Asthma Management
Asthma Management. Mobile Phone Number 01987073965, 01797522136. Asthma management involves a combination of medication, following a written asthma action plan, and lifestyle adjustments like avoiding triggers. Inhalers, including preventers and/or reliever inhalers, are the primary treatment. A good management plan includes regular check-ups, staying active (with appropriate precautions), quitting smoking, maintaining a healthy weight, and managing other conditions like GERD or allergies.
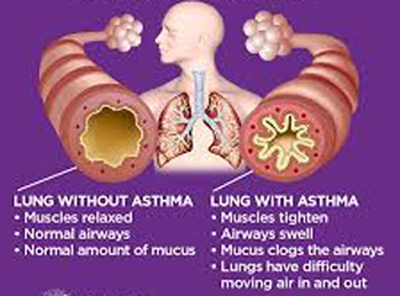
Asthma Management Topics are available in some courses of HRTD Medical Institute. These Courses are Paramedical Courses, DMA Courses, DMS Courses, DPM Courses, DMDS Course, PDT Courses and PGT Courses. All these courses are available in HRTD Medical Institute. These Course are important for First Aid Providers, Primary Treatment Providers, and Village Doctors ( Polly Chikitsok). HRTD Medical Institute is an Organization of HRTD Limited Which is Registered by The Govt of The Peoples Republic of Bangladesh.
Medication
- Inhalers: The main treatment is breathing in medication through an inhaler.
- Reliever inhalers: Used only when symptoms occur.
- Preventer inhalers: Used daily to help prevent symptoms.
- Maintenance and reliever therapy (MART): One inhaler used for both daily maintenance and when symptoms flare up.
- Other medications: Depending on the severity, other drugs like leukotriene modifiers or biologics may be prescribed.
- Inhaler technique: Proper technique is crucial for effective drug absorption, which involves inhaling deeply while pressing the inhaler and holding your breath for about 10 seconds afterward.
Asthma action plan
- Work with a healthcare provider to create a personalized, written asthma action plan.
- This plan provides instructions for routine management and what to do if symptoms worsen or an emergency occurs.
- Regular check-ups to review your symptoms, lung function, and action plan are essential.
Lifestyle adjustments
- Avoid triggers: Identify and avoid personal asthma triggers, which can include smoke, dust mites, and certain allergens.
- Exercise: Engage in regular physical activity, which can strengthen lungs. Talk to your doctor about a safe level of exercise and use medication as needed to prevent symptoms during activity.
- Healthy weight: Maintain a healthy weight, as being overweight can worsen asthma symptoms.
- Quitting smoking: Stop smoking and avoid all forms of tobacco and e-cigarette vapor.
- Other conditions: Treat other health issues that can impact asthma, such as hay fever, allergies, GERD, and sleep apnea.
- Sleep: Ensure you get enough quality sleep by establishing a regular sleep schedule and creating a calming bedtime routine.
Definition of Asthma
Asthma is a chronic lung condition that causes inflammation and narrowing of the airways, leading to recurring episodes of wheezing, coughing, shortness of breath, and chest tightness. Symptoms can vary from mild to severe and are often triggered by factors like allergens, exercise, or cold air. While there is no cure, asthma can be managed and controlled through medication, avoiding triggers, and having an action plan.
Causes of Asthma
Asthma is caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors, leading to inflammation and narrowing of the airways. Risk factors include a family history of asthma or allergies, childhood respiratory infections, and exposure to secondhand smoke or air pollution. Triggers that can cause symptoms include allergens like pollen and dust mites, irritants like smoke and strong odors, respiratory infections, physical activity, and weather changes.
Genetic and environmental factors
- Family history: A family history of asthma or allergies increases your risk.
- Childhood factors: Lower birth weight, premature birth, and certain early childhood illnesses are linked to a higher risk of developing asthma.
- Environmental exposure: Early-life exposure to factors like secondhand smoke, air pollution, and certain substances at work can contribute to its development.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese is a risk factor for developing and having more severe asthma.
Common triggers for asthma attacks
- Allergens: Airborne allergens like pollen, dust mites, mold spores, pet dander, and cockroach waste.
- Irritants: Air pollutants, smoke from tobacco or wood fires, and strong fumes or odors from chemicals, perfumes, or cleaning products.
- Respiratory infections: Illnesses like the common cold, flu, or COVID-19.
- Weather: Cold, dry air, sudden changes in weather, or high humidity.
- Physical activity: Exercise, particularly in cold air.
- Medications: Certain drugs, including some pain relievers like aspirin and other NSAIDs, and some beta-blockers.
- Strong emotions: Stress or other strong emotional responses can trigger symptoms.
- Food additives: Sulfites and other preservatives added to some foods and beverages.
Clinical Feature of Asthma
The clinical manifestations of asthma are the cardinal symptoms of cough, wheezing, shortness of breath, and chest tightness. These symptoms can range from mild to severe and often occur in episodes, which may be triggered by factors like exercise, allergies, or cold air. Symptoms can also worsen at night or in the early morning. During a severe asthma attack, symptoms intensify and require immediate medical attention.
Common symptoms
- Coughing: Often worse at night, a cough can be a primary symptom.
- Wheezing: A high-pitched whistling or rattling sound, particularly when breathing out.
- Shortness of breath: Difficulty breathing, which can range from mild to severe, and may occur after exercise.
- Chest tightness: A feeling of pressure or squeezing in the chest, as if a rope is tightening around it.
Other manifestations
- Worsening symptoms at night or early morning: These episodes can disrupt sleep.
- Symptoms triggered by exercise: An asthma attack can be triggered by physical exertion.
- Difficulty talking: In severe cases, talking may be difficult.
- Signs of a severe attack: In addition to the cardinal symptoms, severe attacks may involve rapid breathing, a pale or sweaty face, and changes in skin color around the lips, fingertips, or nail beds, which may appear bluish or gray/white.
Diagnosis of Asthma
Asthma is diagnosed through a combination of medical history, physical exam, and lung function tests, primarily spirometry, which measures how much air you can breathe out. A doctor will also consider your symptoms, family history, and may perform other tests like allergy tests, a peak flow test, or a FeNO test to confirm the diagnosis and identify triggers.
Key diagnostic tools and tests
- Spirometry: This is the most common and recommended test. You breathe forcefully into a device called a spirometer, which measures the amount of air you can inhale and exhale, and how fast you can do so.
- Peak flow test: You blow into a device called a peak flow meter to measure how fast you can exhale. This can help monitor asthma over time.
- FeNO test: A test that measures the level of nitric oxide in your breath, which can indicate airway inflammation and certain types of allergic asthma.
- Challenge test: If other tests are inconclusive, a doctor may have you breathe in a substance that irritates the airways. This test is done in a hospital and shows how sensitive your airways are.
- Allergy tests: Skin or blood tests can help determine if allergies to things like pollen, dust mites, or animal dander are triggering your symptoms.
- Treatment trial: Your doctor may have you start an asthma treatment to see if your symptoms improve, which can help confirm a diagnosis.
What to expect during diagnosis
- Medical and family history: Your doctor will ask about your symptoms, how often they occur, and any family history of asthma or allergies.
- Physical examination: A doctor will listen to your lungs for wheezing or other sounds and check for other signs like chest tightness.
- Symptom patterns: Your doctor will analyze the pattern of your symptoms, such as if they worsen at night or with exercise.
Important considerations
- Other conditions: Asthma symptoms can overlap with other respiratory conditions, so it’s important for a healthcare professional to rule out other diagnoses.
- No single test: There is no single test that can diagnose asthma; diagnosis is based on a combination of factors.
- Consult a doctor: Only a healthcare professional can provide an accurate diagnosis. If you are concerned you may have asthma, contact your doctor.
Investigation for Asthma
Asthma investigation involves a combination of medical history, physical exam, and lung function tests like spirometry and peak flow measurements. Blood tests for eosinophils, a FeNO test to measure airway inflammation, and sometimes an allergy or CT scan of the sinuses may also be performed. Doctors also use a treatment trial, observing if asthma medications improve symptoms.
Medical history and physical exam
- Your doctor will ask about your symptoms, when they occur, and potential triggers.
- They will perform a physical exam, which includes listening to your lungs.
Lung function tests
- Spirometry: You will breathe forcefully into a machine that measures how much air you can breathe out and how fast. A bronchodilator may be given, and the test repeated to see if your lung function improves.
- Peak flow meter: This is a handheld device that you use at home to measure how fast you can blow air out of your lungs. You may use it for several weeks to track your lung function and identify patterns.
- FeNO (fractional exhaled nitric oxide) test: This test measures the level of nitric oxide in your breath, which can indicate inflammation in your airways.
Other potential tests
- Blood test: Checks for a high number of eosinophils, a type of white blood cell associated with airway inflammation.
- Allergy testing: Can help identify triggers like pollen, dust mites, or pet dander.
- CT scan of sinuses: May be ordered if the doctor suspects a sinus infection (sinusitis), which can worsen asthma.
- Treatment trial: Your doctor may prescribe asthma medication and see if it improves your symptoms.
Important considerations
- There is no single test for asthma; diagnosis relies on a combination of factors.
- Diagnosing asthma in very young children can be difficult, and lung function tests are not possible for those under 5.
- Spirometry is not suitable for all patients, so your doctor will choose the most appropriate test(s) for you.
CT scan of the sinuses
A sinus CT scan is a non-invasive imaging test that uses X-rays to create detailed cross-sectional pictures of the paranasal sinuses, the air-filled cavities in the bones of the face. This scan is the most reliable way to diagnose problems like sinusitis, inflammation, polyps, fluid, and anatomical blockages, helping doctors determine the best course of treatment. The procedure is quick and painless, though you may feel a slight warming sensation and a metallic taste if a contrast dye is used.
What it is
- Imaging technique: A CT scan takes multiple X-ray images from different angles to create detailed cross-sectional views of the sinuses, unlike a standard X-ray.
- Purpose: It is used to diagnose and evaluate a variety of sinus problems, including chronic sinusitis, inflammation, fluid buildup, polyps, and structural abnormalities.
- Accuracy: It is considered the most accurate and best imaging method for evaluating the sinuses.
What to expect
- Preparation: You should wear loose-fitting clothing and remove all metal jewelry, including hairpins and hearing aids, beforehand. You may be asked to avoid eating or drinking for a few hours, especially if contrast dye will be used.
- During the scan: You will lie on a table, and a scanner will rotate around your head to capture the images. The procedure is painless and usually takes less than 5 minutes, although the total appointment may take longer.
- Contrast dye: In some cases, a contrast material is injected through an IV to help highlight structures. This can cause a brief feeling of warmth and a metallic taste.
- After the scan: If contrast dye was used, you may be advised to drink extra fluids. You can return to your normal activities immediately.
Why it’s used
- Diagnosis: It helps diagnose sinus issues with high accuracy.
- Surgical planning: It is an integral part of planning for sinus surgery, providing a detailed “road map” of the anatomy for the surgeon.
- Treatment guidance: The detailed images help doctors create a tailored treatment plan for you.
Why CT scan is important for Asthma Patient
A CT scan is important for asthma patients, especially those with severe or uncontrolled asthma, because it provides more detailed imaging than a chest X-ray, allowing doctors to identify structural changes in the airways. It can help diagnose complications like mucus plugs or bronchiectasis, rule out other conditions, and provide a better understanding of air trapping. This helps in making a correct diagnosis and developing a more effective treatment plan.
Key reasons for importance
- Detailed imaging: CT scans offer a much higher-resolution view of the airways and lung tissue compared to standard X-rays.
- Diagnosis of complications: They can identify structural changes associated with severe asthma, such as thickened airway walls, mucus impaction, and bronchiectasis.
- Differential diagnosis: CT scans help differentiate asthma from other conditions that may have similar symptoms or be mistaken for asthma, such as allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA), eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA), or COPD.
- Assessment of disease severity: In severe asthma, CT can reveal patterns of remodeling and air trapping that correlate with functional decline and disease severity.
- Treatment planning: By identifying the specific structural issues, doctors can create more targeted treatment strategies for difficult-to-treat asthma cases.
Why CT scan of sinuses is important for Asthma Patient
A CT scan is important for asthma patients to identify or rule out underlying chronic rhinosinusitis (sinusitis) and nasal polyps, which can worsen asthma control. It helps doctors diagnose and manage co-existing sinus conditions by showing inflammation, mucosal thickening, or polyps that require specific treatment. Identifying these issues is crucial for selecting the correct treatment, particularly certain types of biologics for severe, eosinophilic asthma with CRSwNP.
Key reasons for CT scans in asthma patients
- Diagnosing and assessing sinus disease: CT scans are the best tool for evaluating the paranasal sinuses and nasal cavity to find conditions like chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS) or nasal polyps, which are common in patients with severe asthma.
- Identifying “treatable traits”: The scan can identify specific issues like nasal polyps that are linked to a type of inflammation (type-2-predominant) that responds well to certain medical treatments, like biologic therapies.
- Improving treatment decisions: By clearly showing the extent of sinus inflammation or obstruction, a CT scan helps doctors choose the most effective treatment plan, which may include a combination of therapies for both the sinuses and the lungs.
- Monitoring treatment response: The scan can be used to monitor how well treatment for sinusitis is working, as demonstrated by improvement in CT scores over time.
- Managing “upper and lower airway” disease simultaneously: The scan allows doctors to address both upper (sinus) and lower (lung) airway inflammation at the same time, which is crucial for achieving better asthma control.
Why CT scan of lungs is important for Asthma Patient
A CT scan is important for asthma patients because it provides detailed anatomical information that helps identify structural changes, diagnose complications, and differentiate asthma from other conditions, especially in severe or difficult-to-treat cases. It can reveal issues like airway wall thickening, mucus plugs, air trapping, and bronchiectasis, which may not be visible on a standard chest X-ray.
Detailed assessment of the lungs
- Visualizes structural changes: CT scans show details like bronchial wall thickening and narrowing, which are key findings in asthma.
- Identifies complications: It helps identify complications that worsen asthma, such as mucus plugs or bronchiectasis.
- Detects air trapping: High-resolution CT (HRCT) can show signs of air trapping, indicating how effectively air is moving in and out of the lungs.
Differential diagnosis
- Rules out other conditions: CT scans help distinguish asthma from other diseases with similar symptoms, like emphysema, chronic bronchitis, or allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA).
- Diagnoses comorbid conditions: It can identify other conditions that may be contributing to a patient’s poor asthma control, such as chronic rhinosinusitis or eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA).
Monitoring and treatment planning
- Assesses severity: CT scans can provide a more detailed assessment of asthma severity and disease progression over time.
- Evaluates treatment response: Quantitative CT techniques are being studied to monitor the effectiveness of treatments by measuring changes in airway structure.
How Pet dander trigger Asthma
Pet dander triggers asthma when a person’s immune system mistakenly identifies the allergens in dander, saliva, or urine as harmful, leading to inflammation and tightening of the airways. The immune response releases chemicals that cause symptoms like coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath, which are characteristic of an asthma attack. The microscopic dander particles can remain airborne, stick to furniture, and travel on clothing, making them difficult to avoid.
The immune system’s response
- Allergen identification: For someone with pet allergies, the immune system creates antibodies that incorrectly flag proteins in pet dander (tiny flakes of skin), saliva, or urine as dangerous.
- Inflammatory response: The next time these allergens are encountered, the immune system overreacts and releases chemicals like histamine into the bloodstream.
- Airway constriction: This chemical release leads to swelling in the airways and causes the muscles around them to tighten, which is the physical response that causes asthma symptoms.
How dander affects the body
- Airborne particles: Dander is very small and can stay airborne for long periods, especially with air circulation.
- Surface contamination: It sticks to surfaces like clothing, carpets, and furniture, making it hard to get rid of.
- Inhalation: When inhaled, these particles can trigger asthma symptoms such as coughing, wheezing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath.
What you can do
- Reduce exposure: Keep pets out of the bedroom and off upholstered furniture.
- Improve air quality: Use HEPA air cleaners and vacuum carpets and furniture regularly with a vacuum that has a HEPA filter.
- Maintain cleanliness: Wash your hands after touching pets, wash bedding and clothes in hot water, and have someone else brush the pet outside to minimize dander release.
পোষা প্রাণীর খুশকি হাঁপানির কারণ হয় যখন একজন ব্যক্তির রোগ প্রতিরোধ ব্যবস্থা ভুল করে খুশকি, লালা বা প্রস্রাবের অ্যালার্জেনকে ক্ষতিকারক হিসেবে শনাক্ত করে, যার ফলে শ্বাসনালীতে প্রদাহ এবং টানটান ভাব দেখা দেয়।রোগ প্রতিরোধ ক্ষমতা এমন রাসায়নিক পদার্থ নির্গত করে যা কাশি, শ্বাসকষ্ট এবং শ্বাসকষ্টের মতো লক্ষণ সৃষ্টি করে, যা হাঁপানির আক্রমণের বৈশিষ্ট্য। ক্ষুদ্র খুশকির কণাগুলি বাতাসে থাকতে পারে, আসবাবপত্রে লেগে থাকতে পারে এবং পোশাকের উপর ভ্রমণ করতে পারে, যার ফলে এগুলি এড়ানো কঠিন হয়ে পড়ে।
রোগ প্রতিরোধ ব্যবস্থার প্রতিক্রিয়া
- অ্যালার্জেন শনাক্তকরণ: পোষা প্রাণীর অ্যালার্জি আছে এমন ব্যক্তির ক্ষেত্রে, রোগ প্রতিরোধ ব্যবস্থা অ্যান্টিবডি তৈরি করে যা পোষা প্রাণীর খুশকি (ত্বকের ক্ষুদ্র খণ্ড), লালা বা প্রস্রাবে থাকা প্রোটিনকে বিপজ্জনক হিসাবে ভুলভাবে চিহ্নিত করে।
- প্রদাহজনক প্রতিক্রিয়া: পরের বার যখন এই অ্যালার্জেনের মুখোমুখি হওয়া হয়, তখন রোগ প্রতিরোধ ব্যবস্থা অতিরিক্ত প্রতিক্রিয়া দেখায় এবং রক্তপ্রবাহে হিস্টামিনের মতো রাসায়নিক পদার্থ ছেড়ে দেয়।
- শ্বাসনালী সংকোচন: এই রাসায়নিক নিঃসরণের ফলে শ্বাসনালীতে ফুলে যায় এবং তাদের চারপাশের পেশীগুলি শক্ত হয়ে যায়, যা হাঁপানির লক্ষণগুলির কারণ শারীরিক প্রতিক্রিয়া।
খুশকি কীভাবে শরীরকে প্রভাবিত করে
- বায়ুবাহিত কণা: খুশকি খুবই ছোট এবং দীর্ঘ সময় ধরে বায়ুবাহিত থাকতে পারে, বিশেষ করে বায়ু সঞ্চালনের সময়।
- পৃষ্ঠ দূষণ: এটি পোশাক, কার্পেট এবং আসবাবের মতো পৃষ্ঠের সাথে লেগে থাকে, যার ফলে এটি অপসারণ করা কঠিন হয়ে পড়ে।
- শ্বাস-প্রশ্বাস: শ্বাস-প্রশ্বাসের মাধ্যমে নেওয়া হলে, এই কণাগুলি হাঁপানির লক্ষণগুলি যেমন কাশি, শ্বাসকষ্ট, বুকে টান এবং শ্বাসকষ্টের সৃষ্টি করতে পারে।
তুমি কি করতে পারো
- এক্সপোজার কমান: পোষা প্রাণীদের শোবার ঘর থেকে দূরে রাখুন এবং আসবাবপত্রের আসবাবপত্র থেকে দূরে রাখুন।
- বাতাসের মান উন্নত করুন: HEPA এয়ার ক্লিনার এবং ভ্যাকুয়াম কার্পেট এবং আসবাবপত্র নিয়মিত ব্যবহার করুন যাতে HEPA ফিল্টার আছে এমন ভ্যাকুয়াম ক্লিনার ব্যবহার করুন।
- পরিষ্কার-পরিচ্ছন্নতা বজায় রাখুন: পোষা প্রাণী স্পর্শ করার পর আপনার হাত ধুয়ে নিন, গরম জলে বিছানা এবং কাপড় ধুয়ে ফেলুন, এবং খুশকি কমাতে অন্য কাউকে পোষা প্রাণীটিকে বাইরে ব্রাশ করতে বলুন।
Biochemicals that are involved in Asthma
Biochemicals involved in asthma include
inflammatory mediators like histamine, leukotrienes, and prostaglandins, which cause bronchoconstriction and swelling. Other key players are cytokines such as IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13, which promote inflammation and allergic responses. Additionally, IgE is a central molecule in the allergic pathway, and there are also biochemical changes involving molecules like periostin and enzymes such as eosinophil peroxidase.
Inflammatory mediators
- Histamine: Released from mast cells, it causes smooth muscle contraction, increased vascular permeability, and mucus secretion.
- Leukotrienes: Specifically, cysteinyl leukotrienes (LTC4, LTD4, LTE4) contribute to bronchoconstriction, mucus production, and inflammation.
- Prostaglandins: Prostaglandin
D2cap D sub 2𝐷2 (
PGD2cap P cap G cap D sub 2𝑃𝐺𝐷2) is released by mast cells and contributes to airway inflammation.
- Bradykinin: Formed by the enzyme kalikrein, it can cause bronchoconstriction and increase vascular permeability.
Cytokines and signaling molecules
- Interleukins (ILs):
- IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13: These Th2 cytokines promote the production of IgE, activate eosinophils, and contribute to airway inflammation.
- IL-33 and TSLP: These are signaling molecules that are significantly elevated in asthmatics and are linked to persistent airway inflammation and reduced lung function.
- T-helper 2 (Th2) pathway: The activation of this immune pathway leads to the release of the aforementioned cytokines.
- Periostin: Elevated levels are associated with IL-13 driven asthma and may indicate a patient who would benefit from therapies that block IL-4/IL-13.
Antibodies and enzymes
- Immunoglobulin E (IgE): This antibody plays a central role in atopic asthma. It binds to mast cells, and upon re-exposure to an allergen, it triggers the release of inflammatory mediators.
- Eosinophil Cationic Protein (ECP): A marker for eosinophil activity and asthma severity.
- Eosinophil Peroxidase: Increased activity is associated with asthma.
- Arginase: Increased activity is linked to asthma.
Other biochemicals
- Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS): Eosinophils can release ROS during an inflammatory response.
- Nitric Oxide (NO): Increased concentrations may occur in asthma, potentially binding to hemoglobin and reducing oxygen capacity.
হাঁপানির সাথে জড়িত জৈব রাসায়নিক পদার্থের মধ্যে রয়েছে
হিস্টামিন, লিউকোট্রিয়েনসএবং প্রোস্টাগ্ল্যান্ডিনেরমতো প্রদাহজনক মধ্যস্থতাকারী , যা ব্রঙ্কোকনস্ট্রিকশন এবং ফোলা সৃষ্টি করে। অন্যান্য গুরুত্বপূর্ণ খেলোয়াড় হল সাইটোকাইন যেমন IL-4, IL-5, এবং IL-13, যা প্রদাহ এবং অ্যালার্জির প্রতিক্রিয়া বৃদ্ধি করে। অতিরিক্তভাবে, IgE হল অ্যালার্জির পথের একটি কেন্দ্রীয় অণু, এবং পেরিওস্টিনেরমতো অণু এবং ইওসিনোফিল পেরোক্সিডেসের মতো এনজাইম জড়িত জৈব রাসায়নিক পরিবর্তনও রয়েছে ।
প্রদাহজনক মধ্যস্থতাকারী
- হিস্টামিন: মাস্তুল কোষ থেকে নিঃসৃত হওয়ায়, এটি মসৃণ পেশী সংকোচন, রক্তনালী প্রবেশযোগ্যতা বৃদ্ধি এবং শ্লেষ্মা নিঃসরণ ঘটায়।
- লিউকোট্রিয়েনস: বিশেষ করে, সিস্টেইনাইল লিউকোট্রিয়েনস (LTC4, LTD4, LTE4) ব্রঙ্কোকনস্ট্রিকশন, শ্লেষ্মা উৎপাদন এবং প্রদাহে অবদান রাখে।
- প্রোস্টাগ্ল্যান্ডিন: প্রোস্টাগ্ল্যান্ডিন
D2cap D sub 2𝐷2 (
PGD2cap P cap G cap D sub 2𝑃𝐺𝐷2) মাস্ট কোষ দ্বারা নিঃসৃত হয় এবং শ্বাসনালীর প্রদাহে অবদান রাখে।
- ব্র্যাডিকিনিন: ক্যালিক্রেইন এনজাইম দ্বারা গঠিত, এটি ব্রঙ্কোকনস্ট্রিকশন সৃষ্টি করতে পারে এবং রক্তনালী প্রবেশযোগ্যতা বৃদ্ধি করতে পারে।
সাইটোকাইন এবং সংকেত অণু
- ইন্টারলিউকিনস (ILs):
- IL-4, IL-5, এবং IL-13: এই Th2 সাইটোকাইনগুলি IgE উৎপাদনকে উৎসাহিত করে, ইওসিনোফিল সক্রিয় করে এবং শ্বাসনালীর প্রদাহে অবদান রাখে।
- IL-33 এবং TSLP: এগুলি হল সংকেত অণু যা হাঁপানি রোগীদের মধ্যে উল্লেখযোগ্যভাবে বৃদ্ধি পায় এবং স্থায়ী শ্বাসনালীর প্রদাহ এবং ফুসফুসের কার্যকারিতা হ্রাসের সাথে যুক্ত।
- টি-হেল্পার ২ (Th2) পথ: এই রোগ প্রতিরোধ ক্ষমতার সক্রিয়করণের ফলে উপরে উল্লিখিত সাইটোকাইন নিঃসরণ হয়।
- পেরিওস্টিন: উচ্চ মাত্রা IL-13 দ্বারা সৃষ্ট হাঁপানির সাথে সম্পর্কিত এবং এটি এমন একজন রোগীকে নির্দেশ করতে পারে যিনি IL-4/IL-13 ব্লক করে এমন থেরাপি থেকে উপকৃত হবেন।
অ্যান্টিবডি এবং এনজাইম
- ইমিউনোগ্লোবুলিন ই (IgE): এই অ্যান্টিবডি অ্যাটোপিক হাঁপানিতে একটি কেন্দ্রীয় ভূমিকা পালন করে। এটি মাস্ট কোষের সাথে আবদ্ধ হয় এবং অ্যালার্জেনের সংস্পর্শে আসার পর, এটি প্রদাহজনক মধ্যস্থতাকারীদের মুক্তির সূত্রপাত করে।
- ইওসিনোফিল ক্যাটানিক প্রোটিন (ECP): ইওসিনোফিল কার্যকলাপ এবং হাঁপানির তীব্রতার একটি চিহ্নিতকারী।
- ইওসিনোফিল পেরোক্সিডেস: বর্ধিত কার্যকলাপ হাঁপানির সাথে সম্পর্কিত।
- আর্জিনেস: বর্ধিত কার্যকলাপ হাঁপানির সাথে সম্পর্কিত।
অন্যান্য জৈব রাসায়নিক পদার্থ
- প্রতিক্রিয়াশীল অক্সিজেন প্রজাতি (ROS): প্রদাহজনক প্রতিক্রিয়ার সময় ইওসিনোফিলগুলি ROS নিঃসরণ করতে পারে।
- নাইট্রিক অক্সাইড (NO): হাঁপানিতে এর ঘনত্ব বৃদ্ধি পেতে পারে, যা হিমোগ্লোবিনের সাথে আবদ্ধ হতে পারে এবং অক্সিজেন ধারণক্ষমতা হ্রাস করতে পারে।
How histamine causes asthma ?
Histamine causes asthma by triggering airway smooth muscle contraction, increasing mucus production, and causing airway swelling (edema). During an allergic reaction, mast cells in the lungs release histamine, which binds to receptors (primarily H1 receptors) on airway smooth muscle, causing it to tighten and narrow the airways, making breathing difficult. This also stimulates excessive mucus and inflammation, worsening asthma symptoms.
How histamine triggers asthma symptoms
- Bronchoconstriction: Histamine stimulates airway smooth muscles to contract, leading to a narrowing of the airways, known as bronchoconstriction.
- Mucus production: It prompts the lungs to produce more mucus, which can clog the airways.
- Airway swelling: Histamine can lead to airway mucosal edema, which is the swelling of the lining of the airways, further obstructing airflow.
- Inflammation: The release of histamine is part of the broader inflammatory response in the lungs, which can involve other immune cells and mediators that contribute to asthma’s chronic inflammation.
- Vagal nerve stimulation: Histamine can also indirectly cause bronchoconstriction by stimulating afferent vagal fibers in the airways.
হিস্টামিন শ্বাসনালীর মসৃণ পেশী সংকোচন, শ্লেষ্মা উৎপাদন বৃদ্ধি এবং শ্বাসনালীর ফোলাভাব (এডিমা) সৃষ্টি করেহাঁপানির কারণ হয় । অ্যালার্জির প্রতিক্রিয়ার সময়, ফুসফুসের মাস্ট কোষগুলিহিস্টামিন নিঃসরণ করে, যা শ্বাসনালীর মসৃণ পেশীতে রিসেপ্টরগুলির (প্রাথমিকভাবে H1 রিসেপ্টর) সাথে আবদ্ধ হয়, যার ফলে এটি শ্বাসনালীকে শক্ত এবং সংকুচিত করে, যার ফলে শ্বাস নিতে অসুবিধা হয়। এটি অতিরিক্ত শ্লেষ্মা এবং প্রদাহকেও উদ্দীপিত করে, যা হাঁপানির লক্ষণগুলিকে আরও খারাপ করে।
হিস্টামিন কীভাবে হাঁপানির লক্ষণগুলিকে ট্রিগার করে
- ব্রঙ্কোকনস্ট্রিকশন: হিস্টামিন শ্বাসনালীর মসৃণ পেশীগুলিকে সংকোচনে উদ্দীপিত করে, যার ফলে শ্বাসনালী সংকুচিত হয়, যা ব্রঙ্কোকনস্ট্রিকশন নামে পরিচিত।
- শ্লেষ্মা উৎপাদন: এটি ফুসফুসকে আরও শ্লেষ্মা উৎপাদন করতে প্ররোচিত করে, যা শ্বাসনালী বন্ধ করে দিতে পারে।
- শ্বাসনালী ফুলে যাওয়া: হিস্টামিনের কারণে শ্বাসনালীতে মিউকোসাল এডিমা হতে পারে, যা শ্বাসনালীর আস্তরণের ফুলে যাওয়া, যা বায়ুপ্রবাহকে আরও বাধাগ্রস্ত করে।
- প্রদাহ: হিস্টামিনের নিঃসরণ ফুসফুসের বৃহত্তর প্রদাহজনক প্রতিক্রিয়ার অংশ, যা অন্যান্য রোগ প্রতিরোধক কোষ এবং মধ্যস্থতাকারীদের জড়িত করতে পারে যা হাঁপানির দীর্ঘস্থায়ী প্রদাহে অবদান রাখে।
- ভ্যাগাল স্নায়ু উদ্দীপনা: হিস্টামিন শ্বাসনালীতে অ্যাফেরেন্ট ভ্যাগাল ফাইবারগুলিকে উদ্দীপিত করে পরোক্ষভাবে ব্রঙ্কোকনস্ট্রিকশন ঘটাতে পারে।
How Leukotrienes cause Asthma
Leukotrienes cause asthma by
causing bronchoconstriction, inflammation, and increased mucus production in the airways. When released during an asthma trigger like an allergen, these molecules bind to specific receptors on airway smooth muscle, causing it to contract and narrow the airways, leading to breathing difficulties. They also increase blood vessel permeability and inflammation in the lungs and draw more inflammatory cells, such as eosinophils, to the area.
How leukotrienes cause asthma symptoms
- Bronchoconstriction: Leukotrienes, particularly cysteinyl leukotrienes (
CysLTscap C y s cap L cap T s𝐶𝑦𝑠𝐿𝑇𝑠), are potent constrictors of airway smooth muscles, leading to the narrowing of the airways.
- Inflammation: They attract inflammatory cells like eosinophils to the airways, which contributes to long-term airway hypersensitivity and swelling.
- Increased mucus production: Leukotrienes stimulate the secretion of mucus, which can further obstruct the airways.
- Increased vascular permeability: They make blood vessels in the airways more permeable, which can lead to swelling (edema) in the airway walls.
- Reduced mucociliary clearance: This effect impairs the lungs’ ability to clear mucus and debris, making breathing more difficult.
Leukotrienes in the asthma cycle
- Triggering: During an asthma attack, mast cells release leukotrienes.
- Action: These leukotrienes then bind to receptors on other cells, including airway smooth muscle.
- Symptoms: This triggers the cascade of effects that lead to bronchoconstriction, inflammation, and mucus production, resulting in an asthma attack.
- Chronic asthma: In chronic asthma, leukotrienes can contribute to the general hyperresponsiveness of the airways by attracting eosinophils that also produce leukotrienes.
লিউকোট্রিয়েনগুলি
শ্বাসনালীতেব্রঙ্কোকনস্ট্রিকশন, প্রদাহএবং শ্লেষ্মা উৎপাদনবৃদ্ধি করে হাঁপানির কারণ হয় । অ্যালার্জেনের মতো হাঁপানির ট্রিগারের সময় এই অণুগুলি শ্বাসনালী মসৃণ পেশীর নির্দিষ্ট রিসেপ্টরের সাথে আবদ্ধ হয়, যার ফলে এটি শ্বাসনালী সংকুচিত এবং সংকুচিত হয়, যার ফলে শ্বাসকষ্ট হয়। এগুলি ফুসফুসে রক্তনালী প্রবেশযোগ্যতা এবং প্রদাহ বৃদ্ধি করে এবং ইওসিনোফিলের মতো আরও প্রদাহজনক কোষগুলিকে ওই অঞ্চলে টেনে আনে।
লিউকোট্রিয়েন কীভাবে হাঁপানির লক্ষণ সৃষ্টি করে
- ব্রঙ্কোকনস্ট্রিকশন: লিউকোট্রিন, বিশেষ করে সিস্টেইনাইল লিউকোট্রিন (
CysLTscap C y s cap L cap T s𝐶𝑦𝑠𝐿𝑇𝑠), শ্বাসনালীর মসৃণ পেশীগুলির শক্তিশালী সংকোচনকারী, যা শ্বাসনালীকে সংকুচিত করে।
- প্রদাহ: তারা ইওসিনোফিলের মতো প্রদাহজনক কোষগুলিকে শ্বাসনালীতে আকর্ষণ করে, যা দীর্ঘমেয়াদী শ্বাসনালীতে অতি সংবেদনশীলতা এবং ফোলাভাব সৃষ্টি করে।
- শ্লেষ্মা উৎপাদন বৃদ্ধি: লিউকোট্রিয়েনস শ্লেষ্মা নিঃসরণকে উদ্দীপিত করে, যা শ্বাসনালীকে আরও বাধাগ্রস্ত করতে পারে।
- রক্তনালীর প্রবেশযোগ্যতা বৃদ্ধি: এগুলি শ্বাসনালীর রক্তনালীগুলিকে আরও প্রবেশযোগ্য করে তোলে, যার ফলে শ্বাসনালীর দেয়ালে ফোলাভাব (এডিমা) দেখা দিতে পারে।
- মিউকোসিলিয়ারি ক্লিয়ারেন্স হ্রাস: এই প্রভাব ফুসফুসের শ্লেষ্মা এবং ধ্বংসাবশেষ পরিষ্কার করার ক্ষমতাকে ব্যাহত করে, যার ফলে শ্বাস-প্রশ্বাস আরও কঠিন হয়ে পড়ে।
হাঁপানি চক্রে লিউকোট্রিয়েনস
- ট্রিগার: হাঁপানির আক্রমণের সময়, মাস্ট কোষগুলি লিউকোট্রিয়েন নিঃসরণ করে।
- ক্রিয়া: এই লিউকোট্রিয়েনগুলি তখন শ্বাসনালীর মসৃণ পেশী সহ অন্যান্য কোষের রিসেপ্টরের সাথে আবদ্ধ হয়।
- লক্ষণ: এটি ব্রঙ্কোকনস্ট্রিকশন, প্রদাহ এবং শ্লেষ্মা উৎপাদনের দিকে পরিচালিত করে এমন প্রভাবের ক্রমবর্ধমান সূত্রপাত করে, যার ফলে হাঁপানির আক্রমণ হয়।
- দীর্ঘস্থায়ী হাঁপানি: দীর্ঘস্থায়ী হাঁপানিতে, লিউকোট্রিনগুলি ইওসিনোফিলগুলিকে আকর্ষণ করে শ্বাসনালীর সাধারণ হাইপাররস্পনসিভনেসে অবদান রাখতে পারে যা লিউকোট্রিনও তৈরি করে।
How Prostaglandins cause Asthma?
Prostaglandins contribute to asthma
by causing inflammation and bronchoconstriction, with different types having opposing effects. For example, prostaglandin
D2cap D sub 2𝐷2 (
PGD2cap P cap G cap D sub 2𝑃𝐺𝐷2), released by mast cells during an allergic reaction, triggers inflammatory cells to accumulate in the lungs, leading to the release of pro-inflammatory substances that worsen asthma symptoms. While prostaglandins like
PGE2cap P cap G cap E sub 2𝑃𝐺𝐸2 can act as bronchodilators and reduce inflammation, the imbalance caused by an overproduction of other prostaglandins can lead to a “bronchospastic stimulus”.
Mechanisms of action
- Inflammation:
PGD2cap P cap G cap D sub 2𝑃𝐺𝐷2 attracts and activates key immune cells like T helper 2 (
TH2cap T sub cap H 2𝑇𝐻2) cells and eosinophils, which release inflammatory cytokines and enzymes that damage lung tissue, cause mucus buildup, and lead to airway hyper-responsiveness.
- Bronchoconstriction: Some prostaglandins, like
PGFcap P cap G cap F𝑃𝐺𝐹 compounds, act as bronchoconstrictors, causing the smooth muscles in the airways to tighten.
PGD2cap P cap G cap D sub 2𝑃𝐺𝐷2 also has this effect, which narrows the airways and makes breathing difficult.
- Increased vascular permeability: Prostaglandins can increase blood flow and the permeability of blood vessels in the lungs, which leads to edema (swelling) that can further obstruct the airways.
- Imbalance of prostaglandins: The overall effect of prostaglandins is often a result of an imbalance. For example,
PGE2cap P cap G cap E sub 2𝑃𝐺𝐸2 can have a protective effect by preventing bronchoconstriction from other triggers like histamine, but this balance can be upset in individuals with asthma.
Prostaglandins in different parts of the asthma cycle
- Asthma triggers: In an allergic reaction, mast cells are activated by allergens and release a cascade of mediators, including
PGD2cap P cap G cap D sub 2𝑃𝐺𝐷2.
- Early response: The released prostaglandins contribute to the immediate bronchoconstriction and inflammation that characterize an asthma attack.
- Ongoing inflammation: The inflammatory cells recruited by prostaglandins continue to release inflammatory mediators, contributing to the chronic inflammation of the airways seen in asthma.
How to control mucus layer of Upper Respiratory Tract?
Controlling the mucus layer in the upper respiratory tract (URT) involves a combination of hydration, humidification, and lifestyle changes, along with over-the-counter or prescription medications if necessary. The primary goal is to keep the mucus thin and mobile so that the body’s natural defense mechanisms (like cilia and coughing) can clear it effectively.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
These methods help maintain the normal function and hydration of the mucous membranes.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of fluids, especially water and warm liquids like broth or tea. Proper hydration keeps mucus thin and less sticky, making it easier to move and clear.
- Humidify the Air: Use a humidifier or steam vaporizer in your home, especially in the bedroom, to add moisture to dry air. Breathing moist air helps soothe irritated airways and keeps mucus from drying out. Inhaling steam from a hot shower or a bowl of hot water can also provide quick relief.
- Avoid Irritants: Steer clear of environmental irritants like smoke (including secondhand smoke), strong fragrances, chemicals, and pollution, which can irritate mucous membranes and trigger increased mucus production.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking paralyzes the cilia (tiny hair-like cells that move mucus out of the airways) and causes the body to produce thicker, more abundant mucus. Quitting smoking is one of the most effective ways to restore normal mucus function.
- Elevate Your Head: Sleeping with your head propped up on pillows can help prevent mucus from pooling in the back of your throat.
- Gargle with Salt Water: Gargling with warm salt water can help clear mucus from the back of the throat and soothe irritation.
- Use Saline Nasal Rinses: A saline nasal spray or a neti pot can flush mucus and allergens out of your nasal passages and sinuses.
Airway Clearance Techniques
For stubborn or excess mucus, specific techniques can aid removal:
- Controlled Coughing/Huffing: Instead of harsh, uncontrolled coughing, try “huff coughing.” Inhale deeply, tense your stomach muscles, and exhale quickly in three short bursts, making a “ha” sound. This helps move mucus from smaller airways to larger ones where it can be coughed up more effectively.
- Physical Exercise: Regular physical activity increases breathing rate and air flow, which can help loosen and move mucus out of the lungs and airways.
Medications
Over-the-counter (OTC) and prescription options are available to manage excessive mucus:
- Expectorants: OTC medications containing guaifenesin (e.g., Mucinex) thin and loosen mucus, making it easier to cough up.
- Mucolytics: These drugs, such as hypertonic saline (inhaled via a nebulizer) or dornase alfa (prescription for chronic conditions like cystic fibrosis), directly break down the chemical bonds within mucus to reduce its viscosity.
- Antihistamines/Decongestants: If excess mucus is due to allergies, antihistamines can help. However, some decongestants may dry secretions too much, making mucus difficult to expel, so use with caution and consult a healthcare provider.
- Bronchodilators: For conditions like asthma or COPD, a doctor may prescribe bronchodilators to open the airways, which can also improve mucus clearance.
When to See a Doctor
While most cases of excess mucus are manageable with home care, consult a healthcare professional if:
- You experience a significant increase in mucus production or a change in its color (green or yellow), which may indicate an infection.
- Your cough lasts for more than a couple of weeks.
- You have difficulty breathing, chest pain, or bloody mucus.
Addressing the underlying cause, whether it’s an infection, allergies, or a chronic condition, is crucial for effective long-term control.
উপরের শ্বাস নালীর (URT) শ্লেষ্মা স্তর নিয়ন্ত্রণের জন্য হাইড্রেশন, আর্দ্রতা এবং জীবনযাত্রার পরিবর্তনেরসমন্বয় প্রয়োজন , সেই সাথে প্রয়োজনে ওভার-দ্য-কাউন্টার বা প্রেসক্রিপশন ওষুধও ব্যবহার করা হয়। প্রাথমিক লক্ষ্য হল শ্লেষ্মাকে পাতলা এবং সচল রাখা যাতে শরীরের প্রাকৃতিক প্রতিরক্ষা ব্যবস্থা (যেমন সিলিয়া এবং কাশি) কার্যকরভাবে এটি পরিষ্কার করতে পারে।
জীবনধারা এবং ঘরোয়া প্রতিকার
এই পদ্ধতিগুলি শ্লেষ্মা ঝিল্লির স্বাভাবিক কার্যকারিতা এবং হাইড্রেশন বজায় রাখতে সাহায্য করে।
- হাইড্রেটেড থাকুন: প্রচুর পরিমাণে তরল পান করুন, বিশেষ করে জল এবং ঝোল বা চা এর মতো উষ্ণ তরল পান করুন। সঠিক হাইড্রেশন শ্লেষ্মাকে পাতলা এবং কম আঠালো রাখে, যা চলাচল এবং পরিষ্কার করা সহজ করে তোলে।
- বাতাসকে আর্দ্র করুন: শুষ্ক বাতাসে আর্দ্রতা যোগ করতে আপনার বাড়িতে, বিশেষ করে শোবার ঘরে, একটি হিউমিডিফায়ার বা স্টিম ভ্যাপোরাইজার ব্যবহার করুন। আর্দ্র বাতাস শ্বাস নেওয়া জ্বালাপোড়া শ্বাসনালীকে প্রশমিত করতে সাহায্য করে এবং শ্লেষ্মা শুকিয়ে যাওয়া থেকে রক্ষা করে। গরম শাওয়ার বা গরম জলের বাটি থেকে বাষ্প শ্বাস নেওয়ার মাধ্যমেও দ্রুত আরাম পাওয়া যেতে পারে।
- জ্বালাপোড়া এড়িয়ে চলুন: পরিবেশগত জ্বালাপোড়া যেমন ধোঁয়া (পরবর্তী ধোঁয়া সহ), তীব্র সুগন্ধি, রাসায়নিক এবং দূষণ থেকে দূরে থাকুন, যা শ্লেষ্মা ঝিল্লিকে জ্বালাপোড়া করতে পারে এবং শ্লেষ্মা উৎপাদন বৃদ্ধি করতে পারে।
- ধূমপান ত্যাগ করুন: ধূমপান সিলিয়া (ছোট চুলের মতো কোষ যা শ্বাসনালী থেকে শ্লেষ্মা বের করে দেয়) পক্ষাঘাতগ্রস্ত করে এবং শরীরকে ঘন, আরও প্রচুর পরিমাণে শ্লেষ্মা তৈরি করতে বাধ্য করে। শ্লেষ্মা স্বাভাবিক কার্যকারিতা পুনরুদ্ধারের সবচেয়ে কার্যকর উপায়গুলির মধ্যে একটি হল ধূমপান ত্যাগ করা।
- মাথা উঁচু করুন: বালিশে মাথা রেখে ঘুমালে গলার পেছনে শ্লেষ্মা জমা হওয়া রোধ করা যায়।
- লবণ পানি দিয়ে গার্গল করুন: উষ্ণ লবণ পানি দিয়ে গার্গল করলে গলার পেছন থেকে শ্লেষ্মা পরিষ্কার হতে পারে এবং জ্বালা প্রশমিত হতে পারে।
- স্যালাইন নাসাল রিন্স ব্যবহার করুন: স্যালাইন নাসাল স্প্রে বা নেটি পট আপনার নাকের পথ এবং সাইনাস থেকে শ্লেষ্মা এবং অ্যালার্জেন বের করে দিতে পারে।
এয়ারওয়ে ক্লিয়ারেন্স কৌশল
একগুঁয়ে বা অতিরিক্ত শ্লেষ্মা অপসারণে, নির্দিষ্ট কৌশলগুলি সাহায্য করতে পারে:
- নিয়ন্ত্রিত কাশি/হাফিং: তীব্র, অনিয়ন্ত্রিত কাশির পরিবর্তে, “হাফিং কাশি” চেষ্টা করুন। গভীরভাবে শ্বাস নিন, আপনার পেটের পেশীগুলিকে টান দিন এবং “হা” শব্দ করে তিনটি ছোট বিস্ফোরণে দ্রুত শ্বাস ছাড়ুন। এটি ছোট শ্বাসনালী থেকে বৃহত্তর শ্বাসনালীতে শ্লেষ্মা স্থানান্তর করতে সাহায্য করে যেখানে এটি আরও কার্যকরভাবে কাশি দেওয়া যেতে পারে।
- শারীরিক ব্যায়াম: নিয়মিত শারীরিক কার্যকলাপ শ্বাস-প্রশ্বাসের হার এবং বাতাসের প্রবাহ বৃদ্ধি করে, যা ফুসফুস এবং শ্বাসনালী থেকে শ্লেষ্মা আলগা করতে এবং বের করে দিতে সাহায্য করে।
ওষুধ
অতিরিক্ত শ্লেষ্মা নিয়ন্ত্রণের জন্য ওভার-দ্য-কাউন্টার (OTC) এবং প্রেসক্রিপশনের বিকল্পগুলি পাওয়া যায়:
- কফের ঔষধ:গুয়াইফেনেসিন (যেমন, মিউসিনেক্স ) ধারণকারী ওটিসি ওষুধ শ্লেষ্মা পাতলা এবং আলগা করে, যার ফলে কাশি সহজ হয়।
- মিউকোলাইটিক্স: এই ওষুধগুলি, যেমন হাইপারটোনিক স্যালাইন (নেবুলাইজারের মাধ্যমে শ্বাস নেওয়া) বা ডোরনেস আলফা (সিস্টিক ফাইব্রোসিসের মতো দীর্ঘস্থায়ী অবস্থার জন্য প্রেসক্রিপশন), শ্লেষ্মার সান্দ্রতা কমাতে সরাসরি রাসায়নিক বন্ধন ভেঙে দেয়।
- অ্যান্টিহিস্টামাইন/ডিকনজেস্ট্যান্ট: যদি অ্যালার্জির কারণে অতিরিক্ত শ্লেষ্মা হয়, তাহলে অ্যান্টিহিস্টামাইন সাহায্য করতে পারে। তবে, কিছু ডিকনজেস্ট্যান্ট স্রাবকে খুব বেশি শুকিয়ে দিতে পারে, যার ফলে শ্লেষ্মা বের করা কঠিন হয়ে পড়ে, তাই সাবধানতার সাথে ব্যবহার করুন এবং একজন স্বাস্থ্যসেবা প্রদানকারীর সাথে পরামর্শ করুন।
- ব্রঙ্কোডাইলেটর: হাঁপানি বা সিওপিডির মতো অবস্থার জন্য, একজন ডাক্তার শ্বাসনালী খোলার জন্য ব্রঙ্কোডাইলেটর লিখে দিতে পারেন, যা শ্লেষ্মা নিষ্কাশনকেও উন্নত করতে পারে।
কখন ডাক্তারের সাথে দেখা করবেন
যদিও অতিরিক্ত শ্লেষ্মা হওয়ার বেশিরভাগ ক্ষেত্রেই ঘরোয়া চিকিৎসার মাধ্যমে নিয়ন্ত্রণ করা সম্ভব, তবে নিম্নলিখিত ক্ষেত্রে একজন স্বাস্থ্যসেবা পেশাদারের সাথে পরামর্শ করুন:
- আপনার শ্লেষ্মা উৎপাদনে উল্লেখযোগ্য বৃদ্ধি বা এর রঙ (সবুজ বা হলুদ) পরিবর্তন অনুভব করা উচিত, যা সংক্রমণের ইঙ্গিত দিতে পারে।
- আপনার কাশি কয়েক সপ্তাহেরও বেশি সময় ধরে থাকে।
- আপনার শ্বাস নিতে কষ্ট হচ্ছে, বুকে ব্যথা হচ্ছে, অথবা রক্তাক্ত শ্লেষ্মা হচ্ছে।
দীর্ঘমেয়াদী কার্যকর নিয়ন্ত্রণের জন্য, অন্তর্নিহিত কারণ, তা সে সংক্রমণ, অ্যালার্জি বা দীর্ঘস্থায়ী অবস্থা যাই হোক না কেন, তার সমাধান করা অত্যন্ত গুরুত্বপূর্ণ।
What is Neti pot?
A neti pot is a nasal irrigation device, resembling a small teapot, that uses a saline (saltwater) solution to rinse mucus and debris from the nasal passages. It is used to relieve congestion from colds, allergies, and sinus infections, as well as to moisturize nasal passages from dry air. Proper and safe use requires using sterile, distilled, or previously boiled water to avoid serious infection.
How a neti pot works
- Flushes out mucus: You tilt your head and pour the saline solution from the neti pot spout into one nostril.
- Flows through nasal cavity: The solution flows through the nasal cavity and drains out of the other nostril.
- Relieves symptoms: This helps to clear out allergens, dust, and loose mucus, reducing symptoms like a stuffy nose and sinus pressure.
Safety and usage tips
- Use safe water: Always use distilled, sterile, or previously boiled and cooled water to prevent the risk of serious infections.
- Clean the device: Thoroughly wash and dry the neti pot after each use.
- Wash hands: Wash and dry your hands before and after using the device.
- Consult a doctor: Talk to a healthcare provider before using a neti pot, especially if you have a compromised immune system or have had recent nasal surgery.
- Make your own solution: You can make a saline solution by mixing non-iodized powdered salt with boiled water, but make a fresh batch each time.
নেটি পট হল একটি নাক সেচের যন্ত্র, যা একটি ছোট চায়ের পাত্রের মতো, যা লবণাক্ত (লবণ জল) দ্রবণ ব্যবহার করে নাকের শ্লেষ্মা এবং ধ্বংসাবশেষ ধুয়ে ফেলা হয়।এটি সর্দি, অ্যালার্জি এবং সাইনাসের সংক্রমণ থেকে রক্তক্ষরণ দূর করতে এবং শুষ্ক বাতাস থেকে নাককে আর্দ্র করতে ব্যবহৃত হয়। গুরুতর সংক্রমণ এড়াতে সঠিক এবং নিরাপদ ব্যবহারের জন্য জীবাণুমুক্ত, পাতিত বা পূর্বে ফুটানো জল ব্যবহার করা প্রয়োজন।
নেটি পট কীভাবে কাজ করে
- শ্লেষ্মা বের করে দেয়: আপনি আপনার মাথা কাত করে নেটি পট স্পাউট থেকে স্যালাইনের দ্রবণ একটি নাকের ছিদ্রে ঢেলে দিন।
- নাকের গহ্বরের মধ্য দিয়ে প্রবাহিত হয়: দ্রবণটি নাকের গহ্বরের মধ্য দিয়ে প্রবাহিত হয় এবং অন্য নাকের ছিদ্র দিয়ে বেরিয়ে যায়।
- লক্ষণগুলি উপশম করে: এটি অ্যালার্জেন, ধুলো এবং আলগা শ্লেষ্মা পরিষ্কার করতে সাহায্য করে, যা নাক বন্ধ হয়ে যাওয়া এবং সাইনাসের চাপের মতো লক্ষণগুলি হ্রাস করে।
নিরাপত্তা এবং ব্যবহারের টিপস
- নিরাপদ পানি ব্যবহার করুন: গুরুতর সংক্রমণের ঝুঁকি এড়াতে সর্বদা পাতিত, জীবাণুমুক্ত, অথবা পূর্বে ফুটানো এবং ঠান্ডা করা পানি ব্যবহার করুন।
- ডিভাইসটি পরিষ্কার করুন: প্রতিটি ব্যবহারের পরে নেটি পটটি ভালোভাবে ধুয়ে শুকিয়ে নিন।
- হাত ধোয়া: ডিভাইসটি ব্যবহারের আগে এবং পরে আপনার হাত ধুয়ে শুকিয়ে নিন।
- ডাক্তারের সাথে পরামর্শ করুন: নেটি পট ব্যবহার করার আগে একজন স্বাস্থ্যসেবা প্রদানকারীর সাথে কথা বলুন, বিশেষ করে যদি আপনার রোগ প্রতিরোধ ক্ষমতা দুর্বল হয়ে পড়ে অথবা সম্প্রতি নাকের অস্ত্রোপচার করা হয়ে থাকে।
- নিজের দ্রবণ নিজেই তৈরি করুন: আপনি ফুটন্ত জলের সাথে নন-আয়োডিনযুক্ত গুঁড়ো লবণ মিশিয়ে একটি লবণাক্ত দ্রবণ তৈরি করতে পারেন, তবে প্রতিবার একটি নতুন ব্যাচ তৈরি করুন।
 HRTD Medical Institute
HRTD Medical Institute




