Arthritis & Osteoporosis (Geriatric Disease)
Arthritis & Osteoporosis (Geriatric Disease). Mobile Phone 01797522136, 01987073965. Arthritis & Osteoporosis are common Geriatric Disease. Geriatric Diseases are those occur in old age. Geriatric Disease are Arthritis, Osteoarthritis, Rheumatoid Arthritis, Gout, Osteoporosis, Ankylosing Spondylitis, Septic Arthritis, Reactive Arthritis, Osteoporosis, Cancer, Chronic Kidney Disease, COPD, Diabetes, etc.
Arthritis & Osteoporosis are discussed in many courses of HRTD Medical Institute including Caregiving Course, Paramedical Course, Diploma Medical Assistant Course, DMS Course, DPM Course, DMDS Course, PDT Medicine Course, PDT Orthopedic Course, etc. All these courses are always available in HRTD Medical Institute.
What is Arthritis
Ans:- Inflammation of bone joints is called Arthritis. হাড়ের জয়েন্টের প্রদাহকে আর্থ্রাইটিস বলে।
How many types of Arthritis?
There are more than 100 types of Arthritis. Common Arthritis are Osteoarthritis, Rheumatoid Arthritis, Gout, Ankylosing Spondylitis, Septic Arthritis, Reactive Arthritis, Shoulder Arthritis, etc. Arthritis can be categorized into groups like degenerative, inflammatory, metabolic, and infectious.
আর্থ্রাইটিসের 100 টিরও বেশি প্রকার রয়েছে। সাধারণ আর্থ্রাইটিস হল অস্টিওআর্থারাইটিস, রিউমাটয়েড আর্থ্রাইটিস, গাউট, অ্যানকিলোজিং স্পন্ডিলাইটিস, সেপটিক আর্থ্রাইটিস, রিঅ্যাকটিভ আর্থ্রাইটিস, শোল্ডার আর্থ্রাইটিস ইত্যাদি। আর্থ্রাইটিসকে ডিজেনারেটিভ, প্রদাহজনক, বিপাকীয় এবং সংক্রামক গ্রুপে শ্রেণীবদ্ধ করা যেতে পারে।
What are the Symptoms of Arthritis?
Symptoms of Arthritis are
Pain
Stiffness
Swelling
Redness
Decreased ranged of motion
What are the causes of Arthritis?
The cause of arthritis depends on the type of arthritis:
- OsteoarthritisCaused by the breakdown of cartilage and other tissues in the joint, usually over time. Risk factors include:
- Aging
- Being overweight or obese
- History of joint injury or surgery
- Overuse from repetitive movements
- Family history
- Rheumatoid arthritisAn autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system attacks the body’s own tissues. Risk factors include:
- Being a woman, especially over age 50
- GoutCaused by a buildup of crystals in the joints. Risk factors include:
- Having high uric acid levels for at least several months
- Infectious arthritisCaused by a bacterium, virus, or fungus that enters a joint. Risk factors include:
- Food poisoning or contamination
- Sexually transmitted infections (STIs)
- Blood-to-blood infection
- অস্টিওআর্থারাইটিস সাধারণত সময়ের সাথে সাথে জয়েন্টের তরুণাস্থি এবং অন্যান্য টিস্যু ভেঙে যাওয়ার কারণে ঘটে। ঝুঁকির কারণগুলির মধ্যে রয়েছে: বার্ধক্য অতিরিক্ত ওজন বা মোটা হওয়া জয়েন্টে আঘাত বা অস্ত্রোপচারের ইতিহাস পুনরাবৃত্তিমূলক আন্দোলন থেকে অতিরিক্ত ব্যবহার পারিবারিক ইতিহাস রিউমাটয়েড আর্থ্রাইটিস একটি অটোইমিউন অবস্থা যেখানে শরীরের রোগ প্রতিরোধ ক্ষমতা শরীরের নিজস্ব টিস্যুতে আক্রমণ করে। ঝুঁকির কারণগুলির মধ্যে রয়েছে: একজন মহিলা, বিশেষ করে 50 বছরের বেশি বয়সী জয়েন্টগুলোতে স্ফটিক তৈরির কারণে গাউট। ঝুঁকির কারণগুলির মধ্যে রয়েছে: কমপক্ষে কয়েক মাস ধরে উচ্চ ইউরিক অ্যাসিডের মাত্রা থাকা একটি বিএ দ্বারা সৃষ্ট সংক্রামক আর্থ্রাইটিস খাদ্যে বিষক্রিয়া বা দূষণ যৌনবাহিত সংক্রমণ (STIs) রক্ত থেকে রক্তের সংক্রমণ
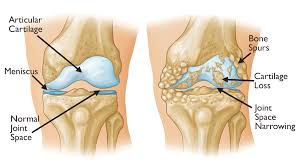
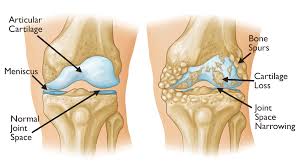
What is Osteoarthritis?
Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease that causes the breakdown of cartilage and other tissues in a joint over time. অস্টিওআর্থারাইটিস হল একটি ডিজেনারেটিভ জয়েন্ট রোগ যা সময়ের সাথে সাথে জয়েন্টে তরুণাস্থি এবং অন্যান্য টিস্যু ভেঙে যায়
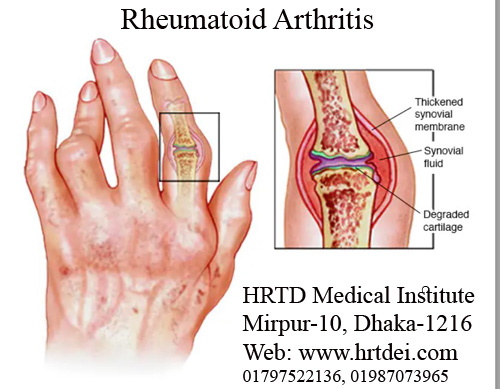
What is Rheumatoid Arthritis?
Rheumatoid Arthritis is an Autoimmune Disease. Immune System attack the synovial membrane. This membrane becomes inflamed and swollen. The disease process can eventually destroy cartilage and bone within the joint. In some people, the condition can damage a wide variety of body systems, including the skin, eyes, lungs, heart and blood vessels.
রিউমাটয়েড আর্থ্রাইটিস একটি অটোইমিউন রোগ। ইমিউন সিস্টেম সাইনোভিয়াল মেমব্রেন আক্রমণ করে। এই ঝিল্লি স্ফীত এবং ফুলে যায়। রোগ প্রক্রিয়া অবশেষে জয়েন্টের মধ্যে তরুণাস্থি এবং হাড় ধ্বংস করতে পারে। কিছু লোকের ক্ষেত্রে, এই অবস্থাটি ত্বক, চোখ, ফুসফুস, হৃদপিণ্ড এবং রক্তনালীগুলি সহ শরীরের বিভিন্ন সিস্টেমের ক্ষতি করতে পারে।
What are the risk factors of Arthritis?
Risk factors of arthritis:
Old age
Genetic cause
Previously joint injury
Overweight and Obesity
What are the complications of arthritis?
Arthritis can lead to a number of complications, including:
- Joint damage-Arthritis can cause cartilage to break down, bones to die, or tendons and ligaments to tear.
- Inflammation-In rheumatoid arthritis, inflammation can spread to other parts of the body, such as the lungs, heart, eyes, and blood vessels.
- Decreased mobility-Arthritis can cause pain and stiffness that make it difficult to move around, especially for daily activities.
- Weight gain-A lack of activity due to arthritis can lead to weight gain, which can worsen arthritis symptoms and increase the risk of other complications.
- Psychological health-Arthritis can increase the risk of depression and anxiety due to pain, inflammation, and loneliness.
- Sleep problems-Arthritis pain can make it difficult to sleep, which can worsen pain and increase the risk of depression.
- Heart disease-Arthritis conditions associated with being overweight can increase the risk of heart disease.
- Diabetes-Arthritis conditions associated with being overweight can increase the risk of type-2 diabetes.
- Hypertension-Arthritis conditions associated with being overweight can increase the risk of hypertension.
- High cholesterol-Arthritis conditions associated with being overweight can increase the risk of high cholesterol.
- Lung disease-Rheumatoid arthritis can lead to a chronic lung disease called rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease (RA-ILD).
- Pregnancy complications-Uncontrolled rheumatoid arthritis during pregnancy can increase the risk of preterm birth and low birth weight.
What are the diagnostic creteria for arthritis?
Diagnostic creteria for arthritis:
Physical examination: Swelling, redness, warmth, and joint movement.
Laboratory Test: Fluid Test (Blood, Urin, and Joint Fluid Test.)
Imaging Test
What are the Laboratory Test for Arthritis?
Blood Test
Urin Test
Joint Fluid Test
What are the Imaging Test for Arthritis?
X- ray
CT scanne ( Computerized Tomography)
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Ultrasound
What are the treatment creteria of Artritis?
Treatment Creteria of Arthritis:
Medication
Physiotherapy
Surgery
What are the Medication Treatment for Arthritis?
NSAIDs– Ibuprofen, Neproxen sodium, etc. Oral, Gel, Injection, and Suppository.
Counterirritants-Menthol or Capsaicin enrished cream and ointment for rubbing on the joint skin.
Steroids- Corticosteroids like Prednisone reduces inflammation and slow joint damage.
Disease Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs)- These drugs can slow the progression of rheumatoid arthritis and save the joint and other tissues from permanent damage. These drugs are Methotrexate, Bericitinib, and Tofacitinib.
What are the surgeries for arthritis management?
Joint repair
Joint replacement
Joint fusion
What do you mean by DMARDs?
DMARDs is stand for Disease Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs. These drugs can slow the progression of rheumatoid arthritis and save the joint and other tissues from permanent damage. These drugs are Methotrexate, Bericitinib, and Tofacitinib.
DMARDs হল রোগ পরিবর্তনকারী অ্যান্টি-রিউমেটিক ড্রাগস। এই ওষুধগুলি রিউমাটয়েড আর্থ্রাইটিসের অগ্রগতি মন্থর করতে পারে এবং জয়েন্ট এবং অন্যান্য টিস্যুকে স্থায়ী ক্ষতি থেকে বাঁচাতে পারে। এই ওষুধগুলি হল মেথোট্রেক্সেট, বেরিসিটিনিব এবং টোফাসিটিনিব।
What are the alternative medicines for arthritis?
Acupuncture
Glucosamine
Chondroitin
Fish oil
Yoga and tai chi
Massage
What do you mean by Osteoporosis?
If bone density decreases and it becomes porous, it is called Osteoporosis.
Bone density কমে গিয়ে ছিদ্রযুক্ত হলে তাকে Osteoporosis বলে ।
What are the symptoms of Osteoporosis?
- Bone fracturesBones affected by osteoporosis can become fragile and break more easily, even from minor falls or bumps. Fractures can also occur spontaneously or from normal stresses like bending, lifting, or coughing.
- Back painCompression fractures in the spine can cause severe pain, especially if the collapsed vertebrae pinch nerves.
- Loss of heightCompression fractures in the spine can cause a loss of height of up to 6 inches or 15 centimeters.
- Stooped postureA stooped or hunched posture, also known as kyphosis, can develop.
- Brittle nailsOsteoporosis can contribute to slow nail growth, which can lead to brittle fingernails.
- হাড়ের ভাঙ্গন অস্টিওপোরোসিসে আক্রান্ত হাড়গুলি ভঙ্গুর হয়ে যেতে পারে এবং আরও সহজে ভেঙে যেতে পারে, এমনকি ছোটখাটো পতন বা বাম্প থেকেও। ফ্র্যাকচারগুলি স্বতঃস্ফূর্তভাবে বা বাঁকানো, উত্তোলন বা কাশির মতো স্বাভাবিক চাপ থেকেও ঘটতে পারে। পিঠে ব্যথা মেরুদণ্ডে কম্প্রেশন ফ্র্যাকচার গুরুতর ব্যথার কারণ হতে পারে, বিশেষ করে যদি ধসে পড়া কশেরুকা স্নায়ু চিমটি করে। উচ্চতা হ্রাস মেরুদণ্ডের সংকোচন ফ্র্যাকচার 6 ইঞ্চি বা 15 সেন্টিমিটার পর্যন্ত উচ্চতা হ্রাস করতে পারে। স্তব্ধ ভঙ্গিএকটি নিচু বা কুঁজো ভঙ্গি, যা কিফোসিস নামেও পরিচিত, বিকাশ করতে পারে। ভঙ্গুর নখ অস্টিওপোরোসিস নখের বৃদ্ধি ধীর করতে অবদান রাখতে পারে, যা ভঙ্গুর নখ হতে পারে।
What are the causes of Osteoporosis?
There are many potential causes of osteoporosis, including:
- Bone density– A diet low in calcium and vitamin D, or a body mass index (BMI) of 19 or less, can increase the risk of osteoporosis.
- Exercise– A lack of exercise or physical activity can increase the risk of osteoporosis.
- HormonesLow levels of estrogen can increase the risk of osteoporosis, especially in women who experience early menopause or have had a hysterectomy.
- MedicationsLong-term use of certain medications, such as those used to treat breast cancer and prostate cancer, can increase the risk of osteoporosis.
- SmokingNicotine in cigarettes slows the production of bone-forming cells and decreases the absorption of calcium.
- AlcoholHeavy drinking can compromise bone health and decrease bone density.
- Medical conditionsSome medical conditions, such as celiac disease, inflammatory bowel disease, kidney or liver disease, cancer, multiple myeloma, and rheumatoid arthritis, can increase the risk of osteoporosis.
- Family historyA family history of osteoporosis or hip fracture can increase the risk of osteoporosis.
- Other factorsBeing confined to bed for a prolonged illness, having an eating disorder, or malabsorption problems can also increase the risk of osteoporosis.
What are the risk factors for Osteoporosis?
There are many risk factors for osteoporosis, including:
- AgeAs you age, your bones become thinner and weaker, and you lose bone faster than you grow new bone.
- SexWomen are more likely to develop osteoporosis than men because they have less bone tissue and lose bone faster during menopause.
- Body sizeSmall, thin-boned people have a higher risk of osteoporosis.
- RaceCaucasian and Asian women have the highest risk of osteoporosis, while African American and Hispanic women have a lower but significant risk.
- Family historyIf a parent or sibling has osteoporosis, you are at greater risk, especially if they fractured a hip.
- DietIf you don’t get enough calcium in your diet, your body will take calcium from your bones.
- SmokingNicotine in cigarettes slows the production of bone-forming cells and decreases the absorption of calcium.
- AlcoholDrinking too much alcohol can thin your bones and increase the risk of fractures.
- MedicationsSome medications can increase the risk of osteoporosis, including glucocorticoids, anticoagulants, and some antidepressants.
- Physical activityLow levels of physical activity can increase the risk of osteoporosis.
- বয়স বাড়ার সাথে সাথে আপনার হাড়গুলি পাতলা এবং দুর্বল হয়ে যায় এবং আপনি নতুন হাড় গজানোর চেয়ে দ্রুত হাড় হারান। সেক্স নারীদের পুরুষদের তুলনায় অস্টিওপরোসিস হওয়ার সম্ভাবনা বেশি কারণ তাদের হাড়ের টিস্যু কম থাকে এবং মেনোপজের সময় হাড় দ্রুত হারায়। শরীরের আকার ছোট, পাতলা হাড়ের মানুষের অস্টিওপোরোসিসের ঝুঁকি বেশি থাকে। রেসককেশিয়ান এবং এশিয়ান মহিলাদের অস্টিওপোরোসিসের ঝুঁকি সবচেয়ে বেশি, যখন আফ্রিকান আমেরিকান এবং হিস্পানিক মহিলাদের কম কিন্তু উল্লেখযোগ্য ঝুঁকি রয়েছে। পারিবারিক ইতিহাস যদি একজন পিতা-মাতা বা ভাইবোনের অস্টিওপরোসিস থাকে, তাহলে আপনি বেশি ঝুঁকিতে থাকেন, বিশেষ করে যদি তাদের নিতম্ব ভেঙে যায়। ডায়েটআপনি যদি আপনার ডায়েটে পর্যাপ্ত ক্যালসিয়াম না পান তবে আপনার শরীর আপনার হাড় থেকে ক্যালসিয়াম নেবে। সিগারেটের ধূমপান নিকোটিন হাড় গঠনকারী কোষের উৎপাদনকে ধীর করে দেয় এবং ক্যালসিয়ামের শোষণকে হ্রাস করে। অ্যালকোহল অত্যধিক অ্যালকোহল পান করা আপনার হাড়কে পাতলা করতে পারে এবং ফ্র্যাকচারের ঝুঁকি বাড়ায়। ওষুধ কিছু ওষুধ অস্টিওপোরোসিসের ঝুঁকি বাড়াতে পারে, যার মধ্যে রয়েছে গ্লুকোকোর্টিকয়েডস, অ্যান্টিকোয়াগুল্যান্টস এবং কিছু অ্যান্টিডিপ্রেসেন্টস। শারীরিক কার্যকলাপ নিম্ন মাত্রার শারীরিক কার্যকলাপ অস্টিওপরোসিসের ঝুঁকি বাড়াতে পারে।
What are the complications of Osteoporosis?
Complications of osteoporosis can include:
- Bone fractures: The most serious complication of osteoporosis is a broken bone in the spine or hip. Fractures in the hip are often caused by a fall and can lead to disability and an increased risk of death. Fractures in the spine can occur even without a fall.
- Osteoarthritis: Misshapen bones can put more stress on nearby joints, which can lead to osteoarthritis.
- Heart failure: A complication of osteoporotic fractures.
- Bone cancer: A complication of bone loss.
- Pulmonary embolism: Patients with osteoporosis have an increased risk of pulmonary embolism.
- Oral health issues: Osteoporosis can decrease the density of the jawbone, making it more difficult to support teeth. This can lead to periodontal disease, a leading cause of tooth loss.
- Other medical complications: Other complications of osteoporotic fractures include cardiac diseases, venous thromboembolism, pneumonia, urinary tract complications, and gastrointestinal tract bleeding.
- হাড় ভেঙ্গে যাওয়া: অস্টিওপোরোসিসের সবচেয়ে গুরুতর জটিলতা হল মেরুদণ্ড বা নিতম্বের হাড় ভেঙে যাওয়া। নিতম্বের ফাটল প্রায়ই পড়ে যাওয়ার কারণে হয় এবং এটি অক্ষমতা এবং মৃত্যুর ঝুঁকি বাড়াতে পারে। এমনকি পড়ে না গিয়েও মেরুদণ্ডের ফ্র্যাকচার হতে পারে। অস্টিওআর্থারাইটিস: মিশাপেন হাড় কাছাকাছি জয়েন্টগুলোতে বেশি চাপ দিতে পারে, যা অস্টিওআর্থারাইটিস হতে পারে। হার্ট ফেইলিউর: অস্টিওপরোটিক ফ্র্যাকচারের একটি জটিলতা। হাড়ের ক্যান্সার: হাড় ক্ষয়ের একটি জটিলতা। পালমোনারি এমবোলিজম: অস্টিওপোরোসিস রোগীদের পালমোনারি এমবোলিজমের ঝুঁকি বেশি থাকে। মৌখিক স্বাস্থ্যের সমস্যা: অস্টিওপোরোসিস চোয়ালের হাড়ের ঘনত্ব কমাতে পারে, যা দাঁতকে সমর্থন করা আরও কঠিন করে তোলে। এটি পেরিওডন্টাল রোগের কারণ হতে পারে, যা দাঁতের ক্ষতির একটি প্রধান কারণ। অন্যান্য চিকিৎসা জটিলতা: অস্টিওপোরোটিক ফ্র্যাকচারের অন্যান্য জটিলতার মধ্যে রয়েছে কার্ডিয়াক ডিজিজ, ভেনাস থ্রম্বোইম্বোলিজম, নিউমোনিয়া, মূত্রনালীর জটিলতা এবং গ্যাস্ট্রোইনটেস্টাইনাল ট্র্যাক্টের রক্তপাত।
What are the prevension of Osteoporosis?
Good nutrition and regular exercise are essential for keeping our bones healthy throughout our life.
Good nutrition: Calcium and Vitamin D
Calcium: Daily Requirement for an adult is 1000 mg to 1200 mg
Sources of Calcium-
Low-fat dairy products
Dark green leafy vegetables
Canned salmon or sardines with bones
Soy products such as tofu
Calcium fortified cereals and orange juice
Supplements ( Calbo-D, Ostocal-D, Sandocal-D, Miracal-D, etc)
Vitamin D: Vitamin D improves the absorption of calcium by our body. Daily requirement for an adult is 600 IU to 800 IU.
Sources of Vitamin D-
Sunlight (But excessive sunlight can cause skin cancer)
Cod liver oil
Supplements
Trout
Salmon
Exercise: Exercise can help building strong bones and slow bone loss.
Strength training exercise- helps strengthen muscles and bones in our arms and upper spine.
Weight bearing exercise- (walking, running, jogging) helps strengthen muscle and bones of our legs, hips, and lower spine.
Balance exercise-( Tai chi) can reduce the risk of falling especially as we get older.
What are the treatment of Osteoporosis?
Treatment depends on bone density test.
Bisphosphonates:
Alendronate
Risedronate
Ibandronate
Zoledronic acid
Denosumab:
Hormone Related Therapy:
Bone Building Medicines:
Teriparatide
Abaloparatide
Romosozumab
What are the hormone releted therapy for osteoporosis?
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) can be used to treat osteoporosis and relieve menopausal symptoms:
- Estrogen therapyPrevents bone loss and reduces the risk of fractures in the spine and hip. Estrogen can be taken as a pill, skin patch, or gel.
- Progesterone-based HRTMay be used in some situations. Progesterone is taken to reduce the risk of uterine cancer unless you’ve had a hysterectomy.
HRT can be a good choice if you need treatment for both osteoporosis and menopausal symptoms. It’s usually started before the age of 60, as the risks may outweigh the benefits as you get older.
The benefit-risk balance of HRT depends on several factors, including: Your individual risk profile, Whether estrogen is opposed or unopposed, The type of estrogens and progestogens, and The doses and routes of administration.
হরমোন রিপ্লেসমেন্ট থেরাপি (এইচআরটি) অস্টিওপরোসিসের চিকিত্সা এবং মেনোপজের লক্ষণগুলি উপশম করতে ব্যবহার করা যেতে পারে: ইস্ট্রোজেন থেরাপি হাড়ের ক্ষয় রোধ করে এবং মেরুদন্ড ও নিতম্বের ফ্র্যাকচারের ঝুঁকি কমায়। ইস্ট্রোজেন একটি বড়ি, ত্বকের প্যাচ বা জেল হিসাবে নেওয়া যেতে পারে। প্রজেস্টেরন-ভিত্তিক HRT কিছু পরিস্থিতিতে ব্যবহার করা যেতে পারে। আপনার হিস্টেরেক্টমি না হওয়া পর্যন্ত জরায়ু ক্যান্সারের ঝুঁকি কমাতে প্রোজেস্টেরন নেওয়া হয়। আপনার যদি অস্টিওপরোসিস এবং মেনোপজের লক্ষণ উভয়ের জন্য চিকিত্সার প্রয়োজন হয় তবে এইচআরটি একটি ভাল পছন্দ হতে পারে। এটি সাধারণত 60 বছর বয়সের আগে শুরু হয়, কারণ আপনার বয়স বাড়ার সাথে সাথে ঝুঁকিগুলি সুবিধার চেয়ে বেশি হতে পারে। এইচআরটি-এর সুবিধা-ঝুঁকির ভারসাম্য বিভিন্ন কারণের উপর নির্ভর করে, যার মধ্যে রয়েছে: আপনার ব্যক্তিগত ঝুঁকির প্রোফাইল, ইস্ট্রোজেন বিরোধী বা অপ্রতিরোধ্য কিনা, ইস্ট্রোজেন এবং প্রোজেস্টোজেনগুলির ধরন এবং প্রশাসনের ডোজ এবং রুট।
 HRTD Medical Institute
HRTD Medical Institute




