সের ডিপ্লোমা, আরএমপি কোর্স, এলএমএএফ কোর্স, প্যারামেডিক্যাল কোর্স, ডিএমএ কোর্স, ডিএমএস কোর্স, নার্সিং কোর্স, ডেন্টাল কোর্স, প্যাথলজি কোর্স, ফিজিওথেরাপি কোর্স, কেয়ারগিভার কোর্স, ইত্যাদির জন্য একটি গুরুত্বপূর্ণ বিষয়। শক, শ্রেণিবিন্যাস শক, শকের কারণ, পর্যায় নিয়ে আলোচনা করুন শক, শকের ক্লিনিকাল বৈশিষ্ট্য, হাইপোভোলেমিক শক, কার্ডিওজেনিক শক, নিউরোজেনিক শক, ট্রমাটিক শক, বার্ন শক, বৈদ্যুতিক শক, সাইকোজেনিক শক, অ্যানাফিল্যাকটিক শক, শকের প্রাথমিক চিকিৎসা, কাটার প্রাথমিক চিকিৎসা, সাপের কামড়ের প্রাথমিক চিকিৎসা, প্রাথমিক চিকিৎসা দুর্ঘটনাজনিত আঘাত, ইত্যাদি
Hematology and Pathology for Diploma in Physiotherapy Technology Course
The study of Blood and Blood Disease is called Hematology and the Study of Pathos and Process of Disease Creation and Diagnosis is called Pathology. In Hematology and Pathology, we discuss blood cells, their structure and functions, Blood Diseases, Common Pathos and their pathogenesis, Atrophy, Hypertrophy, Metaplasia, Gangrene, Pathological Tests like TC, DC, ESR, Hemoglobin Percentage, etc.
রক্ত ও রক্তের রোগের অধ্যয়নকে বলা হয় হেমাটোলজি এবং স্টাডি অফ প্যাথোস এবং রোগ সৃষ্টি ও নির্ণয়ের প্রক্রিয়াকে প্যাথলজি বলা হয়। হেমাটোলজি এবং প্যাথলজিতে, আমরা রক্তের কোষ, তাদের গঠন এবং কার্যকারিতা, রক্তের রোগ, সাধারণ প্যাথোস এবং তাদের প্যাথোজেনেসিস, অ্যাট্রোফি, হাইপারট্রফি, মেটাপ্লাসিয়া, গ্যাংগ্রিন, প্যাথলজিকাল টেস্ট যেমন TC, DC, ESR, হিমোগ্লোবিন শতাংশ ইত্যাদি নিয়ে আলোচনা করি।
Microbiology and Antimicrobial Drugs for Diploma in Physiotherapy Technology
The Study of Microorganisms is called Microbiology. The Drugs that are used for the treatment of Infectious Diseases are Antimicrobial Drugs. Microorganisms are Bacteria, Protozoa, Fungus, and Virus. Antimicrobial Drugs are Antibiotic Drugs ( Antibacterial Drugs), Anti Protozoal Drugs, Anti Fungal Drugs, and Anti Viral Drugs. Antibacterial Drugs are Azithromycin, Erythromycin, Clarithromycin, Cefaclor, Cefixime, Cefuroxime, Ceftriaxone, Ciprofloxacin, Moxifloxacin, Doxicicline, Gentamycin, Neomycin, Flucloxacillin, Amoxicillin, Clindamycin, etc. Antiprotozoal Drugs are Metronidazole, Secnidazole, Tinidazole, Ornidazole, Nitazoxanide, etc. Antifungal Drugs are Fluconazole, Ketoconazole, Itraconazole, Econazole, Miconazole, Terbinafine, etc.
অণুজীবের অধ্যয়নকে মাইক্রোবায়োলজি বলা হয়। সংক্রামক রোগের চিকিত্সার জন্য যে ওষুধগুলি ব্যবহার করা হয় তা হল অ্যান্টিমাইক্রোবিয়াল ড্রাগ। অণুজীব হল ব্যাকটেরিয়া, প্রোটোজোয়া, ফাঙ্গাস এবং ভাইরাস। অ্যান্টিমাইক্রোবিয়াল ড্রাগগুলি হল অ্যান্টিবায়োটিক ড্রাগস (অ্যান্টিব্যাকটেরিয়াল ড্রাগস), অ্যান্টি প্রোটোজোয়াল ড্রাগস, অ্যান্টি ফাঙ্গাল ড্রাগস এবং অ্যান্টি ভাইরাল ড্রাগস। ব্যাকটেরিয়ারোধী ওষুধগুলি হল Azithromycin, Erythromycin, Clarithromycin, Cefaclor, Cefixime, Cefuroxime, Ceftriaxone, Ciprofloxacin, Moxifloxacin, Doxicicline, Gentamycin, Neomycin, Flucloxacillin, Amoxicillin, ক্লিন্ডাজোল, ক্লিন্ডামাইসিন, ক্লিনিডামাইসিন ইত্যাদি। Secnidazole, Tinidazole, Ornidazole, Nitazoxanide, ইত্যাদি অ্যান্টিফাঙ্গাল ওষুধ হল Fluconazole, Ketoconazole, Itraconazole, Econazole, Miconazole, Terbinafine ইত্যাদি।
Treatment/Practice of Medicine for Diploma in Physiotherapy Technology Course
The study of Disease and Treatment is called the Practice of Medicine. This subject is important for a Diploma Medical Practitioner, Diploma Medical Assistant, and Rural Medical Practitioner. This subject discusses some common diseases. The discussion points for the Practice of Medicine are the Definition of Disease, Causes of Disease, Clinical Features of Disease ( Symptoms and Signs), Investigation of Disease, Treatment of Disease, Complication of Disease, and Advice for the Patients. To understand the diseases, the movement of doctors, and their prescriptions, this subject should be studied by physiotherapy students.
রোগ ও চিকিৎসার অধ্যয়নকে বলা হয় মেডিসিনের অনুশীলন। এই বিষয় একজন ডিপ্লোমা মেডিকেল প্র্যাকটিশনার, ডিপ্লোমা মেডিকেল অ্যাসিস্ট্যান্ট এবং গ্রামীণ চিকিৎসা অনুশীলনকারীর জন্য গুরুত্বপূর্ণ। এই বিষয়ে কিছু সাধারণ রোগ নিয়ে আলোচনা করা হয়েছে। মেডিসিন অনুশীলনের আলোচনার বিষয়গুলি হল রোগের সংজ্ঞা, রোগের কারণ, রোগের ক্লিনিক্যাল বৈশিষ্ট্য (লক্ষণ এবং লক্ষণ), রোগের তদন্ত, রোগের চিকিৎসা, রোগের জটিলতা এবং রোগীদের জন্য পরামর্শ। রোগগুলি, ডাক্তারদের গতিবিধি এবং তাদের প্রেসক্রিপশন বোঝার জন্য, এই বিষয়টি ফিজিওথেরাপি শিক্ষার্থীদের দ্বারা অধ্যয়ন করা উচিত।
Therapeutic Exercise-1 for Diploma in Physiotherapy Technology Course
Exercise Therapies are discussed in Therapeutic Exercise. After completing Theory Classes, Practical Classes are done. Topics for Therapeutic Exercise-1 are Lever, Types of Lever, 1st Degree Lever, Pulley, Types of Pulley, Movable Pulley, Energy, Types of Energy, Kinetic Energy, Axis, Types of Axis, Plane, Types of Plane, Names of Shoulder Movement, Names of Hip Movement, Names of Wrist Movement, MCP Movement, Range of Motion of Elbow Joint, Muscle action, Types of Muscle action, Muscle work, Types of Muscle work, Types of Fundamental Position, Pelvic tilt, Types o Pelvic tilt, Relax Passive Movement, Indication of Relax Passive Movement, Contraindication of Relax Passive Movement.
ব্যায়াম থেরাপি থেরাপিউটিক ব্যায়াম আলোচনা করা হয়. থিওরি ক্লাস শেষ করার পর ব্যবহারিক ক্লাস করা হয়। থেরাপিউটিক এক্সারসাইজ-১-এর বিষয়গুলো হলো লিভার, লিভারের ধরন, ১ম ডিগ্রি লিভার, পুলি, পুলির প্রকার, চলনশীল পুলি, শক্তি, শক্তির প্রকার, গতিশক্তি, অক্ষ, অক্ষের প্রকার, সমতল, সমতলের ধরন, নাপুল। আন্দোলন, নিতম্ব আন্দোলনের নাম, কব্জির নড়াচড়ার নাম, MCP মুভমেন্ট, কনুই জয়েন্টের গতির পরিসর, পেশীর ক্রিয়া, পেশীর ক্রিয়ার ধরন, পেশীর কাজ, পেশীর কাজের ধরন, মৌলিক অবস্থানের ধরন, শ্রোণী কাত, পেলভিক কাত, শিথিলকরণ, নিষ্ক্রিয় গতির ধরন প্যাসিভ আন্দোলন শিথিল করুন, প্যাসিভ মুভমেন্ট শিথিল করার বিরোধীতা,
Types of skeletal muscle fibers, Clinical Examination of the Motor Nervous System, Clinical Examination of the Sensory Nervous System, Clinical Examination of Cranial Nerves, Clinical Examination of the Cardiovascular System, Measurement of the Pelvic Angle of Inclination, Factors affecting the Joint Range of Motion, Starting and Derived Positions, Suspension therapy, Advantage of Suspension therapy, Names of Suspension Instrument, Types of Suspension Therapy, etc.
কঙ্কালের পেশী তন্তুর ধরন, মোটর স্নায়ুতন্ত্রের ক্লিনিকাল পরীক্ষা, সংবেদনশীল স্নায়ুতন্ত্রের ক্লিনিকাল পরীক্ষা, ক্রানিয়াল স্নায়ুর ক্লিনিকাল পরীক্ষা, কার্ডিওভাসকুলার সিস্টেমের ক্লিনিক্যাল পরীক্ষা, পেলভিক প্রবণতার কোণ পরিমাপ, জোড়ের সীমাকে প্রভাবিত করার কারণগুলি , শুরু এবং প্রাপ্ত অবস্থান, সাসপেনশন থেরাপি, সাসপেনশন থেরাপির সুবিধা, সাসপেনশন যন্ত্রের নাম, সাসপেনশন থেরাপির প্রকারভেদ ইত্যাদি।
Electro Therapy for Diploma in Physiotherapy Technology Course
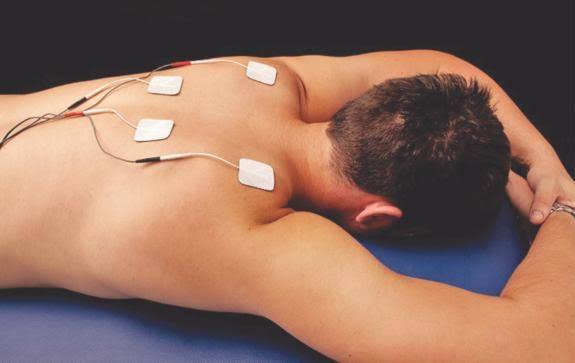
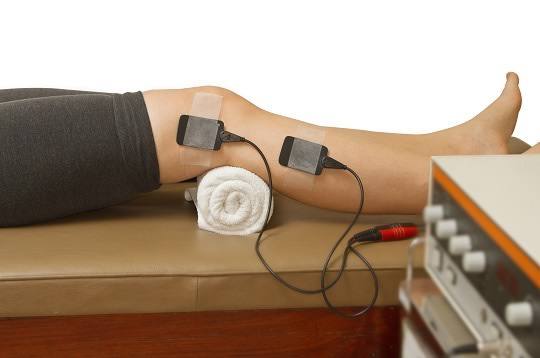
Electrotherapy uses electrical currents for medical treatment, primarily to relieve pain, reduce inflammation, and stimulate muscles, commonly seen in physiotherapy with devices like TENS or NMES, but also extends to psychiatric uses like Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT) for severe mood disorders, and even cosmetic treatments for skin. It works by applying electrical energy to tissues, affecting nerve signals or muscle contractions for therapeutic effects, often complementing other active therapies for better results.
Common Types & Uses:
- Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS): Mild currents through skin pads to block pain signals (gate control theory).
- Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation (NMES): Stronger currents to contract muscles, preventing atrophy, retraining muscles after injury, or improving strength.
- Interferential Current (IFC): Uses two currents for deeper pain relief and increased circulation.
- Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT): Controlled electric seizure for severe depression, bipolar disorder, or catatonia, when other treatments fail.
- Galvanic Current (Cosmetic): Uses direct current for skin cleansing (desincrustation) and nourishing (iontophoresis) to improve skin conditions like aging or acne.
How it Works (General):
- Pain Relief: Interrupts pain signals or triggers endorphin release.
- Muscle Rehab: Stimulates nerve & muscle fibers, improving tone, strength, or re-education.
- Healing: Can accelerate healing and reduce swelling by improving local circulation.
Key Considerations:
- Not a Replacement: Best when combined with exercise and manual therapy, not as a standalone solution.
- Skilled Application: Effectiveness depends on the therapist choosing the right type, intensity, and duration for the individual.
Cardiovascular Anatomy & Physiology for Diploma in Physiotherapy Technology Course
Cardiovascular Anatomy is a branch of Anatomy, and Cardiovascular Physiology is a branch of Physiology. These two subjects are related to cardiology. Cardiovascular Anatomy and Physiology are being studied in a single subject for Diploma Medical Courses, Paramedical Courses, and All Short Medical Courses.
কার্ডিওভাসকুলার অ্যানাটমি হল অ্যানাটমির একটি শাখা এবং কার্ডিওভাসকুলার ফিজিওলজি হল ফিজিওলজির একটি শাখা। এই দুটি বিষয় কার্ডিওলজি সম্পর্কিত। কার্ডিওভাসকুলার অ্যানাটমি এবং ফিজিওলজি ডিপ্লোমা মেডিকেল কোর্স, প্যারামেডিক্যাল কোর্স এবং সমস্ত শর্ট মেডিকেল কোর্সের জন্য একটি একক বিষয়ে অধ্যয়ন করা হচ্ছে।
We discuss here the Anatomy of the Heart, Cardiac Chambers, Cardiac Valves, Cardiac Wall, Cardiac Septum, Right Heart, Left Heat, Function of Right Heat, Functions of Left Heart, Aorta, Venecava, Artery, Vein, Capillary, Pulmonary Blood Circulation, Cerebral Blood Circulation, Renal Blood Circulation, Hepatic Blood Circulation, Portal Vein and Portal Circulation, Heart Beat, Pulse, Pulse Rate, Tachycardia, Bradycardia, Blood Pressure, Normal Blood Pressure, Hypertension, Hypotension, Stroke Volume, Cardiac Output, Heart Failure, etc. This Subject is the most essential for the Diploma in Medicine and Diploma in Surgery Course.
আমরা এখানে হার্টের অ্যানাটমি, কার্ডিয়াক চেম্বার, কার্ডিয়াক ভালভ, কার্ডিয়াক ওয়াল, কার্ডিয়াক সেপ্টাম, ডান হার্ট, বাম তাপ, ডান তাপের ফাংশন, বাম হার্টের কাজ, অ্যাওর্টা, ভেনেকাভা, ধমনী, শিরা, কৈশিক, পালমোনারি রক্ত সঞ্চালন নিয়ে আলোচনা করি। , সেরিব্রাল ব্লাড সার্কুলেশন, রেনাল ব্লাড সার্কুলেশন, হেপাটিক ব্লাড সঞ্চালন, পোর্টাল ভেইন এবং পোর্টাল সঞ্চালন, হার্ট বিট, পালস, পালস রেট, টাকাইকার্ডিয়া, ব্র্যাডিকার্ডিয়া, রক্তচাপ, স্বাভাবিক রক্তচাপ, উচ্চ রক্তচাপ, হাইপোটেনশন, স্ট্রোক ভলিউম, কার্ডিয়াক আউটপুট, হার্ট ফেইলিউর ইত্যাদি। ডিপ্লোমা ইন মেডিসিন এবং ডিপ্লোমা ইন সার্জারি কোর্স।
Orthopedic Anatomy & Physiology for Diploma in Physiotherapy Technology Course
Orthopedic Anatomy & Physiology describe the anatomy of bone, physiology of bone, anatomy of skeletal muscle, physiology of skeletal muscle, anatomy of tendon, physiology of tendon, anatomy of ligament physiology of ligament, anatomy of cartilage, physiology of cartilage, anatomy of joints, physiology of joints, etc.
অর্থোপেডিক অ্যানাটমি এবং ফিজিওলজি হাড়ের অ্যানাটমি, হাড়ের শারীরবৃত্তি, কঙ্কালের পেশীর শারীরবৃত্তি, কঙ্কালের পেশীর শারীরবৃত্তি, টেন্ডনের শারীরবৃত্তি, টেন্ডনের শারীরবৃত্তি, লিগামেন্টের অ্যানাটমি অফ লিগামেন্ট ফিজিওলজি, লিগামেন্টের অ্যানাটমি, কারটিলেজের শারীরবৃত্তি, কার্টিলেজের শারীরবৃত্তবিদ্যা, কার্টিলেজের শারীরবৃত্তির বর্ণনা দেয়। জয়েন্ট, ইত্যাদি
Physiotherapy Equipment for Diploma in Physiotherapy Technology Course
Physiotherapy equipment includes electrotherapy devices (TENS, EMS, IFT for pain/muscle), thermal modalities (ultrasound, diathermy, hot/cold packs for healing), exercise tools (resistance bands, exercise balls, balance boards, pulleys for strength/mobility), and traction units (cervical/lumbar) for spinal issues, all helping with pain, recovery, and restoring movement. Equipment ranges from basic items like foam rollers and therapy putty to complex machines like shortwave diathermy and CPM machines (Continuous Passive Motion).
Electrotherapy & Modalities
- TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation): Pain relief.
- EMS (Electrical Muscle Stimulation): Muscle strengthening/re-education.
- IFT (Interferential Therapy): Deep tissue stimulation, pain relief.
- Ultrasound Therapy: Deep heating for tissue repair, inflammation.
- Diathermy (Shortwave/Longwave): Deep heat for muscle relaxation.
- Laser Therapy: Tissue regeneration, pain reduction.
Exercise & Mobility Tools
- Resistance Bands: Strengthening.
- Exercise Balls (Swiss Balls): Core stability, balance.
- Balance Boards/Pads: Proprioception, balance training.
- Foam Rollers: Myofascial release, flexibility.
- TRX System: Bodyweight resistance training.
- Stretching Straps: Improving flexibility.
- CPM Machines: Passive joint movement after surgery.
Traction & Support
- Cervical/Lumbar Traction Units: Spinal decompression, disc relief.
- Treatment Tables: For manual therapy and exercise.
- Inversion Tables: Spinal decompression.
Other
- Hydrocollator/Paraffin Wax Baths: Heat therapy.
- Dynamometer: Strength measurement.
- Therapy Putty: Hand/grip strengthening.
TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation) for Diploma in Physiotherapy Technology
TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation) uses mild electrical currents for pain relief, indicated for various acute/chronic pain types, but is contraindicated (shouldn’t be used) with pacemakers, on broken/irritated skin, over the eyes/throat/chest (anterior), or while driving/sleeping; precautions include using cautiously with epilepsy, during pregnancy (avoiding abdomen), near tumors/metal implants, or over areas with poor circulation. Always consult a doctor, especially with heart conditions, and avoid sensitive areas like the head, neck, and trunk simultaneously.
Indications (When to Use)
- Chronic Pain: Back pain, arthritis, fibromyalgia.
- Acute Pain: Post-surgical pain, labor pain (with caution).
- Neuropathic Pain: Nerve pain, sciatica.
- Musculoskeletal Pain: Muscle spasms, joint pain.
Contraindications (When NOT to Use)
- Cardiac Devices: Pacemakers, defibrillators, or other electrical implants.
- Skin Issues: Broken, infected, irritated, or numb skin, open wounds, or blisters.
- Body Areas: Over the eyes, mouth, throat (anterior neck), or testes.
- Pregnancy: On the abdomen or lower back.
- Cancer: Over active, treatable tumors or cancerous areas.
- Other: Undiagnosed pain, deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
Precautions (Use with Caution)
- Epilepsy: Use with extreme caution, avoid head/neck application.
- Pregnancy: Use only under medical guidance, avoiding the abdomen.
- Driving/Machinery: Never use while operating vehicles or heavy machinery.
- Metal Implants: Use near, not directly over, metal implants (e.g., stents).
- Transdermal Patches: Avoid placing electrodes near drug delivery patches.
- Children: Use with extra care and supervision.
- Heart Conditions: Use with caution if you have heart disease.
General Safety Tips
- Placement: Avoid applying electrodes to the chest and back at the same time.
- Hygiene: Clean skin before use for better conductivity.
- Intensity: Use a strong but comfortable sensation; avoid pain.
EMS (Electrical Muscle Stimulation) for Diploma in Physiotherapy Technology
Electrical Muscle Stimulation (EMS) is a modality that uses electrical impulses to elicit muscle contractions for therapeutic and rehabilitation purposes.
Indications
EMS is used in physical therapy and rehabilitation to address a variety of muscular and neuromuscular conditions.
- Preventing or slowing disuse atrophy: Particularly useful for patients who are partially or totally immobilized (e.g., after surgery or a stroke).
- Muscle re-education and strengthening: Helps re-establish the connection between the nerve and muscle, and is used to strengthen weakened muscles (e.g., quadriceps after knee surgery).
- Relaxing muscle spasms: Helps to reduce and relieve painful muscle spasms.
- Increasing local blood circulation: Muscle contractions enhance blood flow, which aids in tissue healing.
- Maintaining or increasing range of motion: Induced muscle contractions help move joints, preventing stiffness.
- Pain management: While TENS is more common for pain, EMS can help manage pain through muscle relaxation and improved circulation.
- Support for neurological conditions: Used in patients with stroke, spinal cord injuries, or multiple sclerosis to manage spasticity and maintain muscle strength.
Contraindications
EMS should not be used in the presence of certain conditions as it may be harmful.
- Presence of a pacemaker or other implanted electronic devices: Electrical currents can interfere with these devices.
- Pregnancy: Avoid use, especially over the abdominal and pelvic floor regions.
- Active cancer or tumors: May speed up metastasis.
- Epilepsy or seizure disorders: The electrical stimulation may trigger a seizure.
- Presence of thrombosis or thrombophlebitis: Increasing blood circulation and muscle contraction could cause a blood clot to dislodge.
- Open wounds, skin lesions, or infections: Risk of transmitting bacteria or worsening the condition.
- Hemorrhagic conditions: Conditions involving bleeding disorders or active hemorrhage.
- Over the carotid sinus, eyes, or anterior neck: Can cause dangerous changes in heart rate or blood pressure.
Precautions
Certain conditions require medical consultation and careful application of EMS.
- Impaired sensation: The patient might not feel if the intensity is too high, leading to skin irritation or burns.
- Metal implants/prostheses: While not always a strict contraindication, caution is advised and placement may need adjustment.
- Uncontrolled high blood pressure: Requires medical clearance and careful monitoring.
- Recent surgery: Requires physician consultation to ensure the tissue is healed enough for stimulation.
- Diabetes mellitus: Can cause a drop in glucose levels; requires monitoring.
- Impaired cognition or communication: Patient must be able to understand instructions and provide feedback on sensation and comfort levels.
- Children: Use requires specialized training and careful consideration.
IFT (Interferential Therapy) for Diploma in Physiotherapy Technology
Interferential Therapy (IFT) uses medium-frequency currents for pain relief, muscle stimulation, and edema reduction, indicated for musculoskeletal issues like strains, arthritis, and back pain. Contraindicated with pacemakers, pregnancy, malignancy, active infections, and over open wounds/thrombosis; precautions include impaired sensation, epilepsy, arterial disease, and potential potentiation with opioids like tramadol, requiring careful monitoring and lower settings.
Indications (When to Use)
- Pain Management: Acute/chronic pain, muscle spasms, nerve pain.
- Musculoskeletal Issues: Strains, sprains, osteoarthritis, low back pain, sports injuries.
- Edema/Swelling: To reduce swelling and promote healing.
- Tissue Healing: To improve blood flow and accelerate wound healing (e.g., ulcers).
Contraindications (When NOT to Use)
- Pacemakers/Implanted Devices: Do not use near these devices.
- Pregnancy: Avoid application over the pregnant uterus.
- Malignancy/Cancer: Avoid areas with tumors or active cancer.
- Infection: Active infections or febrile (feverish) conditions.
- Thrombosis: Recent Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) or arterial thrombosis.
- Open Wounds/Skin Issues: Over large open wounds, broken skin, or irritations.
- Hemorrhage: Areas prone to bleeding.
Precautions (Use with Caution)
- Epilepsy/Seizure Disorders: Risk of triggering seizures.
- Impaired Sensation: Loss of feeling (numbness) requires lower intensity and careful monitoring.
- Arterial Disease: Compromised blood flow.
- Metal Implants: Over or near metal implants.
- Opioids: May intensify effects of opioids like tramadol; use lower doses/intensity.
- Unreliable Patients: Difficulty understanding instructions.
- Menstruation: Avoid application over the uterus during menstruation.
Ultrasound Therapy for Diploma in Physiotherapy Technology
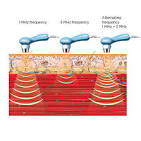
Ultrasound therapy uses high-frequency sound waves (inaudible to humans) delivered via a transducer head to promote healing and reduce pain in soft tissues, working by creating vibrations that increase blood flow, stimulate collagen production, reduce inflammation, and break down scar tissue, making it a non-invasive treatment for muscle/joint issues, swelling, and sometimes wound healing or nerve regeneration. It’s applied with a conductive gel, can heat deep tissues (thermal effect) or cause cellular vibration (non-thermal effect) for various musculoskeletal and soft tissue conditions.
How It Works
- Piezoelectric Effect: An electrical current causes crystals in the ultrasound head to vibrate, producing sound waves.
- Energy Transfer: These waves travel through a gel into the body, vibrating cells in the targeted soft tissues (muscles, tendons, ligaments).
- Thermal Effects (Continuous Mode): Deep heating increases circulation, relaxes tight muscles, and reduces pain.
- Non-Thermal Effects (Pulsed Mode): High-frequency vibrations stimulate cell activity, promote healing, and can help break down calcium deposits or scar tissue.
Common Uses & Benefits
- Pain Relief: Reduces pain from sprains, strains, and inflammation.
- Tissue Repair: Accelerates healing for injuries by stimulating collagen and cellular activity.
- Scar Tissue Reduction: Helps break down scar tissue after surgeries like carpal tunnel.
- Inflammation: Reduces swelling and promotes a healthy inflammatory response for repair.
- Wound Healing: Can promote protein synthesis and tissue remodeling in wounds.
- Phonophoresis: Delivers medication through the skin without needles.
What to Expect
- A smooth transducer head is moved over the skin with gel.
- It’s generally painless; some might feel warmth or mild tingling.
- Treatments are short, often a few minutes, and sessions are repeated.
Safety
- Painless, non-invasive, and generally considered safe for most people.
- Not used over open wounds (except specific protocols), pacemakers, or cancerous areas.
Diathermy (Shortwave/Longwave) for Diploma in Physiotherapy Technology
Diathermy is a therapeutic technique in physical therapy that uses high-frequency electric currents to generate deep heat within body tissues, promoting pain relief, increased blood flow, and tissue healing. The primary difference between shortwave diathermy (SWD) and longwave diathermy (LWD) lies in their operating frequencies, depth of penetration, and application methods.
Shortwave Diathermy (SWD)
Shortwave diathermy uses high-frequency electromagnetic waves, typically at a frequency of 27.12 MHz.
- Penetration: It is commonly used to treat deep muscles and joints, such as the hip, that are covered by a heavy mass of soft tissue.
- Application: The energy is applied using condenser plates or induction coils placed near the body part being treated.
- Modes: It can be applied in continuous mode for thermal effects or pulsed mode for athermal effects, which helps in managing acute inflammation.
- Conditions Treated: Effective for conditions such as arthritis, back pain, bursitis, tendonitis, and muscle spasms.
Longwave Diathermy (LWD)
Longwave diathermy operates at lower frequencies, typically around 1 MHz.
- Penetration: Despite its name, LWD is often considered to target superficial to moderate depths, with some sources indicating it can penetrate deep into joints. It is particularly effective for ligaments and tendons.
- Application: It is often applied using a single, portable applicator head with a coupling cream, based on the capacitor field method.
- Advantages: LWD machines are generally more compact, portable, and less expensive than SWD units. A key benefit is minimal interference with other electronic equipment, and it can potentially be used with patients who have certain metal implants (though a healthcare professional must always be consulted).
- Conditions Treated: Beneficial for chronic pain, arthrosis, ligament injuries, myalgia, and ankle sprains.
Key Differences at a Glance
| Feature | Shortwave Diathermy (SWD) | Longwave Diathermy (LWD) |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency | High frequency (typically 27.12 MHz) | Lower frequency (around 1 MHz) |
| Depth | Deep tissue penetration for deep muscles and joints | Deeper tissue penetration into high-density tissues like ligaments and tendons |
| Modes | Thermal and non-thermal (pulsed) | Primarily thermal (heat-based) |
| Portability | Machines are larger, less portable | Devices are more compact and portable |
| Interference | Can interfere with other electronic devices | Minimal to no interference with other equipment |
Important Safety Information
All types of diathermy are contraindicated for individuals with implanted electronic devices such as cardiac pacemakers, metal bone pins, or intrauterine devices (IUDs), due to the risk of severe burns or device interference. It should also be avoided over areas of active cancer, infection, open wounds, or in pregnant patients. Treatment should always be performed by a qualified healthcare professional who can adjust the settings and monitor the patient for comfort and safety.
Laser Therapy
Laser therapy uses focused light to treat various conditions by stimulating cells, reducing pain/inflammation, or destroying tissue, with applications from eye surgery/cancer treatment (high-power) to physical therapy/dermatology (low-level/cold laser) for healing, pain relief, and skin rejuvenation, working by triggering cellular processes like photobiomodulation. It’s non-invasive in many forms, promoting faster healing than surgery in some cases, but requires proper wavelengths and can have risks like bleeding or scarring, notes MedlinePlus and American Society for Dermatologic Surgery.
How it works
- LASER: Stands for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation, creating a powerful, focused beam of light.
- Photobiomodulation (Low-Level/Cold Laser): Light photons enter skin/tissue, react with mitochondria, increase cellular energy, boost circulation, and reduce inflammation, speeding healing.
- High-Power Lasers: Precisely cut, burn, or destroy abnormal tissue, allowing treatment without harming surrounding areas.
Common Uses
- Physical Therapy/Pain: Arthritis, back pain, sprains, tendonitis, nerve pain, muscle recovery (e.g., tennis elbow).
- Ophthalmology: Vision correction (LASIK), detached retina repair.
- Dermatology/Cosmetic: Skin rejuvenation, removing lesions, hair removal, reducing wrinkles, treating precancerous spots.
- Surgery: Prostate, kidney stones, tumors, varicose veins, skin surgery.
What to expect
- Before: Doctor reviews history, avoids sun/tanning/irritants/blood thinners for weeks prior.
- During: A handheld device applies light; often painless, but some high-power uses may involve local anesthetic.
- After: Recovery varies; skin might be red/tender; usually faster than surgery; requires follow-ups and sun protection.
Types of Laser Therapy
- Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT) / Cold Laser: Non-invasive, stimulates healing, reduces pain (e.g., for sports injuries).
- High-Energy Laser Therapy: More invasive, used for precise tissue destruction (e.g., in surgery or oncology).
Laser Physiotherapy for Diploma in Physiotherapy Technology
Laser physiotherapy, or Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT), uses low-intensity laser light to stimulate cells, promoting faster healing, reducing pain and inflammation, and improving tissue function for musculoskeletal issues. It’s a non-invasive treatment that accelerates cellular repair (photobiomodulation), boosts metabolism, increases blood flow, and helps break down scar tissue, offering relief for conditions like arthritis, back pain, and tendon injuries.
How it works
- Photobiomodulation: Specific wavelengths of light penetrate the skin and are absorbed by mitochondria in cells.
- Cellular Boost: This energy increases ATP (cellular energy) production, enhancing cell function and accelerating repair.
- Anti-inflammatory: It reduces swelling, promotes oxygen/nutrient delivery, and removes cellular debris.
- Pain Relief: Stimulates nerve endings to provide immediate analgesic effects and reduces muscle spasms.
Key benefits
- Reduces pain, inflammation, and swelling.
- Speeds up tissue repair and regeneration.
- Increases blood flow and cellular metabolism.
- Improves flexibility and breaks down scar tissue.
- Can be used alongside other physical therapy treatments.
Common uses in physiotherapy
- Arthritis and bursitis
- Sprains, strains, and ligament/tendon injuries (e.g., Achilles tendon, meniscus)
- Chronic back pain (lumbago, sciatica)
- Neck pain (cervical radiculopathy)
- Plantar fasciitis
Types
- LLLT (Low-Level Laser Therapy): Focuses on biostimulation for healing.
- MLS Laser Therapy: Uses dual wavelengths for deeper penetration and faster treatment.
- High-Power Laser Therapy (HPLT): Higher intensity for deeper tissue and more significant pain relief.
Exercise Balls for Diploma in Physiotherapy Technology
Exercise balls, also known as stability or Swiss balls, are versatile fitness tools used for improving core strength, balance, and flexibility. They come in various types and sizes, each designed for specific fitness goals.
Types of Exercise Balls
- Stability Balls (Yoga Balls / Swiss Balls): These are large, inflatable balls (typically 55-75 cm in diameter) primarily used to add instability to exercises, forcing engagement of stabilizer muscles, especially the core and back muscles. They are also popular for physical therapy, general fitness routines, and as an alternative to office chairs to promote better posture (though prolonged use is not recommended).
- Medicine Balls: These are weighted balls (ranging from 2 to 25 pounds) used for strength training, plyometrics, and core conditioning. Their weight and design are ideal for explosive, functional movements like throws and slams, which improve power and coordination.
- Slam Balls: Similar to medicine balls, these are specifically engineered with a tough exterior (often filled with sand or gel) to withstand high-impact slams into the ground without bouncing. They are ideal for high-intensity interval training (HIIT) and developing explosive power.
- Pilates Balls (Mini Exercise Balls): These are small (around 7-9 inches in diameter) inflatable balls used for low-impact exercises, providing support, resistance, or instability for targeted movements, particularly in Pilates and physical therapy. They help activate smaller muscles and improve alignment.
Top Product Recommendations
Based on expert reviews and user feedback, here are some highly-rated options for general fitness:
- Retrospec Luna Exercise Ball
- Reviewers on Verywell Fit praise it as a versatile, fairly priced choice for both workouts and office use.
- It features a grippy, comfortable texture and comes with useful accessories like a plug puller for easy deflation.
- SmarterLife Workout Exercise Ball
- Considered a great choice for beginners because it includes an inflation measuring tape to ensure correct sizing and a downloadable exercise guide.
- Testers found it solid, stable, and very lightweight, making it easy to move for various exercises.
- TheraBand Pro Series Fitness Ball
- Experts like physical therapists recommend this ball for its high quality, durable, non-toxic, and anti-burst material, with a thickness roughly twice that of many competitors.
- It offers a taut, supportive feel for workouts and sitting and features a grippy surface to prevent slippage.
- GalSports Anti-Sport Yoga Ball
- This is a budget-friendly option that performs well, offering good comfort and a non-slip grip.
- Reviewers noted it was surprisingly easy and quick to inflate.
How to Choose the Right Size
Choosing the correct size is essential for effective and safe use. When sitting on a properly inflated stability ball, your knees should be at a 90-degree angle with your feet flat on the floor.
A general sizing guide based on user height is as follows:
- 45 cm diameter: For individuals 5’0″ and under
- 55 cm diameter: For individuals between 5’1″ and 5’8″
- 65 cm diameter: For individuals between 5’9″ and 6’2″
- 75 cm diameter: For individuals between 6’3″ and 6’7″
Balance Boards for Diploma in Physiotherapy Technology
Balance boards are unstable platforms, often wood or plastic, used to improve balance, coordination, core strength, and rehabilitation by challenging your stability through wobbling, tilting, and circular motions, benefiting athletes, physical therapy patients (especially for ankle/knee injuries), and even office workers at standing desks. They come in various types, like round wobble boards or rocker boards, offering fun ways to do squats, push-ups, and balance poses, helping prevent injuries and improving overall fitness.
Types of Balance Boards
- Wobble Boards (Round): Allow movement in multiple directions (side-to-side, front-to-back, circular) and are common in rehab for ankle sprains.
- Rocker Boards: Simpler, often used by kids or for basic balance, acting like a seesaw.
- Roller Boards: Feature a cylinder underneath for dynamic, challenging balance training, ideal for board sport enthusiasts.
- Stability Discs: Smaller, often textured discs for core work and stability training.
Benefits & Uses
- Injury Prevention & Rehab: Strengthens lower leg muscles (like peroneals) and helps prevent falls and sports injuries, especially for ankles and knees.
- Core Strength: Engages abdominal and oblique muscles for better posture and reduced back pain.
- Athletic Training: Excellent for surfers, snowboarders, and other athletes to improve board control and agility.
- General Fitness: Used for squats, push-ups, and yoga poses to increase intensity.
- Standing Desks: Helps combat sedentary effects, increases circulation, and burns extra calories.
How They Work
When you stand on a balance board, your body constantly makes micro-adjustments to stay upright, activating stabilizer muscles that aren’t typically engaged, improving proprioception (your body’s awareness in space).
Foam Rollers for Diploma in Physiotherapy Technology
Foam rollers are versatile, cylindrical tools used for self-myofascial release (self-massage) to help relieve muscle tension, improve flexibility, and speed up recovery from workouts. They come in various sizes, densities, and textures to suit different needs and preferences.
Types and Features
Foam rollers are primarily categorized by their density and surface texture, which determine the intensity of the massage.
- Standard (Smooth) Foam Rollers: These have a smooth, even surface and are ideal for beginners or general muscle maintenance. The pressure is less intense, allowing users to get accustomed to the practice with minimal discomfort. Examples include the Amazon Basics High-density Round Foam Roller and the OPTP Silver AXIS Standard Foam Roller.
- Textured Foam Rollers: Featuring ridges, knobs, or bumps, these rollers are designed to provide a deeper, more targeted massage by mimicking the hands of a massage therapist. They are effective for working on specific muscle knots or trigger points. An example is the PowX Textured Foam Roller for Muscle Massage.
- High-Density Foam Rollers: These offer a firm, consistent pressure and are made from durable materials (like EPP foam) that retain their shape over time. They are suitable for athletes or individuals experienced with foam rolling who need deep tissue pressure. The Balanced Body High-Density Foam Roller is an example of this type.
- Hollow Core Rollers: These are lightweight and often feature a textured outer layer with a hollow center, making them suitable for travel.
Benefits
Regular use of foam rollers offers several physical benefits:
- Muscle Soreness and Tension Relief: Helps reduce tightness, soreness, and inflammation in muscles and soft tissues.
- Improved Flexibility and Range of Motion: Enhances flexibility and helps joints move more easily through their full range of motion, especially when used as part of a warm-up routine.
- Enhanced Circulation: Improves blood flow to targeted areas, aiding in faster muscle recovery.
- Injury Prevention: By targeting and releasing tight areas, foam rolling can help prevent injuries during workouts.
Usage Tips
- Start Gently: If new to foam rolling, begin with a softer, smooth roller and apply gentle pressure, gradually increasing intensity as your body adjusts.
- Target Soft Tissue: Focus on soft, fleshy muscle tissue and avoid rolling over bony areas like knees, the pelvis, or the lower back, as this can cause injury.
- Slow and Controlled Movements: Slowly roll back and forth over the targeted muscle group, holding on tender spots for 20-30 seconds.
- Consistency is Key: For optimal results, aim to foam roll for about 30-60 seconds per muscle group at least twice a week, or even daily.
 HRTD Medical Institute
HRTD Medical Institute






One comment
Pingback: Diploma in Physiotherapy 4 Years Long Course in Bangladesh