Nursing Courses in Dhaka Details:
Nursing Course 6 Months, 1 Year, 2 Years, 3 Years, and 4 Years. Mobile No. 01941-123488. The common Subjects for Nursing Course are Human Anatomy & Physiology, Chemistry & Pharmacology, First Aid & OTC Drugs, General Nursing & Clinical Nursing.
6 Months Best Nursing Courses:

6 Months Nursing Course. Mobile No: 01987-073965. 6 Months Nursing Training Course (NTC 6 Months). Admission Fee Tk 7500, Monthly Fee Tk 2500×6=Tk 15000, Exam Fee Tk 3000/-. Total Subjects 5, Total Exam Marks 500. The Subjects are Human Anatomy & Physiology, Chemistry & Pharmacology, First Aid & OTC Drugs, General Nursing & Clinical Nursing.
1 Year Best Nursing Courses:

Nursing Training Course( 1 Year): Mobile No. 01941-123488, 01797-522136. This Nursing course contains 10 subjects in 2 semesters. 1st semester contains 5 subjects which are Human Anatomy & Physiology, Chemistry & Pharmacology, First Aid & Treatment, Study of OTC Drugs, and Hematology & Pathology. The 2nd semester contains 5 subjects which are Cardiovascular Nursing, Orthopedic Nursing, General Nursing, Gynecological Nursing, and Clinical Nursing with Practical.
Diploma in Nursing Assistant (DNA 2 Years) Course:

Diploma in Nursing Assistant ( 2 Year) Best Nursing Training Courses: Mobile No. 01941-123488, 01797-522136. This course contains 18 subjects in 4 semesters. 1st semester contains 5 subjects which are Human Anatomy & Physiology, Chemistry & Pharmacology, First Aid & Treatment, Study of OTC Drugs, and Hematology & Pathology. The 2nd semester contains 5 subjects which are Cardiovascular Nursing, Orthopedic Nursing, General Nursing, Gynecological Nursing, and Clinical Nursing with Practical.

Nursing Course 3 Years in Mirpur Details
Nursing Course 3 Years in Mirpur Contains 24 Subjects. Total Course Fee Tk 152500/-. Admission Fee Tk 26500/-, Monthly Fee Tk 3000/- and Exam Fee. This 3 Years Nursing Course is Divided into 6 Semesters. Each of the 1st and 2nd Semester Contains 5 Subjects and Each of the 3rd and 4th Semester Contains 4 Subjects. Each of the 5th and 6th Semesters contains 3 Subjects.
Nursing Course 4 Years in Mirpur Details
Nursing Course 4 Years in Mirpur Contains 30 Subjects. Total Course Fee Tk 198500/-. Admission Fee Tk 30500/-, Monthly Fee Tk 3000/- and Exam Fee. This 4 Years Nursing Course is Divided into 8 Semesters. Each of the 1st and 2nd Semester Contains 5 Subjects and Each of the 3rd and 4th Semester Contains 4 Subjects. Each of the 5th and 6th Semesters contains 3 Subjects. Each of the 7th and 8th Semesters Contains 3 Subjects.
Location of Nursing Course in Mirpur
Location of Nursing Course 6 Months. Mobile No: 01987-073965, 01797-522136. HRTD Medical Institute, Section-6, Block-Kha, Road-1, Plot-11, Metro Rail Piller No. 249, Mirpur-10 Golchattar, Dhaka-1216. It is just by the side of Islami Bank Bangladesh Limited, Janata Bank Limited, and Agrani Bank Limited.
Why Nursing Courses Are Important?
Nursing Courses are important because these courses are essential in our daily life. New diseases are occurring daily due to our polluted environment and toxic foods. Air pollution, Water pollution, and Soil pollution are causing new diseases. Chemical-mixing foods are destroying our vital organs like kidneys, lungs, hearts, and brains. As a result, nursing works are essential in our daily family life. Hospitals, Clinics, and all other health-related organizations require more and more nurses. Nursing job is available everywhere in the world. If you want to complete your Nursing Courses in Mirpur, please contact with us.
What nursing means?
Nursing is a profession that is focused on providing healthcare to individuals, families, and communities, so they can attain, maintain, or recover optimal health and quality of life. It encompasses a wide range of care activities from helping people stay healthy to providing medical care, as well as providing emotional, psychological, and spiritual support. If you want to complete your Nursing Courses in Mirpur, please contact with us.
Nursing is an incredibly diverse profession. Nurses are involved in every aspect of healthcare, from working in hospitals and clinics to visiting homebound patients to conducting research. They are also involved in educating the public about health and safety and advocating for policy changes that improve access to quality care. If you want to complete your Nursing Courses in Mirpur, please contact with us.
Nurses are highly trained professionals who must pass rigorous licensing exams to practice. They must be able to assess patient needs, develop care plans, and provide direct care. They must also be able to work as part of a team, communicating and collaborating with other healthcare professionals. If you want to complete your Nursing Courses in Mirpur, please contact with us.
What is the best career in nursing?
Nursing course is a rewarding and exciting career path with many opportunities for growth and advancement. It is a profession that is in high demand, and with the right education and experience, nurses can find a job in almost any field. But which nursing career is the best? If you want to complete your Nursing Courses in Mirpur, please contact with us.
The best career in nursing depends on what you’re looking for. Some nursing careers offer higher pay, while others offer more flexible schedules and job satisfaction. Some nursing roles offer more specialized training, while others require general knowledge. If you want to complete your Nursing Courses in Mirpur, please contact with us.
For those who are looking for a career in nursing that is both financially and emotionally rewarding, Registered Nurse (RN) is the best choice. With an RN designation, nurses can work in a variety of settings, such as hospitals, long-term care facilities, and even home health care. They can specialize in areas such as gerontology, pediatrics, or critical care. And they can continue their education to become a nurse practitioner or nurse anesthetist, both of which offer higher salaries and greater autonomy. If you want to complete your Nursing Courses in Mirpur, please contact with us.
For those who enjoy working with people, Certified Nursing Assistants (CNAs) may be a great choice. CNAs work with patients in many different settings, such as hospitals, long-term care facilities, and even in private homes. They provide basic care, such as bathing and feeding, and they can also help with medical procedures. CNAs may also have the opportunity to advance to become a Licensed Practical Nurses (LPN) or Registered Nurses (RN). If you want to complete your Nursing Courses in Mirpur, please contact with us.
For those who want a job that is both challenging and rewarding, Nurse Practitioners (NPs) may be the best choice. NPs are advanced-practice registered nurses who have completed additional coursework and clinical training. They can diagnose and treat illnesses, and order and interpret tests. If you want to complete your Nursing Courses in Mirpur, please contact with us.
Document for admission in Nursing Courses in Mirpur
Photocopy of Certificate, Photocopy of NID, Passport Size Photo 4 Pcs. Without NID, a Birth Certificate is allowed for an emergency case.
Practical Works for Nursing Courses in Mirpur
Practical Works for Nursing Course:
Understanding of heartbeat, Heart Rate, Pulse Rate, Weak Pulse, Strong Pulse, Normal Pulse, Tachycardia, Bradycardia, Heart Sound, Normal Heart Sound, Measurement of Blood Pressure, Systolic Blood Pressure, Diastolic Blood Pressure, Pulse Pressure, Mean Blood Pressure,
Hypertension, Hypotension, Hypertension Emergency, Emergency Management of Hypertension, Emergency Management of Hypotension, Emergency Management of Hypertension Urgency,
Pushing Injection, Pushing IM Injection, Pushing IV Injections, Setting of Cannula, Cleaning, Dressing, Bandaging, Stitching, Diabetic Checking, Blood Glucose Measurement, Report Understanding of Diabetic Patient, Report Understanding of Hypertensive Patient, Prescription Understanding of Diabetic Patient, Prescription Understanding of Hypertensive Patient, Prescription Understanding of Hypotensive Patient,
Application of Ophthalmic Drugs, Application of Pediatric Drugs, Inhalation, Exhalation, Use of Inhaler, Use of Rotahaler, Use of Nebulizer Machine, Management of Oral Dose Schedule, Application of Ointment and Cream, Setting Splinter, First Aid of Shock, First Aid of Snake Bite, First Aid of Burn, First Aid of Electric Shock, Emergency Management of Anaphylactic Shock, CPR Application Process, Uges of Antiseptic Drugs, Dosage forms of Drugs, Application of Sublingual Rout, etc
Nursing Courses in Mirpur
Other Nursing Courses Except for the 6-month nursing Course, We have some diploma-type nursing Courses of Duration 1 Year, 2 Years, 3 Years, and 4 Years. These courses are more valuable and demandable not only in Bangladesh but also over the world. Nursing Course 1 Year Tk 52500/-, Nursing Course 2 Years Tk 92500/-, Nursing Course 3 Years Tk 142500/-, and Nursing Course 4 Years Tk 182500/-. Payment System: Admission Fee, Monthly Fee, and Exam Fee.
Nursing Training Course Outline:
Introduction to Nursing: Overview of nursing as a profession, its history and development, scope, and role of a nurse in healthcare.
Anatomy and Physiology: Study of the structure and function of human body systems and organs.
Medical-Surgical Nursing: Basic knowledge of medical-surgical nursing, common diseases, and treatments.
Pediatrics Nursing: Understanding the principles of pediatric nursing and care of children and infants.
Obstetrics and Gynecology Nursing: Knowledge of prenatal care, childbirth, and postpartum care of women.
Mental Health Nursing: Understanding of mental health, psychiatric disorders, and nursing care for patients with mental health problems.
Community Health Nursing: Principles of community health nursing and public health promotion.
Clinical Skills Laboratory: Hands-on training in basic nursing procedures, such as bed making, wound care, and administration of medications.
Clinical Practicum: Supervised clinical experience in a healthcare setting to apply knowledge and skills learned in the course.
About HRTD Medical Institute:
HRTD Medical Institute is a leading nursing training institute located in Dhaka, Bangladesh. The Institute offers a comprehensive nursing training program that includes both theoretical and practical training.
The course is taught by experienced and knowledgeable faculty members, who use a combination of lectures, practical sessions, and clinical experience to ensure that students receive a well-rounded education. Upon completion of the program, students are equipped with the knowledge and skills necessary to provide quality nursing care in a variety of healthcare settings.
Teachers for Nursing Course
Dr. Md. Sakulur Rahman, MBBS, CCD (BIRDEM), Course Director
Dr. Sanjana Binte Ahmed, BDS, MPH, Assistant Course Director
Dr. Tisha, MBBS, PGT Gyne, Assistant Course Director
Dr. Suhana, MBBS, PGT Medicine
Dr. Danial Hoque, MBBS, C-Card
Dr. Tisha, MBBS
Dr. Afrin Jahan, MBBS, PGT Medicine
Dr. Ananna, MBBS
Dr. Lamia Afroze, MBBS
Dr. Amena Afroze Anu, MBBS, PGT Gyne, Assistant Course Director
Dr. Farhana Antara, MBBS,
Dr. Nazmun Nahar Juthi, BDS, PGT
Dr. Farhana Sharna, MBBS
Dr. Bushra, MBBS
Dr. Turzo, MBBS
Dr. Kamrunnahar Keya, BDS, PGT (Dhaka Dental College)
Dr. Shamima, MBBS, PGT Gyne
Dr. Alamin, MBBS
Dr. Benzir Belal, MBBS
Dr. Disha, MBBS
Dr. Mahinul Islam, MBBS
Dr. Tisha, MBBS, PGT Medicine
Dr. Anika, MBBS, PGT
Dr. Jannatul Ferdous, MBBS, PGT Gyne
Dr. Jannatul Aman, MBBS, PGT
Dr. Rayhan, BPT
Dr. Abu Hurayra, BPT
Dr. Sharmin Ankhi, MBBS, PGT Medicine
Md. Monir Hossain, B Pharm, M Pharm
Md. Monirul Islam, B Pharm, M Pharm
Md. Feroj Ahmed, BSc Pathology, PDT Medicine
Eti Zahan (BSc Nurse)
Total Nursing Courses in Dhaka of HRTD Medical Institute
- 6 Months Nursing Course
- 1 Year Nursing Course
- 2 Years Nursing Course
- 3 Years Nursing Course
- 4 Years Nursing Course
Subjects for Nursing Course 6 month
- Anatomy & Physiology
- First Aid & Pharmacology-1
- Study of OTC
- Pediatric Nursing
- Geriatric Nursing
Subjects for Nursing Course 1 Year
1st Semester Subjects
- Anatomy & Physiology
- Chemistry & Pharmacology-1
- Study of OTC
- First Aid & Treatment
- Hematology & Pathology for Medical Practice
2nd Semester Subjects
- Cardiovascular Nursing & Clinical Nursing
- Orthopedic Nursing
- Surgical Nursing
- Gynecological Nursing
- Medical Diagnosis & Treatment
Subjects for Nursing Course 2 Years
1st Semester Subjects
- Anatomy & Physiology
- Chemistry & Pharmacology-1
- Study of OTC
- First Aid & Treatment
- Hematology & Pathology for Medical Practice
2nd Semester Subjects
- Cardiovascular Nursing & Clinical Nursing
- Basic Orthopedic Nursing
- Surgical Nursing
- Gynecological Nursing
- Medical Diagnosis & Treatment
3rd Semester Subjects
- Gastro Anatomy & Physiology
- Gastrological Drug & Pharmacology
- Normal Delivery & Complications
- Menstrual Complications
4th Semester Subjects
- Neuron Orthopedic Nursing-1
- Midwifery Nursing-1
- Medical Diagnosis
- Geriatric Nursing & Treatment
Subjects for Nursing Course 3 Years
1st Semester Subjects
- Anatomy & Physiology
- Chemistry & Pharmacology-1
- Study of OTC
- First Aid & Treatment
- Hematology & Pathology for Medical Practice
2nd Semester Subjects
- Cardiovascular Nursing & Clinical Nursing
- Basic Orthopedic Nursing
- Surgical Nursing
- Gynecological Nursing
- Medical Diagnosis & Treatment
3rd Semester Subjects
- Gastro Anatomy & Physiology
- Gastrological Drug & Pharmacology
- Normal Delivery & Complications
- Menstrual Complications
4th Semester Subjects
- Midwifery Nursing-1
- Medical Diagnosis
- Gastro Intestinal Nursing
- Neuron Orthopedic Nursing
5th Semester Subjects
- Geriatric Nursing
- Neuron Orthopedic Nursing-1
- Pediatric Nursing-1
6th Semester Subjects
- Abortion/Miscarriage
- Common childhood Disease
- Nutrition & Dietetics
Subjects for Nursing Course 4 Years
1st Semester Subjects
- Anatomy & Physiology
- Chemistry & Pharmacology-1
- Study of OTC
- First Aid & Treatment
- Hematology & Pathology for Medical Practice
2nd Semester Subjects
- Cardiovascular Nursing & Clinical Nursing
- Basic Orthopedic Nursing
- Surgical Nursing
- Gynecological Nursing
- Medical Diagnosis & Treatment
3rd Semester Subjects
- Gastro Anatomy & Physiology
- Gastrological Drug & Pharmacology
- Normal Delivery & Complications
- Gastro Intestinal Drug
4th Semester Subjects
- Menstrual Complication Treatment
- Neuron Orthopedic Nursing
- Midewifery Nursing-1
- Nursing in Dermatology
5th Semester Subjects
- Geriatric Nursing
- Neuron Orthopedic Nursing-2
- Pediatric Nursing-1
6th Semester Subjects
- Abortion/Miscarriage
- Common childhood Disease
- Nutrition & Dietetics-1
7th Semester Subjects
- Nutrition & Dietetics-2
- Male Reproductive Ana & Physiology
- Female Reproductive Ana & Physiology
8th Semester Subjects
- Pregnancy & Lactation Care
- Pediatric Nursing-2
- Psychiatric Nursing
Practical Class For Nursing Course
- Heart Beat, Heart Rate
- Heart Sound,Pulse
- BP,Hypertension,Hypotension
- First Aid Box
- Auscultation
- Inhaler,Rotahaler
- Nebulizer
- Blood Glucose
- Injection- I/V
- Injection I/M
- Cleaning ,Dressing, Bandaging
- Saline
- CPR
- Stitch
- Body Temperature
- Blood Grouping
- Nasal Tube , Hand Wash
- Cyanosis, Dehydration

Human Anatomy and Physiology Details for Nursing Courses in Dhaka, Bangladesh
Human Anatomy and physiology is a subject of Medical Science that describes the structure and functions of the human body, such as the heart, lungs, kidneys, liver, brain, skeleton, skin, muscle, fat, and blood. This subject is important for Paramedical Courses.
This subject is common for all medical and dental students. There are some systems of the Human body: the Respiratory System, Digestive System, Blood and circulatory System, Nervous System, Endocrine System, Skeletal System, Muscular System, Immune System, Reproductive System, Integumentary System, Excretory System, Urinary System, Hepatobiliary System, Lymphatic System, etc. Every System is made up of some organs The digestive System is made up of The Oral Cavity, Tongue, Teeth Esophagus, Stomach or Gastro, Small Intestine, Large Intestine, Appendix, Rectum, and Anus. The respiratory System comprises the Nasal Cavity, Nasal conchae, Pharynx, Larynx, Trachea, bronchi, Right Lung, Left Lung, alveoli, and Pleura
শারীরিক গঠন এবং এর কার্যাবলীর অধ্যয়ন হল অ্যানাটমি এবং ফিজিওলজি। এখানে আমরা মানবদেহের সিস্টেম এবং এর অঙ্গ, টিস্যু এবং কোষ নিয়ে আলোচনা করি। মানবদেহের সিস্টেমগুলি হ’ল হজম সিস্টেম, শ্বাসযন্ত্র, কার্ডিওভাসকুলার সিস্টেম, কঙ্কাল সিস্টেম, পেশীতন্ত্র, স্নায়ুতন্ত্র, এন্ডোক্রাইন সিস্টেম, ইমিউন সিস্টেম, লিম্ফ্যাটিক সিস্টেম, ইন্টিগুমেন্টারি সিস্টেম এবং ইউরিনারি সিস্টেম
Definition of Anatomy-Anatomy is the scientific study of the structure of the human body and its parts, including bones, muscles, organs, tissues, and cells.
Anatomy হচ্ছে মানবদেহের কাঠামো বা গঠন নিয়ে বৈজ্ঞানিক অধ্যয়ন।
এর মধ্যে হাড়, পেশী, অঙ্গ-প্রত্যঙ্গ, টিস্যু ও কোষ—সবকিছুর গঠন কীভাবে সাজানো আছে তা শেখানো হয়।
Definition of Physiology-Physiology is the scientific study of the functions and activities of the parts of the human body and how they work together to maintain life.
Physiology হচ্ছে মানবদেহের বিভিন্ন অংশের কাজ বা কার্যক্রম নিয়ে বৈজ্ঞানিক অধ্যয়ন।
দেহের প্রতিটি অঙ্গ কীভাবে কাজ করে এবং একসাথে জীবনের কার্যক্রম বজায় রাখে—তা ব্যাখ্যা করে
সহজভাবে মনে রাখার ট্রিক:
- Anatomy = Structure (গঠন)
- Physiology = Function (কাজ)
Human Body Systems
- Skeletal System(অস্থি তন্ত্র)
- Muscular System(পেশী তন্ত্র)
- Nervous System(স্নায়ুতন্ত্র)
- Endocrine System(হরমোন তন্ত্র)
- Respiratory System(শ্বাসযন্ত্র)
- Cardiovascular / Circulatory System(রক্ত সঞ্চালন তন্ত্র)
- Digestive System(পরিপাক তন্ত্র)
- Urinary System(মূত্র তন্ত্র)
- Reproductive System(প্রজনন তন্ত্র — Male/Female)
- Integumentary System(ত্বক তন্ত্র — Skin, hair, nail)
- Immune / Lymphatic System(রোগ প্রতিরোধ ও লসিকা তন্ত্র)
- Special Sense Organ System(ইন্দ্রিয় তন্ত্র — চোখ, কান, নাক, জিহ্বা, ত্বক)
কয়েকটি সিস্টেম সম্পর্কে আলোচনা করা হলো:
Skeletal System (অস্থি তন্ত্র)
Anatomy
- শরীরের মোট হাড়: প্রায় 206 টি
- প্রধান অংশ:
- Skull (মস্তিষ্কের খুলি)
- Vertebral column (মেরুদণ্ড)
- Rib cage (বক্ষপিঞ্জর)
- Upper limb bones (হাতের হাড়)
- Lower limb bones (পায়ের হাড়)
- Jaw bone (Mandible—দাঁতের গুরুত্বপূর্ণ)
Physiology (কাজ)
- শরীরকে কাঠামো দেয়
- অভ্যন্তরীণ অঙ্গকে রক্ষা করে
- চলাফেরায় সাহায্য করে (muscles এর সাথে joint)
- RBC তৈরি হয় Bone marrow-তে
- Calcium ও Minerals storage
Muscular System (পেশী তন্ত্র)
Anatomy:
- Skeletal muscles (ইচ্ছামতো নড়ানো যায়)
- Smooth muscles (অটোমেটিক—intestine, blood vessels)
- Cardiac muscle (হৃদপেশী)
Physiology:
- শরীর নড়া–চড়া
- Walking, running, chewing (দাঁতের জন্য গুরুত্বপূর্ণ)
- Posture ঠিক রাখা
- Body heat উৎপাদন
- Heart beating (cardiac muscle)
Nervous System (স্নায়ুতন্ত্র)
Anatomy:
- Brain
- Spinal cord
- Peripheral nerves
- 12 pairs Cranial nerves (Trigeminal nerve – dental pain sensation)
Physiology:
- Sensation (pain, touch, temperature)
- শরীরের প্রতিটি কাজ নিয়ন্ত্রণ
- Reflex action
- Muscle movement control
- Body coordination
Respiratory System (শ্বাসযন্ত্র)
Anatomy:
Nose → Pharynx → Larynx → Trachea → Bronchi → Lungs → Alveoli
Physiology:
- Oxygen শরীরে প্রবেশ
- Carbon dioxide বের করে
- Acid-base balance
- Speech / Voice production
Digestive System (পরিপাক তন্ত্র)
Anatomy:
Mouth → Esophagus → Stomach → Small intestine → Large intestine → Liver → Pancreas
Physiology:
- খাদ্য ভাঙ্গা (digestion)
- পুষ্টি শোষণ
- Energy supply
- Waste elimination
Nursing importance: Nutrition, ORS, Feeding tube care

General Chemistry for Nursing Courses in Dhaka, Bangladesh
General Chemistry is an important subject in medical science. This Subject is important for understanding Pharmaceutical Chemicals and Biochemicals. With the help of general chemistry, we can study drugs and medicine, and biochemicals.
What is Chemistry? (সংজ্ঞা)
Chemistry হলো এমন একটি বিজ্ঞান শাখা যেখানে পদার্থের গঠন, উপাদান, বৈশিষ্ট্য এবং রাসায়নিক বিক্রিয়া নিয়ে আলোচনা করা হয়।
Chemistry হলো পদার্থ (matter)-এর
- গঠন (composition),ধর্ম (properties),পরিবর্তন (change/reaction) নিয়ে অধ্যয়ন।
Nursing ব্যবহার:
IV fluid, electrolyte, medicine interaction, pH balance বুঝতে chemistry দরকার।
Matter (পদার্থ)
- Matter = যেকোনো কিছু যার ভর আছে ও স্থান দখল করে।
Types:
- Solid (কঠিন) – bone, ice
- Liquid (তরল) – blood, water
- Gas (গ্যাস) – oxygen, CO₂
Atom & Molecule
- Atom: পদার্থের ক্ষুদ্রতম কণা (Proton + Neutron + Electron)
- Molecule: দুই বা ততোধিক atom যুক্ত হলে molecule।
উদাহরণ: H₂O, O₂
Element, Compound, Mixture
- Element: এক ধরনের atom, যেমন O, H, Na
- Compound: দুই বা ততোধিক element chemically যুক্ত, যেমন NaCl, H₂O
- Mixture: রাসায়নিক বিক্রিয়া ছাড়া মিশ্রণ, যেমন air, saline
Acid, Base & Salt
- Acid: pH < 7, H⁺ দেয়, টক স্বাদ (HCl, Vinegar)
- Base: pH > 7, OH⁻ দেয়, তিতা (NaOH, Soap)
- Salt: Acid + Base → Salt + Water (NaCl)
Nursing: IV saline, ORS, electrolyte balance
pH Scale
- Scale: 0–14
- pH 7 → Neutral, <7 Acid, >7 Base
- Normal blood pH: 7.35–7.45
- As imbalance → acidosis / alkalosis
Electrolytes
- Charged ions in body fluids
Major: Na⁺, K⁺, Ca²⁺, Mg²⁺, Cl⁻, HCO₃⁻
Nursing: IV therapy, cardiac monitoring, dehydration treatment
Solution
- Solute + Solvent = Solution
- Example: NaCl + water = saline
- Types: Isotonic, Hypotonic, Hypertonic
Chemical Reactions
- Combination: A + B → AB
- Decomposition: AB → A + B
- Displacement: A + BC → AC + B
- Neutralization: Acid + Base → Salt + Water
Biochemistry Basics
- Carbohydrates: Energy, Glucose, Starch
- Proteins: Body building, meat, egg
- Lipids (Fat): Energy storage, butter, oil
- Vitamins & Minerals: Metabolism & body function control
Water
- 60–70% of body
- Functions: Temperature regulation, Transport, Digestion, Lubrication
- Nursing: IV saline, ORS
Nursing Short Notes Summary
- Matter = Solid + Liquid + Gas
- Atom = Proton + Neutron + Electron
- pH normal = 7.35–7.45
- Saline = NaCl solution
- Acid + Base = Salt + Water
- Electrolyte = Na⁺, K⁺, Ca²⁺, Mg²⁺, Cl⁻, HCO₃⁻
- Glucose = main energy source
Pharmacology Details for Nursing Courses in Dhaka, Bangladesh
Pharmacology is an important subject in medical science. The study of Drugs and Medicine is called Pharmacology. We study drug knowledge here. The most common points of drug knowledge are drug descriptions, Indications, dosage forms, Doses, Contraindications, Side Effects, Pregnancy categories, Drug Interactions, and drug Storage.
In Pharmacology-1, We provide drug knowledge of group-wise drugs and medicine such as Anti Inflammatory Drugs, NSAID Drugs, Steroid Drugs, Antiulcer Drugs, Anti Bacterial Drugs (Antibiotic Drugs), Anti Fungal Drugs, Anti Protozoa Drugs, Anti Viral Drugs, Anti Histamine Drugs, Anti Asthmatic Drugs, Analgesic Drugs, Anti Pyretic Drugs, Anthelmintic Drugs, Cardiovascular Drugs, Beta Blocker Drugs, Calcium Channel Blocker Drugs, Antiplatelet Drugs, Anti Diabetic Drugs, etc.
Definition of Pharmacology- Pharmacology is the science of drugs, including their origin, properties, effects, and therapeutic uses.
Pharmacology হলো ঔষধ সম্পর্কিত বিজ্ঞান, যা ঔষধের উৎস, গঠন, প্রভাব ও চিকিৎসাগত ব্যবহার নিয়ে আলোচনা করে।
Objectives of Pharmacology
- রোগীর চিকিৎসায় ঔষধের সঠিক ব্যবহার নিশ্চিত করা।
- Drug interactions ও side effects বোঝা।
- Nurse হিসেবে medication administration এবং monitoring করা।
- Patient safety ও therapeutic outcome নিশ্চিত করা।
Classification of Drugs
1. According to Action
- Analgesics (Pain relief) – Paracetamol, Morphine
- Antibiotics (Infection control) – Amoxicillin
- Antipyretics (Fever reduction) – Paracetamol
- Antihypertensives (Blood pressure) – Atenolol
- Diuretics – Furosemide
2. According to Source
- Natural – Plants, Animals (Morphine, Digoxin)
- Synthetic – Chemically made (Paracetamol)
3. According to Effect
- Local – Topical creams, ointments
- Systemic – Oral, IV drugs
Routes of Drug Administration
- Oral (PO) – Tablets, syrup
- Parenteral – IV, IM, Subcutaneous
- Topical – Cream, lotion, eye drops
- Inhalation – Nebulizer, inhalers
- Sublingual / Buccal – Under tongue
Pharmacokinetics (Drug Movement in Body)
- Absorption – Drug enter blood
- Distribution – Drug reaches target tissue
- Metabolism – Liver converts drug to active/inactive form
- Excretion – Kidney / Bile eliminates drug
Pharmacodynamics (Drug Effect on Body)
- Mechanism of drug action
- Receptor binding
- Therapeutic effect
- Side effects / adverse reactions
Nursing Considerations in Pharmacology
- Check patient’s allergy history
- Check vital signs before & after administration
- Correct dose & route
- Observe side effects & reactions
- Maintain drug chart & documentation
- Educate patient regarding drug use & precautions
Common Drug Groups in Nursing Practice
| Drug Group | Examples | Nursing Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Analgesics | Paracetamol, Morphine | Pain assessment before/after |
| Antibiotics | Amoxicillin, Ceftriaxone | Check for allergy, complete course |
| Antipyretics | Paracetamol | Monitor temperature |
| Antihypertensives | Atenolol, Enalapril | Monitor BP, pulse |
| Diuretics | Furosemide | Monitor electrolytes, urine output |
| Anticoagulants | Heparin, Warfarin | Monitor bleeding, PT/INR |
| Sedatives / Hypnotics | Diazepam | Monitor consciousness |
| Insulin | Regular / NPH | Monitor blood sugar |
| Bronchodilators | Salbutamol | Observe respiratory response |
Side Effects & Adverse Drug Reactions
- Common: Nausea, vomiting, headache, rash
- Severe: Anaphylaxis, hypotension, arrhythmia
Nursing Action: Stop drug, report doctor, monitor patient
Patient Education
- Explain purpose of medication
- Correct dose & timing
- Possible side effects
- Avoid self-medication
- Compliance is essential
First Aid & Treatment For Nursing Courses in Dhaka, Bangladesh
First Aid & Treatment is an important subject for the Nursing Assistant Course. Topics of First Aid Treatment are: Definition of First Aid, Purposes of First Aid, First Aid for Bleeding, First Aid for Cuts, First Aid for Snake Bites, Definition of Shock, Classification of Shock, Causes of Shock, Stages of Shock. Hypovolemic shock, Cardiogenic Shock, Neurogenic Shock, Burn Shock, Electric Shock, Anaphylactic Shock, Etc. Topics of Treatment are Causes of Sinusitis, Clinical Features os Sinusitis, Treatment of Sinusitis, Causes of Tonsilitis, Clinical Features of Tonsilitis, Treatment of Tonsilitis, Causes of Laryngitis, Clinical Featurse of Laryngitis, Treatment of Laryngitis, Causes of Vomiting, Treatment of Vomiting, Causes of Fever, Treatmeent of Fever, Causes of Diarrhea, Treatment of Diarrhea, Name of Diarrheal Diseases, etc.
First Aid is the immediate, temporary care given to a sick or injured person until professional medical help is available.
First Aid হলো আহত বা অসুস্থ ব্যক্তিকে দ্রুত এবং অস্থায়ী যত্ন প্রদান করা, যতক্ষণ না পেশাদার চিকিৎসা পাওয়া যায়।
Objectives of First Aid
- জীবন রক্ষা করা (Preserve life)
- অবস্থার অবনতি প্রতিরোধ করা (Prevent further injury)
- রোগীর আরাম ও স্বস্তি দেওয়া (Promote recovery & comfort)
- জরুরি চিকিৎসার জন্য প্রস্তুতি নেওয়া (Prepare for medical care)
Principles of First Aid
- Safety First – নিজের এবং রোগীর নিরাপত্তা নিশ্চিত করা
- Assessment – Patient evaluation (Airway, Breathing, Circulation)
- Immediate Action – দ্রুত ব্যবস্থা নেওয়া
- Professional Help – যত দ্রুত সম্ভব চিকিৎসকের সাহায্য নিন
- Do No Harm – ক্ষতি না করা
Primary Survey (ABC Method)
A – Airway
- Ensure airway is open
- Remove obstruction
B – Breathing
- Check breathing
- Provide artificial respiration if needed
C – Circulation
- Check pulse & bleeding
- Start CPR if pulse absent
Common First Aid Measures
- Bleeding / Wounds
- Apply direct pressure
- Elevate limb
- Clean with antiseptic
- Bandage
- Burns
- Cool burn with water
- Apply sterile dressing
- Do not apply oil/ointment immediately
- Fractures / Sprains
- Immobilize limb
- Apply splint
- Avoid movement
- Shock
- Lie patient down
- Keep warm
- Monitor vitals
- Seek medical help
- Choking / Airway obstruction
- Heimlich maneuver (abdominal thrust)
- Back blows for infants
- Poisoning / Drug overdose
- Identify poison
- Do not induce vomiting unless instructed
- Call poison control / hospital
- Electric Shock
- Switch off electricity source
- Check ABC
- Treat burns & monitor vitals
- Heat Stroke / Hypothermia
- Move patient to safe place
- Cool or warm body gradually
- Hydration
- Seizures / Epilepsy
- Protect head
- Clear surrounding objects
- Do not restrain limbs
- Monitor breathing
Role of Nurse in First Aid
- Prompt assessment & care
- Maintain patient safety
- Monitor vitals & condition
- Documentation & reporting
- Educate patient & family
- Coordinate with emergency team
First Aid Kit Essentials
- Bandages, gauze, adhesive tape
- Antiseptic, ointments
- Scissors, gloves, tweezers
- Thermometer, stethoscope
- CPR mask, splints, ice packs
- Emergency drugs (as allowed)
Hematology In Nursing Course
Hematology is the branch of medicine focused on the study, diagnosis, and treatment of blood and bone marrow disorders. It encompasses both benign and malignant blood-related conditions, including blood cancers like leukemia and lymphoma. Hematologists and hematopathologists are specialists in this field.
Definition- Hematology is the branch of medical science that deals with the study of blood, blood-forming organs, and blood disorders.
Hematology হলো রক্ত, রক্ত সংশ্লেষক অঙ্গ (যেমন bone marrow, spleen) এবং রক্তের অসুখ নিয়ে অধ্যয়ন।
Objectives of Hematology in Nursing
- Understand composition and functions of blood.
- Recognize normal vs abnormal blood parameters.
- Assist in diagnosis and treatment of blood disorders.
- Monitor patient safety during transfusion.
- Educate patients about blood-related health issues.
Composition of Blood
- Plasma – 55%
- Water, Proteins (Albumin, Globulin, Fibrinogen), Electrolytes, Nutrients
- Formed Elements – 45%
- RBC (Red Blood Cells / Erythrocytes) → Oxygen transport
- WBC (White Blood Cells / Leukocytes) → Infection defense
- Platelets (Thrombocytes) → Blood clotting
Functions of Blood
- Oxygen & CO₂ transport (RBC)
- Immune defense (WBC)
- Clotting (Platelets & clotting factors)
- Nutrient & hormone transport
- Temperature regulation
- Acid-base balance
Hematopoiesis (Blood Formation)
- Occurs in bone marrow, mainly in:
- Vertebra, sternum, pelvis, ribs
- Stem cells differentiate into RBC, WBC, Platelets
Normal Hematological Values
| Component | Normal Range |
|---|---|
| Hemoglobin (Hb) | Male: 13–17 g/dL, Female: 12–16 g/dL |
| RBC count | Male: 4.5–5.5 million/µL, Female: 4–5 million/µL |
| WBC count | 4,000–11,000 /µL |
| Platelet count | 150,000–450,000 /µL |
| Hematocrit (HCT) | Male: 40–54%, Female: 36–48% |
Common Blood Disorders
- Anemia – Low RBC or Hb
- Types: Iron deficiency, Megaloblastic, Hemolytic
- Nursing: Monitor fatigue, pallor, oxygen saturation
- Leukemia – Malignant WBC proliferation
- Nursing: Infection control, monitor WBC, patient education
- Thrombocytopenia – Low platelet count
- Nursing: Bleeding precautions, monitor bruising
- Polycythemia – High RBC count
- Nursing: Monitor for blood clots, hydration
- Hemophilia – Clotting factor deficiency
- Nursing: Prevent trauma, monitor bleeding
Blood Transfusion in Nursing
- Indications: Severe anemia, blood loss, surgery
- Types: Whole blood, Packed RBC, Platelets, Plasma
- Nursing Role:
- Verify patient & blood group
- Monitor for reaction (fever, rash, hypotension)
- Maintain sterile technique
- Record transfusion time & volume
Laboratory Tests in Hematology
- Complete Blood Count (CBC)
- Blood smear
- Coagulation tests (PT, aPTT)
- Bone marrow examination
- Blood typing & crossmatch
Role of Nurse in Hematology
- Collect blood samples safely
- Administer blood & blood products
- Monitor for side effects / transfusion reactions
- Educate patient about anemia, nutrition, medication
- Document findings & report abnormal results
Hematology:
- Bone Marrow: Hematology also involves the study of the bone marrow, the site of blood cell production.
- Diagnosis and Treatment:Hematologists use various tests and techniques to diagnose blood disorders and develop appropriate treatment plans.
- Specialization: Hematology is often combined with oncology, leading to hematologic oncologists who specialize in blood cancers and related disorders.
- Blood Disorders:Hematology deals with a wide range of conditions affecting the blood and its components, including anemia, blood-clotting disorders, and infections.
- Blood Cancers:It plays a crucial role in the diagnosis and treatment of blood cancers, such as leukemia, lymphoma, and myeloma.
Pathology for Medical Practice In Nursing Course
Pathology plays a crucial role in medical practice by diagnosing diseases, advising on treatment, and monitoring patient conditions through laboratory tests and analysis of tissues and fluids. It is a bridge between science and medicine, providing the necessary diagnostic information for clinicians to make informed decisions. Pathologists, specialized medical professionals, analyze samples to identify the cause and nature of diseases, ultimately impacting patient care across various specialties.
Key Functions of Pathology in Medical Practice:
- Diagnosis: Pathologists help diagnose diseases by examining tissues, fluids, and cells, providing crucial information for determining the nature and cause of illness.
- Treatment Guidance: Pathology findings, such as identifying the type of cancer or the presence of an infection, guide treatment decisions, including the selection of appropriate medications, surgical interventions, or other therapies.
- Monitoring Patient Conditions: Pathology tests, like blood analysis or tissue biopsies, enable the monitoring of disease progression and the effectiveness of treatment, allowing for timely adjustments to patient care.
- Advancing Medical Knowledge: Pathology research and advancements in laboratory techniques contribute to a deeper understanding of diseases, leading to new diagnostic tools, treatments, and preventative measures.
Definition Pathology-Pathology is the study of diseases, their causes, mechanisms, structural and functional changes, and effects on the body.
Pathology হলো রোগের কারণ, প্রক্রিয়া, দেহের গঠন ও কাজের পরিবর্তন, এবং রোগের প্রভাব অধ্যয়নের বিজ্ঞান।
Objectives of Pathology
- Understand disease causes (etiology) – রোগের উৎপত্তি।
- Study pathogenesis – রোগ কীভাবে শরীরে প্রভাব ফেলে।
- Identify morphological changes – দেহের টিস্যু বা অঙ্গের পরিবর্তন।
- Guide diagnosis & treatment – চিকিৎসা ও নার্সিং পরিকল্পনায় সাহায্য।
Branches of Pathology
| Branch | English | Bangla |
|---|---|---|
| General Pathology | Study of disease mechanisms, cell injury, inflammation, tissue repair | রোগ প্রক্রিয়া, কোষ ক্ষতি, প্রদাহ, টিস্যু মেরামত অধ্যয়ন |
| Systemic Pathology | Study of specific organ systems & related diseases | নির্দিষ্ট অঙ্গ-প্রণালী ও সংশ্লিষ্ট রোগ অধ্যয়ন |
| Clinical Pathology | Laboratory study of blood, urine, body fluids | রক্ত, মূত্র, শরীরের তরল পরীক্ষার মাধ্যমে রোগ নির্ণয় |
| Surgical Pathology | Examination of tissues removed during surgery | অস্ত্রোপচারের সময় সরানো টিস্যুর পরীক্ষা |
Causes of Disease (Etiology)
- Genetic – Congenital diseases, Sickle cell anemia
- Infectious – Bacteria, Virus, Fungi, Parasites
- Environmental – Toxins, Radiation, Pollution
- Nutritional – Vitamin & mineral deficiency/excess
- Trauma / Physical injury – Burns, Fracture
Bangla:
রোগের কারণ হতে পারে বংশগত, সংক্রমণজনিত, পরিবেশজনিত, পুষ্টি জনিত, আঘাতজনিত।
Pathogenesis (Disease Mechanism)
- Disease process = How disease develops in body
- Example: Infection → Inflammation → Tissue damage → Symptoms
Bangla:
রোগের প্রক্রিয়া = রোগ কীভাবে শরীরে শুরু হয় ও টিস্যু ক্ষতি ঘটায়।
উদাহরণ: সংক্রমণ → প্রদাহ → টিস্যু ক্ষতি → লক্ষণ
Cell Injury & Death
- Reversible injury – Temporary damage (e.g., mild hypoxia)
- Irreversible injury / Cell death – Necrosis, Apoptosis
Bangla:
কোষ ক্ষতি: উল্টানোযোগ্য (অস্থায়ী), উল্টানো অসম্ভব (মৃত কোষ)
Inflammation (প্রদাহ)
- Acute – Short-term, redness, swelling, pain, heat
- Chronic – Long-term, tissue destruction, fibrosis
Bangla:
প্রদাহ = শরীরের প্রতিক্রিয়া সংক্রমণ বা আঘাতের প্রতি।
Acute = হঠাৎ, Chronic = দীর্ঘস্থায়ী
Tissue Repair (টিস্যু পুনরায় নির্মাণ)
- Regeneration – Damaged cells replaced by same type
- Repair / Scar formation – Fibrous tissue replaces lost cells
Bangla:
কোষ বা টিস্যু ক্ষতির পরে শরীরের পুনরায় গঠন বা দাগ তৈরি প্রক্রিয়া।
Disorders Common in Nursing
| Disease Type | English | Bangla | Nursing Focus |
|---|---|---|---|
| Blood Disorders | Anemia, Leukemia | রক্তের অসুখ | Monitor CBC, transfusion care |
| Infectious Diseases | TB, Malaria, Hepatitis | সংক্রমণজনিত রোগ | Infection control, isolation |
| Cardiovascular | Hypertension, MI | হৃদরোগ | Monitor vitals, medication |
| Respiratory | Pneumonia, Asthma | শ্বাসযন্ত্রের রোগ | Oxygen therapy, airway care |
| Metabolic | Diabetes, Thyroid disorder | পুষ্টি ও হরমোন জনিত রোগ | Blood sugar, medication |
| Renal | CKD, UTI | বৃক্কের রোগ | Fluid balance, urine monitoring |
Role of Nurse in Pathology
- Sample collection: Blood, urine, sputum
- Assist in lab tests & diagnosis
- Monitor patient condition & vitals
- Educate patient & family on disease
- Maintain infection control & hygiene
- Documentation & reporting
Study of OTC Drugs & Medicines For Nursing Course in Dhaka, Bangladesh
The drugs that can be bought or sold without a prescription from doctors are OTC drugs. OTC Drugs stand for Over-the-counter Drugs. There are 39 OTC Drugs & Medicines in Bangladesh, but this range is very high in some countries like Japan and the USA. The OTC drugs are Paracetamol, Albendazole, Omeprazole, Bengyl Benzoate Lotion, Permethrin, Vitamin B Complex, Calciium, etc. In the Study of OTC Drugs & Medicine, students can learn about the drug knowledge administration practice of OTC Drugs and Medicine. The common points of Drug Knowledge are Description, Mode of action, Indication, Contraindication, Side effects, Dose form, Daily dose, Pregnancy category, Drug interaction, and Storage.
OTC Drugs Definition-OTC (Over-The-Counter) drugs are medicines that can be purchased without a doctor’s prescription.
OTC ঔষধ হলো এমন ঔষধ যা ডাক্তারি প্রেসক্রিপশন ছাড়া সরাসরি কেনা যায়।
Objectives / Importance in Nursing
- Recognize common OTC drugs patients may use.
- Educate patients about safe use of OTC drugs.
- Prevent overdose, side effects, and drug interactions.
- Promote self-care and minor illness management.
Examples of OTC Drugs
| Drug Category | English | Bangla | Nursing Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Analgesics / Painkillers | Paracetamol, Ibuprofen | ব্যথানাশক | Monitor dose, liver/kidney function |
| Antacids / Acid Reducers | Ranitidine, Omeprazole | এসিড নিয়ন্ত্রক | Prevent misuse, monitor heartburn symptoms |
| Cough & Cold | Dextromethorphan, Chlorpheniramine | কাশি ও সর্দি ঔষধ | Avoid overuse, check allergies |
| Laxatives / Anti-Constipation | Lactulose, Senna | কোষ্ঠকাঠিন্য নিয়ন্ত্রক | Monitor bowel movement, hydration |
| Topical Creams / Ointments | Antifungal cream, Hydrocortisone | ত্বকের ক্রিম | Clean area before application, avoid prolonged use |
| Vitamins & Supplements | Vitamin C, Multivitamins | ভিটামিন ও সম্পূরক | Check daily dose, advise balanced diet |
| Antihistamines | Loratadine, Cetirizine | অ্যালার্জি ঔষধ | Monitor drowsiness, allergic reaction |
Advantages of OTC Drugs
- Easy accessibility
- Quick relief for minor ailments
- Cost-effective
- Promote self-care
Disadvantages / Risks
- Misuse or overdose
- Side effects & drug interactions
- Masking serious disease symptoms
- Delay in proper medical treatment
Nursing Role with OTC Drugs
- Patient education – Explain correct dose & frequency.
- Monitor for side effects – Rash, dizziness, nausea.
- Check interactions – With prescription medicines.
- Document use – Especially in elderly or chronic patients.
- Advise consulting doctor – If symptoms persist > few d
Cardiovascular Nursing for Nursing Course in Dhaka, Bangladesh
Cardiovascular Nursing is an important subject for all Nursing students. We can learn here about Blood Pressure, Heart Rate, heartbeat, Atrial Beat, Ventricular Beat, Heart Sound, Tachycardia, Bradycardia, Atrial Fibrillation, Pulse, Pulse Rate, weak pulse, Strong Pulse, Hypertension or High Blood Pressure, Hypotension or Low Blood Pressure, Systolic BP, Diastolic BP, Pulse BP, Mean BP, Hypertension Management, Hypotension Management, Tachycardia Management, Bradycardia Management, Systolic Hypertension, Diastolic Hypertension, Portal Hypertension, Pulmonary Hypertension, Heart Failure, Congestive Heart Failure, Shock, Hypovolemic Shock, etc.
Definition-Cardiovascular Nursing is the branch of nursing that deals with care of patients with heart and blood vessel diseases, including prevention, monitoring, and treatment.
Cardiovascular Nursing হলো এমন নার্সিং শাখা যা হৃদয় ও রক্তনালীর রোগযুক্ত রোগীর যত্ন, প্রতিরোধ, পর্যবেক্ষণ এবং চিকিৎসার সঙ্গে যুক্ত।
Objectives
- Understand heart anatomy & physiology.
- Recognize common cardiovascular diseases.
- Monitor patient vitals & cardiovascular status.
- Administer medications & interventions safely.
- Educate patients for prevention & lifestyle modification.
Common Cardiovascular Disorders
| Disorder | English | Bangla | Nursing Focus |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hypertension (HTN) | High BP | উচ্চ রক্তচাপ | Monitor BP, meds adherence, lifestyle counseling |
| Hypotension | Low BP | নিম্ন রক্তচাপ | Monitor BP, prevent falls, fluid therapy |
| Myocardial Infarction (MI) | Heart attack | হৃদযন্ত্রের আঘাত | Monitor vitals, oxygen therapy, meds, ECG |
| Heart Failure (HF) | Weak heart pumping | হৃদযন্ত্রের দুর্বলতা | Fluid balance, daily weight, oxygen therapy |
| Arrhythmias | Irregular heartbeat | অনিয়মিত হৃদস্পন্দন | ECG monitoring, med administration, patient education |
| Angina Pectoris | Chest pain | বুকে ব্যথা | Pain assessment, nitroglycerin admin, lifestyle advice |
| Peripheral Vascular Disease (PVD) | Blood flow obstruction | শিরা সংক্রান্ত রোগ | Monitor circulation, prevent ulcers, patient education |
Vital Signs Monitoring in Cardiovascular Nursing
- Blood Pressure (BP)
- Pulse – rate, rhythm, volume
- Respiration rate
- Temperature
- Oxygen saturation (SpO₂)
Nursing Interventions
- Medication Administration – Antihypertensives, Antiarrhythmics, Diuretics, Anticoagulants
- Oxygen Therapy – For hypoxia, HF, MI
- ECG Monitoring – Detect arrhythmias, ischemia
- Fluid & Diet Management – Low salt, fluid restriction if needed
- Lifestyle Education – Smoking cessation, exercise, stress management
- Patient Observation – Signs of chest pain, edema, fatigue
Emergency Care in Cardiovascular Nursing
- CPR – Cardiac arrest
- Defibrillation – Life-threatening arrhythmias
- Nitroglycerin – Acute angina
- Rapid assessment – MI, shock
Patient Education
- Take medications regularly
- Follow low salt, low fat diet
- Monitor blood pressure at home
- Avoid smoking & alcohol
- Recognize early warning signs – chest pain, dizziness, palpitations
Clinical Nursing for Nursing Course in Dhaka, Bangladesh
Clinical Nursing is the branch of nursing that deals with the direct care of patients in hospitals or healthcare settings, focusing on assessing, planning, implementing, and evaluating nursing care.
Clinical Nursing হলো রোগীর সরাসরি যত্ন এবং চিকিৎসা প্রক্রিয়ার সঙ্গে যুক্ত নার্সিং শাখা।
এতে রোগীর অবস্থা পর্যবেক্ষণ, চিকিৎসা প্রয়োগ, এবং যত্ন পরিকল্পনা ও বাস্তবায়ন অন্তর্ভুক্ত থাকে।
Objectives of Clinical Nursing
- রোগীর শারীরিক ও মানসিক অবস্থা পর্যবেক্ষণ।
- রোগীর যত্ন ও চিকিৎসা প্রদান।
- রোগীর জীবনমান উন্নত করা।
- রোগী ও পরিবারের স্বাস্থ্য শিক্ষার মাধ্যমে সচেতনতা বৃদ্ধি।
- রোগীর সুরক্ষা ও নিরাপত্তা নিশ্চিত করা।
1. Medical-Surgical Nursing
- রোগীকে post-operative এবং chronic illness-এর যত্ন দেওয়া।
- Example: Wound care, IV therapy, medication administration
2. Pediatric Nursing
- শিশু রোগীর যত্ন
- Growth & development monitoring, vaccination, nutrition care
3. Geriatric Nursing
- বয়স্ক রোগীর যত্ন
- Chronic disease management, mobility support, fall prevention
4. Obstetric & Gynecological Nursing
- মাতৃত্বকালীন ও মহিলা রোগীর যত্ন
- Antenatal, postnatal care, labor support
5. Psychiatric Nursing
- মানসিক রোগীর যত্ন
- Behavior management, counseling, therapeutic communication
6. Community / Public Health Nursing
- Community health care, vaccination, health education, disease prevention
Roles of Clinical Nurse
- Direct patient care
- Health assessment & monitoring
- Medication administration
- Wound care & emergency care
- Infection control & safety
- Patient education & advocacy
- Documentation & reporting
Importance in Nursing
- Ensures patient safety
- Improves patient recovery & health outcomes
- Promotes health education
- Reduces hospital-acquired infection risk
- Strengthens professional nursing skills
Orthopedic Nursing for Nursing Course in Dhaka, Bangladesh
Orthopedic nursing is a specialized area of nursing that focuses on the care of patients with musculoskeletal conditions, disorders, and injuries. These nurses provide care for individuals with a wide range of conditions, including fractures, joint replacements, arthritis, and other musculoskeletal problems.
Here’s a more detailed look at orthopedic nursing:
What orthopedic nurses do:
- Assist with pain management: They help manage pain and discomfort associated with musculoskeletal conditions and injuries.
- Educate patients about their conditions and treatment plans:They provide information and support to patients and their families.
- Assist with rehabilitation:They work with physical therapists and other healthcare professionals to help patients regain mobility and function after injuries or surgeries.
- Care for patients with musculoskeletal issues:They provide care for patients with a variety of orthopedic problems, including fractures, joint replacements, and chronic conditions like arthritis and osteoporosis.
- Provide pre- and post-operative care:Orthopedic nurses are involved in the care of patients before and after orthopedic surgeries.
Specific skills and knowledge required:
- Knowledge of musculoskeletal anatomy and physiology:Orthopedic nurses need a strong understanding of the structure and function of bones, joints, muscles, and tendons.
- Experience with pain management techniques:They are skilled in using various methods to relieve pain, including medication and alternative therapies.
- Ability to assess and monitor patients:They can assess patients’ pain levels, monitor their vital signs, and identify potential complications.
- Knowledge of orthopedic devices and techniques:They are familiar with casting, traction, and other devices used in orthopedic care.
- Excellent communication and interpersonal skills:They need to be able to communicate effectively with patients, families, and other healthcare professionals.
Surgical Nursing for Nursing Course in Dhaka, Bangladesh
Surgical nursing, also known as perioperative nursing, is a specialized area of nursing that focuses on the care of patients before, during, and after surgery. Surgical nurses, or operating room nurses, work in the operating room (OR) and may be involved in tasks like setting up the room, preparing surgical tools, and assisting surgeons during procedures. They also provide post-operative care, including monitoring vital signs, managing pain, and preparing patients for discharge.
Definition-Surgical Nursing is the branch of nursing that deals with the care of patients before, during, and after surgery, ensuring safety, preventing complications, and promoting recovery.
Surgical Nursing হলো এমন নার্সিং শাখা যা রোগীর অপারেশন পূর্ব, অপারেশনকালীন ও অপারেশন পরবর্তী যত্ন, নিরাপত্তা, জটিলতা প্রতিরোধ এবং দ্রুত সুস্থতা নিশ্চিত করার সঙ্গে যুক্ত।
Objectives
- Prepare patient for surgery safely.
- Provide intraoperative care.
- Monitor postoperative recovery.
- Prevent surgical complications (infection, bleeding).
- Educate patient and family about pre- and post-operative care.
Phases of Surgical Nursing
| Phase | English | Bangla | Nursing Role |
|---|---|---|---|
| Preoperative | Before surgery | অপারেশনের পূর্ববর্তী | Patient assessment, consent, labs, premedication, hygiene, education |
| Intraoperative | During surgery | অপারেশনের সময় | Assist surgeon & anesthetist, maintain sterile field, monitor vitals |
| Postoperative | After surgery | অপারেশনের পরে | Monitor vitals, pain management, wound care, prevent complications, patient education |
Preoperative Nursing Care
- Assessment: History, vitals, lab tests
- Preparation: Fasting, skin prep, bowel prep
- Education: Procedure explanation, postoperative care, breathing exercises
- Consent: Ensure informed consent is obtained
Intraoperative Nursing Care
- Maintain asepsis & sterile technique
- Monitor patient’s vitals & anesthesia
- Assist with surgical instruments & positioning
- Observe for complications (bleeding, hypotension, arrhythmias)
Postoperative Nursing Care
- Vital Signs Monitoring – BP, pulse, respiration, temperature
- Pain Management – Analgesics, positioning
- Wound Care – Dressing, drainage tubes, signs of infection
- Respiratory Care – Breathing exercises, prevent atelectasis
- Fluid & Electrolyte Balance – IV fluids, intake/output monitoring
- Early Mobilization – Prevent DVT, improve circulation
- Patient Education – Medications, wound care, activity restrictions
Common Postoperative Complications & Nursing Interventions
| Complication | English | Nursing Intervention |
|---|---|---|
| Hemorrhage | রক্তপাত | Monitor vitals, apply pressure, notify surgeon |
| Infection | সংক্রমণ | Aseptic dressing, antibiotics, monitor temperature |
| Shock | শক | Maintain airway, oxygen, fluids, monitor vitals |
| Thrombosis / DVT | রক্তের থ্রম্বাস | Early mobilization, compression stockings |
| Respiratory complications | শ্বাসনালী সমস্যা | Encourage deep breathing, oxygen therapy |
| Pain | ব্যথা | Analgesics, repositioning |
Nursing Responsibilities
- Pre, intra, and postoperative care
- Maintain aseptic technique
- Monitor vital signs and labs
- Administer medications & fluids
- Educate patient & family
- Document care & complications
General Nursing for Nursing Course in Dhaka, Bangladesh
General Nursing is a broad nursing specialty that encompasses a wide range of patient care settings and conditions, from hospitals to community health centers. It involves providing care to patients of all ages and with a variety of health needs, and it is a foundational role in the healthcare system. General nurses are trained to develop their nursing knowledge and skills, become effective team members, and advocate for positive health behaviors.
Definition-General Nursing is the branch of nursing that deals with the comprehensive care of individuals, families, and communities, promoting health, preventing illness, restoring health, and providing care for the sick.
General Nursing হলো এমন নার্সিং শাখা যা ব্যক্তিগত, পারিবারিক ও সমাজিক পর্যায়ে সম্পূর্ণ যত্ন প্রদান করে, স্বাস্থ্য উন্নয়ন, রোগ প্রতিরোধ, স্বাস্থ্য পুনঃস্থাপন এবং অসুস্থদের যত্ন নিশ্চিত করে।
Objectives of General Nursing
- Promote health and wellness in individuals & communities.
- Prevent diseases and complications.
- Restore health of sick patients.
- Provide safe and effective nursing care.
- Educate patients and communities about health practices.
- Develop professional nursing skills and ethical practice.
Principles of Nursing
- Patient-Centered Care – Focus on patient’s needs
- Safety & Comfort – Prevent harm & ensure comfort
- Asepsis & Infection Control – Maintain hygiene & prevent infection
- Observation & Reporting – Monitor patient condition accurately
- Communication & Empathy – Effective interaction with patient & family
- Documentation – Maintain accurate records of care
Scope of General Nursing
| Area | English | Bangla | Nursing Role |
|---|---|---|---|
| Medical Nursing | Care for medical patients | চিকিৎসা রোগীর যত্ন | Monitor vitals, administer meds, patient education |
| Surgical Nursing | Pre-, intra-, post-op care | অপারেশনকালীন যত্ন | Prepare patient, wound care, monitor complications |
| Pediatric Nursing | Child care | শিশু যত্ন | Growth monitoring, vaccination, nutrition care |
| Geriatric Nursing | Elderly care | বয়স্ক রোগীর যত্ন | Chronic disease management, mobility support |
| Obstetric & Gynecologic Nursing | Maternal & female care | মাতৃত্বকালীন ও মহিলা যত্ন | Antenatal, postnatal, labor support |
| Community Nursing | Public health care | সমাজ স্বাস্থ্য | Vaccination, health education, disease prevention |
| Psychiatric Nursing | Mental health care | মানসিক রোগীর যত্ন | Therapeutic communication, behavior management |
| Emergency / Critical Care | Acute & life-threatening care | জরুরি ও জীবনহুমকির যত্ন | CPR, monitoring, triage, resuscitation |
Nursing Process (Steps in General Nursing)
- Assessment – Collect physical, psychological, social data
- Diagnosis / Nursing Diagnosis – Identify patient problems
- Planning – Develop patient-centered care plan
- Implementation – Execute interventions (medication, care, procedures)
- Evaluation – Check effectiveness & revise plan if necessary
Roles & Responsibilities of General Nurse
- Direct Patient Care – Bathing, feeding, dressing, mobilization
- Medication Administration – Oral, IV, injections
- Monitoring – Vital signs, fluid balance, lab reports
- Health Education – Disease prevention, lifestyle advice
- Infection Control – Hand hygiene, sterilization, PPE use
- Documentation & Reporting – Accurate records of patient care
- Emergency Response – CPR, first aid, rapid assessment
Skills Required in General Nursing
- Observation & Critical Thinking
- Communication & Counseling
- Technical Skills – IV, injections, catheterization, wound care
- Empathy & Compassion
- Teamwork & Coordination
- Time Management
Common Procedures in General Nursing
- Vital signs measurement
- Medication administration (oral, IV, IM, subcutaneous)
- Wound dressing & care
- Catheterization (urinary)
- Oxygen therapy & nebulization
- CPR & basic life support (BLS)
- Health education & counseling
Patient Education in General Nursing
- Importance of medication adherence
- Hygiene & personal care
- Nutrition & diet advice
- Exercise & mobility guidance
- Early recognition of symptoms & when to seek care
Gynecological Nursing for Nursing Course in Dhaka, Bangladesh
Definition-Gynecological Nursing is the branch of nursing that deals with the care of women with reproductive system disorders, including prevention, diagnosis, treatment, and education.Gynecological Nursing is a Main Subject of Nursing Course.
Gynecological Nursing হলো নার্সিং শাখা যা নারীর প্রজনন সংক্রান্ত রোগ, প্রতিরোধ, নির্ণয়, চিকিৎসা এবং শিক্ষার সঙ্গে যুক্ত।
Objectives
- Provide care for women with reproductive health issues.
- Educate women on reproductive health and hygiene.
- Assist in diagnosis and treatment of gynecological disorders.
- Promote early detection and prevention.
- Ensure safe and effective nursing care.
Scope of Gynecological Nursing
| Area | English | Bangla | Nursing Role |
|---|---|---|---|
| Menstrual Disorders | Dysmenorrhea, Amenorrhea, Menorrhagia | মাসিক সংক্রান্ত সমস্যা | Monitor symptoms, provide education, administer meds |
| Infections | Vaginitis, STIs | সংক্রমণ | Hygiene education, med administration, monitor response |
| Cancers | Cervical, Ovarian, Breast | ক্যান্সার | Support, medication, post-op care, patient education |
| Reproductive Surgery | Hysterectomy, Oophorectomy | প্রজনন অঙ্গের অস্ত্রোপচার | Pre/post-op care, wound management, monitoring |
| Pregnancy Complications | Ectopic pregnancy, Miscarriage | গর্ভাবস্থা জটিলতা | Assist in treatment, monitor vitals, emotional support |
| Contraception & Family Planning | Pills, IUD, Implants | গর্ভনিরোধ ও পরিবার পরিকল্পনা | Patient education, follow-up, counselling |
Common Gynecological Disorders & Nursing Care
| Disorder | Nursing Focus / Care |
|---|---|
| Vaginitis | Hygiene education, medications, symptom monitoring |
| PCOS (Polycystic Ovary Syndrome) | Weight management, hormonal therapy, patient education |
| Endometriosis | Pain management, medication, patient support |
| Cervical Dysplasia / Cancer | Screening education, post-op care, emotional support |
| Menstrual Disorders | Monitor bleeding, provide analgesics, counseling |
Nursing Responsibilities
- Assess symptoms & menstrual history
- Administer medications & hormonal therapy
- Educate hygiene, nutrition, reproductive health
- Provide emotional support & counseling
- Assist in diagnostic procedures (Pap smear, ultrasound, lab tests)
- Pre/postoperative care for gynecological surgery
Patient Education
- Menstrual hygiene & self-care
- Safe sexual practices & STI prevention
- Family planning & contraception methods
- Early recognition of abnormal symptoms (bleeding, pain, discharge)
- Importance of routine check-ups & screenings
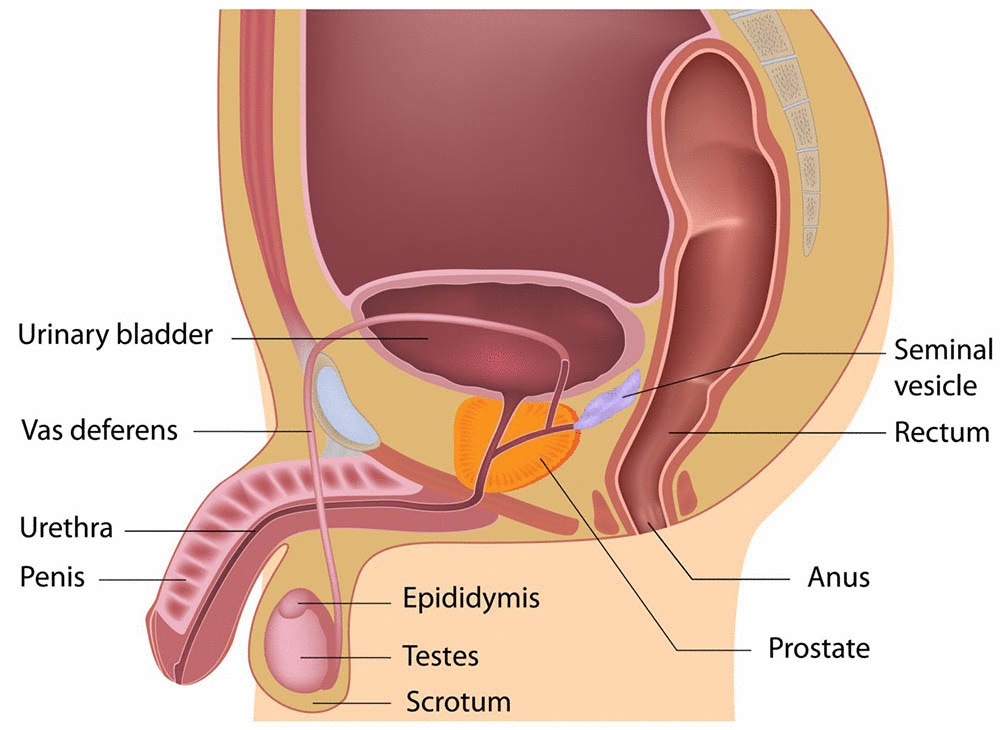
Medical Diagnosis for Nursing Course in Dhaka, Bangladesh
Medical Diagnosis is the process by which a physician identifies a disease or condition based on patient history, physical examination, laboratory tests, and other investigations. It is an important in Nursing Course.
Medical Diagnosis হলো সেই প্রক্রিয়া যার মাধ্যমে চিকিৎসক রোগী থেকে সংগৃহীত তথ্য, পরীক্ষা, ল্যাব রিপোর্ট ও অন্যান্য নিরীক্ষার মাধ্যমে রোগ নির্ধারণ করে।
Objectives of Medical Diagnosis
- Identify the nature and cause of disease.
- Provide accurate information for treatment.
- Guide nursing care and patient management.
- Predict prognosis of the disease.
- Assist in preventive care and health education.
Steps in Medical Diagnosis
| Step | English | Bangla | Nursing Role |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient History | Collect symptoms, past illness, family history | রোগীর ইতিহাস সংগ্রহ | Document accurately, assist doctor |
| Physical Examination | Inspection, palpation, percussion, auscultation | শারীরিক পরীক্ষা | Prepare patient, monitor vitals |
| Laboratory Tests | Blood, urine, stool, microbiology | ল্যাব পরীক্ষাসমূহ | Collect & handle samples properly |
| Imaging / Radiology | X-ray, Ultrasound, MRI, CT | ছবি নিরীক্ষা | Prepare patient, assist in procedure |
| Specialized Tests | ECG, Endoscopy, Biopsy | বিশেষ পরীক্ষা | Ensure safety, monitor patient |
| Diagnosis & Documentation | Identify disease & record | রোগ নির্ণয় ও নথিভুক্তকরণ | Nursing care planning & reporting |
Types of Diagnosis
- Clinical Diagnosis – Based on history & physical exam
- Laboratory Diagnosis – Based on lab test results
- Radiological Diagnosis – Based on imaging studies
- Differential Diagnosis – Considering multiple possible diseases
Nursing Role in Medical Diagnosis
- Collect accurate history & vital signs
- Assist in physical examination
- Prepare patient for lab and imaging tests
- Ensure proper sample collection & handling
- Monitor patient for reaction or complications
- Document & report findings to healthcare team
- Educate patient about tests, procedures, and results
Common Diagnostic Tools in Nursing Practice
| Tool | Purpose | Nursing Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Blood Test | Check CBC, biochemistry | Proper labeling & timing |
| Urine / Stool Test | Detect infection, metabolic disorders | Clean sample collection |
| ECG | Heart rhythm & ischemia | Correct lead placement, monitor during procedure |
| X-ray / Ultrasound | Detect structural abnormalities | Patient positioning & radiation safety |
| Biopsy | Tissue examination | Prepare patient, sterile technique, post-procedure care |
| Endoscopy | Visual inspection of internal organs | Fasting prep, sedation monitoring |
Medical Diagnosis – Quick Reference Table (Nursing)
| Step / Tool | English | Bangla | Nursing Role / Consideration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient History | Collect symptoms, past illness, family history | রোগীর ইতিহাস সংগ্রহ | Document accurately, assist doctor, gather complete info |
| Physical Examination | Inspection, palpation, percussion, auscultation | শারীরিক পরীক্ষা | Prepare patient, monitor vitals, assist in exam |
| Laboratory Tests | Blood, urine, stool, microbiology | ল্যাব পরীক্ষাসম |
Gastro Anatomy & Physiology in Nursing Course
Gastro Anatomy & Physiology covers the digestive system’s structure (mouth, esophagus, stomach, intestines, liver, pancreas, etc.) and its function: ingesting, mechanically/chemically breaking down food, absorbing nutrients, and excreting waste, coordinated by nerves, hormones, and muscle contractions (peristalsis) to process food into usable energy and eliminate byproducts. Key processes involve enzymatic digestion (like pepsin in the stomach for proteins), nutrient absorption (mostly in the small intestine), and bile’s role (from liver/gallbladder) in fat digestion. Gastro Anatomy is an important Subject for Nursing Course.
Anatomy (The Organs)
- GI Tract (Hollow Organs): Mouth, Pharynx, Esophagus, Stomach, Small Intestine (duodenum, jejunum, ileum), Large Intestine (colon, rectum, anus).
- Accessory Organs (Solid Organs/Glands):
- Teeth, Tongue, Salivary Glands, Liver, Gallbladder, Pancreas.
Physiology (The Functions)
- Ingestion & Propulsion: Food enters the mouth, chewed (mechanical) and mixed with saliva, then swallowed and moved by muscle waves (peristalsis) through the esophagus to the stomach.
- Digestion (Mechanical & Chemical):
- Stomach: Churns food, secretes acid (HCl) and pepsin to break down proteins, turning food into liquid chyme.
- Small Intestine: Receives chyme, bile (from liver/gallbladder) for fats, pancreatic juices (enzymes, bicarbonate) to neutralize acid and digest carbs/fats/proteins.
- Absorption: Nutrients (sugars, fats, amino acids, vitamins, minerals, water) are absorbed from the small intestine into the bloodstream.
- Elimination: The large intestine absorbs water and forms feces, which are expelled through the rectum and anus.
The gastrointestinal tract is a continuous passageway, while accessory organs help in the breakdown of food.
Organs of the GI Tract
- Mouth: The entry point for food where mechanical digestion (chewing) and initial chemical digestion (saliva breaks down starches and some lipids) begin.
- Pharynx & Esophagus: The pharynx (throat) leads to the esophagus, a muscular tube that transports food to the stomach via rhythmic contractions called peristalsis.
- Stomach: A J-shaped muscular organ that stores food temporarily and mixes it with strong stomach acids and enzymes to break down proteins and form chyme (a semi-liquid mixture).
- Small Intestine: The primary site for chemical digestion and nutrient absorption. It is divided into three parts:
- Duodenum: Receives chyme from the stomach and digestive juices from the pancreas, liver, and gallbladder.
- Jejunum: The main area for absorbing nutrients.
- Ileum: Absorbs remaining nutrients, especially vitamin B12 and bile salts, and leads into the large intestine.
- Large Intestine: Absorbs most of the remaining water and electrolytes, converts waste into stool (feces), and moves it to the rectum. It includes the cecum, colon (ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid), rectum, and anus.
- Rectum & Anus: The rectum stores feces until it is eliminated from the body through the anus during a bowel movement.
Accessory Organs
- Salivary Glands: Produce saliva to moisten food and begin starch breakdown.
- Liver: Produces bile, which emulsifies fats to aid in digestion.
- Gallbladder: Stores and concentrates bile from the liver and releases it into the small intestine when needed.
- Pancreas: Secretes digestive enzymes (for carbohydrates, fats, and proteins) and bicarbonate (to neutralize stomach acid) into the small intestine.
Physiology of Digestion
The digestive system’s main functions are achieved through six key activities:
- Ingestion: Taking food into the body (eating).
- Propulsion: Movement of food through the GI tract via swallowing and peristalsis.
- Mechanical Digestion: Physical breakdown of food (chewing, churning in the stomach, segmentation in the small intestine).
- Chemical Digestion: Enzymatic breakdown of complex food molecules into smaller, absorbable components (e.g., proteins into amino acids, carbohydrates into simple sugars, fats into fatty acids and glycerol).
- Absorption: The process where digested nutrients and water cross the intestinal lining into the bloodstream or lymphatic system.
- Defecation: Elimination of indigestible waste products (feces) from the body.
These processes are regulated by a complex interplay of nerves (enteric nervous system) and hormones that control motility and secretion of digestive juices.
Gastrointestinal Pharmacology for Best Nursing Course in Dhaka, Bangladesh
Gastrointestinal (GI) pharmacology involves drugs that modify GI function, primarily secretion and motility, to treat various disorders like peptic ulcers, GERD, diarrhea, and constipation. Gastrointestinal (GI) pharmacology refers to the study and application of drugs used to treat conditions and symptoms related to the digestive system (the mouth, esophagus, stomach, intestines, liver, pancreas, and gallbladder).This is an Important subject for Nursing Course.
গ্যাস্ট্রোইনটেস্টাইনাল (Gastrointestinal – GI) ফার্মাকোলজি বলতে পরিপাকতন্ত্র (মুখ, খাদ্যনালী, পাকস্থলী, অন্ত্র, যকৃত, অগ্ন্যাশয় এবং পিত্তথলি) সম্পর্কিত অবস্থা এবং উপসর্গগুলির চিকিৎসায় ব্যবহৃত ওষুধগুলির অধ্যয়ন এবং প্রয়োগকে বোঝায়।
Common Classes of Gastrointestinal Drugs
Medications are classified by their action and the condition they treat.
Drugs for Acid-Related Disorders
These agents manage conditions such as heartburn, GERD, and peptic ulcers by controlling or neutralizing stomach acid.
- Antacids (e.g., calcium carbonate, aluminum hydroxide, magnesium hydroxide).
- Mechanism: They are over-the-counter (OTC) bases that quickly neutralize existing gastric acid in the stomach lumen, which also inactivates pepsin.
- Note: Aluminum salts can cause constipation, while magnesium salts can cause diarrhea; they are often combined to balance side effects.
- Histamine-2 Receptor Antagonists (H2 Blockers) (e.g., famotidine, cimetidine).
- Mechanism: They block H2 receptors on stomach parietal cells, reducing the amount of acid the cells secrete. They are less potent than PPIs but last longer than antacids.
- Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs) (e.g., omeprazole, pantoprazole, esomeprazole).
- Mechanism: PPIs irreversibly bind to and block the hydrogen-potassium ATPase enzyme system (the “proton pump”) in parietal cells, the final step in acid production. They are the most potent acid suppressors and are widely prescribed.
- Mucosal Protectants (e.g., sucralfate).
- Mechanism: Sucralfate forms a protective barrier over ulcerated areas, shielding them from further damage by acid and pepsin.
Drugs for Motility Disorders
These drugs address issues with excessive or inadequate movement of the GI tract.
- Laxatives (e.g., lactulose, bisacodyl, docusate).
- Mechanism: Used to treat constipation, they work through various mechanisms, including increasing bulk, drawing water into the intestines (osmotic), or stimulating bowel contractions.
- Antidiarrheals (e.g., loperamide, bismuth subsalicylate).
- Mechanism: These drugs, often opioids or absorbents, slow down intestinal motility to reduce the frequency of bowel movements.
- Prokinetic Agents (e.g., metoclopramide).
- Mechanism: These agents increase GI motility and the rate of gastric emptying.
Other Key Drug Classes
- Antiemetics (e.g., ondansetron, promethazine).
- Mechanism: Used to prevent nausea and vomiting, some block serotonin receptors in the GI tract and brain, while others act as dopamine antagonists.
- H. pylori Eradication Agents: Antibiotics (e.g., amoxicillin, clarithromycin) are used in combination with PPIs or H2 blockers and bismuth compounds to eliminate the H. pylori bacteria, a common cause of peptic ulcers.
- 5-aminosalicylates (5-ASA) (e.g., mesalamine, sulfasalazine).
- Mechanism: These anti-inflammatory drugs treat inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), such as ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease.
Core Concepts in Geriatric Nursing
- Holistic Care: Focuses on overall well-being, not just illness, addressing biological, physiological, and psychological changes.
- Chronic Conditions: Special attention to common issues like hypertension, diabetes, heart disease, and mental health disorders (depression).
- Safety & Dignity: Ensuring compassionate, safe care that preserves the elderly person’s well-being.
- The 5 Ms: A framework for comprehensive care: Mobility, Mind, Medications, Multicomplexity, and What Matters Most.
What You Learn in a Course
- Health Promotion: Educating on wellness and healthy aging.
- Disease Management: Assessing, treating, and educating on age-related illnesses.
- Safety: Preventing falls and other risks.
- Unique Needs: Understanding the effects of aging on the body and mind.
Career Path & Importance
- Growing Field: High demand due to longer life expectancies and increased healthcare costs for older adults.
- Work Settings: Hospitals, long-term care facilities, skilled nursing, assisted living, home health.
- Roles: Staff nurse, wound care, case manager, infection control, director.
How to Study It
- Degree: BSN or ADN to become an RN, with specialized knowledge added through experience or further education.
- Methods: Classes use lectures, discussions, simulations, and online learning.
- Certification: Opportunities for board certification (RN-BC) after gaining experience.
 HRTD Medical Institute
HRTD Medical Institute






One comment
Pingback: 1 Year Best Nursing Course in dhaka. Mobile No. 01987-073965