Body Fluids and Their Functions
Body Fluid. Hotline Number 01969947171. Body fluids include blood, lymph, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), saliva, mucus, tears, sweat, urine, semen, vaginal fluids, and various types of serous fluids (like pleural, pericardial, and peritoneal fluids). Other examples include bile, breast milk, amniotic fluid, and digestive fluids.
These fluids are essential for various bodily functions, including nutrient transport, waste removal, and maintaining a stable internal environment.
To study Body Fluids and Everything about it there are some Paramedical Courses and Diploma Medical Courses like Paramedical, DMA Course, DMS Course, DMDS Course, Diploma Nursing, Diploma Pathology, Diploma Physiotherapy, Diploma Dental, etc. All these courses are available in HRTD Medical Institute. This Institute is an Organization of HRTD Limited which is registered by the Govt of the People Republic of Bangladesh.
Names of Total Body Fluids
1. Blood: A complex fluid tissue containing plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets, circulating throughout the body.
2. Lymph: A clear fluid that circulates through the lymphatic system, collecting waste and transporting immune cells.
রক্ত: প্লাজমা, লোহিত রক্তকণিকা, শ্বেত রক্তকণিকা এবং প্লেটলেট সমন্বিত একটি জটিল তরল টিস্যু, যা সারা শরীরে সঞ্চালিত হয়। ২. লিম্ফ: একটি স্বচ্ছ তরল যা লিম্ফ্যাটিক সিস্টেমের মধ্য দিয়ে সঞ্চালিত হয়, বর্জ্য সংগ্রহ করে এবং রোগ প্রতিরোধক কোষ পরিবহন করে।
3. Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF): A fluid surrounding the brain and spinal cord, providing protection and acting as a shock absorber.
4. Saliva: A fluid secreted in the mouth, aiding in digestion and oral hygiene.
5. Mucus: A viscous fluid produced by mucous membranes, protecting and lubricating body surfaces.
6. Tears: A fluid secreted by the lacrimal glands, lubricating the eyes and providing protection.
7. Sweat: A fluid secreted by sweat glands, helping to regulate body temperature.
8. Urine: A liquid waste product of the kidneys, containing metabolic waste and excess water.
9. Semen: A fluid produced by the male reproductive system, containing sperm.
10. Vaginal fluids: Fluids produced by the female reproductive system, lubricating and cleansing the vagina.
11. Serous Fluids: These include pleural fluid (around the lungs), pericardial fluid (around the heart), and peritoneal fluid (around the abdominal organs).
12. Bile: A digestive fluid produced by the liver, aiding in the digestion of fats.
13. Breast Milk: A fluid secreted by mammary glands, providing nourishment for infants.
14. Amniotic Fluid: The fluid surrounding a developing fetus in the womb.
সেরিব্রোস্পাইনাল ফ্লুইড (CSF): মস্তিষ্ক এবং মেরুদণ্ডের চারপাশে একটি তরল পদার্থ যা সুরক্ষা প্রদান করে এবং শক শোষক হিসেবে কাজ করে।
৪. লালা: মুখের মধ্যে নিঃসৃত একটি তরল পদার্থ যা হজম এবং মৌখিক স্বাস্থ্যবিধিতে সহায়তা করে।
৫. শ্লেষ্মা: শ্লেষ্মা ঝিল্লি দ্বারা উৎপাদিত একটি সান্দ্র তরল পদার্থ যা শরীরের পৃষ্ঠকে সুরক্ষা এবং তৈলাক্ত করে।
৬. অশ্রু: অশ্রু গ্রন্থি দ্বারা নিঃসৃত একটি তরল পদার্থ যা চোখকে তৈলাক্ত করে এবং সুরক্ষা প্রদান করে।
৭. ঘাম: ঘাম গ্রন্থি দ্বারা নিঃসৃত একটি তরল পদার্থ যা শরীরের তাপমাত্রা নিয়ন্ত্রণে সহায়তা করে।
৮. প্রস্রাব: কিডনির একটি তরল বর্জ্য পদার্থ, যাতে বিপাকীয় বর্জ্য এবং অতিরিক্ত জল থাকে।
৯. বীর্য: পুরুষ প্রজনন ব্যবস্থা দ্বারা উৎপাদিত একটি তরল পদার্থ, যাতে শুক্রাণু থাকে।
১০. যোনিপথের তরল পদার্থ: মহিলা প্রজনন ব্যবস্থা দ্বারা উৎপাদিত তরল পদার্থ যা যোনিপথকে তৈলাক্ত করে এবং পরিষ্কার করে।
১১. সিরাস তরল পদার্থ: এর মধ্যে রয়েছে প্লুরাল তরল (ফুসফুসের চারপাশে), পেরিকার্ডিয়াল তরল (হৃদয়ের চারপাশে), এবং পেরিটোনিয়াল তরল (পেটের অঙ্গগুলির চারপাশে)।
১২. পিত্ত: লিভার দ্বারা উৎপাদিত একটি পরিপাক তরল, যা চর্বি হজমে সহায়তা করে।
১৩. বুকের দুধ: স্তন্যপায়ী গ্রন্থি দ্বারা নিঃসৃত একটি তরল যা শিশুদের পুষ্টি সরবরাহ করে।
১৪. অ্যামনিওটিক তরল: গর্ভে একটি বিকাশমান ভ্রূণকে ঘিরে থাকা তরল।
15. Digestive Fluids: Various fluids secreted by the digestive system, including gastric juices and pancreatic fluid.
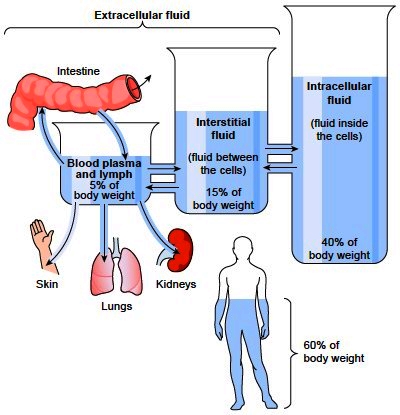
16. Interstitial Fluid: The fluid that fills the spaces between cells.
17. Intracellular Fluid: The fluid contained inside cells.
১৫. পরিপাক তরল: পাচনতন্ত্র দ্বারা নিঃসৃত বিভিন্ন তরল, যার মধ্যে রয়েছে গ্যাস্ট্রিক রস এবং অগ্ন্যাশয় তরল। ১৬. ইন্টারস্টিশিয়াল ফ্লুইড: কোষের মধ্যবর্তী স্থান পূরণ করে এমন তরল। ১৭. ইন্ট্রাসেলুলার ফ্লুইড: কোষের ভিতরে থাকা তরল।
These fluids play vital roles in maintaining homeostasis, protecting the body, and facilitating various physiological processes.
এই তরলগুলি হোমিওস্ট্যাসিস বজায় রাখতে, শরীরকে রক্ষা করতে এবং বিভিন্ন শারীরবৃত্তীয় প্রক্রিয়াগুলিকে সহজতর করতে গুরুত্বপূর্ণ ভূমিকা পালন করে।
Blood is Number 1 Body Fluid
Blood, a fluid connective tissue, is found circulating throughout the body via blood vessels. Its primary functions include transportation of oxygen and nutrients to cells, removal of waste products, regulation of body temperature and pH, and protection against infections.
রক্ত, একটি তরল সংযোজক টিস্যু, রক্তনালীর মাধ্যমে সারা শরীরে সঞ্চালিত হয়। এর প্রাথমিক কাজগুলির মধ্যে রয়েছে কোষে অক্সিজেন এবং পুষ্টি পরিবহন, বর্জ্য পদার্থ অপসারণ, শরীরের তাপমাত্রা এবং pH নিয়ন্ত্রণ এবং সংক্রমণের বিরুদ্ধে সুরক্ষা।
- Blood resides within the circulatory system, specifically within arteries, veins, and capillaries.
- It originates in the bone marrow, where blood cells are produced.
- Blood is constantly pumped by the heart through this network of vessels, delivering oxygen and nutrients to all parts of the body.
রক্ত সংবহনতন্ত্রের মধ্যে থাকে, বিশেষ করে ধমনী, শিরা এবং কৈশিকগুলির মধ্যে। এটি অস্থি মজ্জা থেকে উৎপন্ন হয়, যেখানে রক্তকণিকা তৈরি হয়। রক্তনালীগুলির এই নেটওয়ার্কের মাধ্যমে হৃৎপিণ্ড ক্রমাগত রক্ত পাম্প করে, শরীরের সমস্ত অংশে অক্সিজেন এবং পুষ্টি সরবরাহ করে।
Functions:
- Transportation: Blood carries oxygen from the lungs to the cells and transports carbon dioxide, a waste product, back to the lungs for exhalation. It also delivers nutrients absorbed from the digestive system and hormones from endocrine glands to their target cells.
- Regulation: Blood helps regulate body temperature by distributing heat and maintains water balance within cells through dissolved substances like sodium and proteins.
- Protection: Blood contains white blood cells, which are crucial for fighting infections and protecting against foreign microbes. Platelets in the blood help in blood clotting, preventing excessive blood loss from injuries.
পরিবহন: রক্ত ফুসফুস থেকে কোষে অক্সিজেন বহন করে এবং কার্বন ডাই অক্সাইড, একটি বর্জ্য পদার্থ, শ্বাস-প্রশ্বাসের জন্য ফুসফুসে ফিরিয়ে নিয়ে যায়। এটি পরিপাকতন্ত্র থেকে শোষিত পুষ্টি এবং অন্তঃস্রাবী গ্রন্থি থেকে হরমোনগুলি তাদের লক্ষ্য কোষে পৌঁছে দেয়। নিয়ন্ত্রণ: রক্ত তাপ বিতরণ করে শরীরের তাপমাত্রা নিয়ন্ত্রণ করতে সাহায্য করে এবং সোডিয়াম এবং প্রোটিনের মতো দ্রবীভূত পদার্থের মাধ্যমে কোষের মধ্যে জলের ভারসাম্য বজায় রাখে। সুরক্ষা: রক্তে শ্বেত রক্তকণিকা থাকে, যা সংক্রমণের বিরুদ্ধে লড়াই এবং বিদেশী জীবাণু থেকে রক্ষা করার জন্য অত্যন্ত গুরুত্বপূর্ণ। রক্তে প্লেটলেট রক্ত জমাট বাঁধতে সাহায্য করে, আঘাতের ফলে অতিরিক্ত রক্তক্ষরণ রোধ করে।
Lymph is a Body Fluid
Lymph is a clear fluid that circulates throughout the lymphatic system, which is a network of vessels, nodes, and organs that plays a crucial role in fluid balance, immune function, and fat absorption.
Lymph circulates through the body, collecting excess fluid, proteins, and waste products from tissues and returning them to the bloodstream.
It also plays a vital role in the immune system by filtering out harmful substances and transporting lymphocytes (white blood cells) to fight infections.
লিম্ফ হল একটি স্বচ্ছ তরল যা লিম্ফ্যাটিক সিস্টেম জুড়ে সঞ্চালিত হয়, যা রক্তনালী, নোড এবং অঙ্গগুলির একটি নেটওয়ার্ক যা তরল ভারসাম্য, রোগ প্রতিরোধ ক্ষমতা এবং চর্বি শোষণে গুরুত্বপূর্ণ ভূমিকা পালন করে। লিম্ফ শরীরের মধ্য দিয়ে সঞ্চালিত হয়, টিস্যু থেকে অতিরিক্ত তরল, প্রোটিন এবং বর্জ্য পদার্থ সংগ্রহ করে এবং রক্তপ্রবাহে ফিরিয়ে আনে। এটি ক্ষতিকারক পদার্থ ফিল্টার করে এবং সংক্রমণের বিরুদ্ধে লড়াই করার জন্য লিম্ফোসাইট (শ্বেত রক্তকণিকা) পরিবহন করে রোগ প্রতিরোধ ব্যবস্থায় গুরুত্বপূর্ণ ভূমিকা পালন করে।
Location:
- Lymphatic vessels are found throughout the body, similar to blood vessels, forming a network that collects fluid from tissues.
- Lymph nodes, small, bean-shaped structures, are located along these vessels, particularly in the neck, armpits, chest, abdomen, and groin.
- Lymphatic tissue is also present in other organs like the tonsils, spleen, and bone marrow.
রক্তনালীর মতোই সারা শরীরে লিম্ফ্যাটিক নালী পাওয়া যায়, যা টিস্যু থেকে তরল সংগ্রহ করে এমন একটি নেটওয়ার্ক তৈরি করে। লিম্ফ নোড, ছোট, শিমের আকৃতির কাঠামো, এই নালীগুলির পাশে অবস্থিত, বিশেষ করে ঘাড়, বগলে, বুকে, পেটে এবং কুঁচকিতে। লিম্ফ্যাটিক টিস্যু টনসিল, প্লীহা এবং অস্থি মজ্জার মতো অন্যান্য অঙ্গেও উপস্থিত থাকে।
Functions:
- Fluid Balance: The lymphatic system helps maintain fluid balance by collecting excess interstitial fluid (fluid between cells) and returning it to the bloodstream.
- Immune Function: Lymph nodes act as filters, trapping bacteria, viruses, and cancer cells, while lymphocytes within the nodes attack and destroy these harmful substances.
- Fat Absorption: The lymphatic system, specifically the lacteals (specialized lymphatic capillaries in the small intestine), absorbs fats and fat-soluble nutrients from the digestive system.
- Waste Removal: Lymphatic vessels transport waste products and cellular debris away from tissues and towards lymph nodes for disposal.
তরল ভারসাম্য: লিম্ফ্যাটিক সিস্টেম অতিরিক্ত ইন্টারস্টিশিয়াল তরল (কোষের মধ্যে তরল) সংগ্রহ করে এবং রক্তপ্রবাহে ফিরিয়ে এনে তরল ভারসাম্য বজায় রাখতে সাহায্য করে। রোগ প্রতিরোধ ক্ষমতা: লিম্ফ নোডগুলি ফিল্টার হিসাবে কাজ করে, ব্যাকটেরিয়া, ভাইরাস এবং ক্যান্সার কোষগুলিকে আটকে রাখে, যখন নোডের মধ্যে লিম্ফোসাইটগুলি এই ক্ষতিকারক পদার্থগুলিকে আক্রমণ করে এবং ধ্বংস করে। চর্বি শোষণ: লিম্ফ্যাটিক সিস্টেম, বিশেষ করে ল্যাকটিল (ছোট অন্ত্রের বিশেষায়িত লিম্ফ্যাটিক কৈশিক), পাচনতন্ত্র থেকে চর্বি এবং চর্বি-দ্রবণীয় পুষ্টি শোষণ করে। বর্জ্য অপসারণ: লিম্ফ্যাটিক জাহাজগুলি বর্জ্য পণ্য এবং কোষীয় ধ্বংসাবশেষ টিস্যু থেকে দূরে এবং নিষ্কাশনের জন্য লিম্ফ নোডের দিকে পরিবহন করে।
Cerebrospinal Fluid is a Cushion Body Fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, plasma-like liquid that surrounds the brain and spinal cord, acting as a protective cushion and supporting vital functions. It’s produced in the brain’s ventricles, specifically by the choroid plexus.
CSF circulates through the ventricles, the subarachnoid space, and is eventually reabsorbed into the bloodstream.
সেরিব্রোস্পাইনাল ফ্লুইড (CSF) হল একটি স্বচ্ছ, প্লাজমার মতো তরল যা মস্তিষ্ক এবং মেরুদণ্ডকে ঘিরে থাকে, একটি প্রতিরক্ষামূলক কুশন হিসেবে কাজ করে এবং গুরুত্বপূর্ণ কার্যকলাপকে সমর্থন করে। এটি মস্তিষ্কের ভেন্ট্রিকলে উৎপাদিত হয়, বিশেষ করে কোরয়েড প্লেক্সাস দ্বারা। CSF ভেন্ট্রিকলে, সাবঅ্যারাকনয়েড স্থানের মধ্য দিয়ে সঞ্চালিত হয় এবং অবশেষে রক্তপ্রবাহে পুনরায় শোষিত হয়।
Location:
- Ventricles: CSF is produced within the four ventricles of the brain.
- Subarachnoid Space: It circulates around the brain and spinal cord within the subarachnoid space, a region between the arachnoid and pia mater membranes.
- Central Canal: A small amount of CSF also flows into the central canal of the spinal cord.
ভেন্ট্রিকল: মস্তিষ্কের চারটি ভেন্ট্রিকলের মধ্যে CSF উৎপন্ন হয়।
সাবরাকনয়েড স্পেস: এটি মস্তিষ্ক এবং মেরুদণ্ডের চারপাশে ঘুরতে থাকে সাবরাকনয়েড স্পেসের মধ্যে, যা অ্যারাকনয়েড এবং পিয়া ম্যাটার মেমব্রেনের মধ্যবর্তী একটি অঞ্চল।
সেন্ট্রাল ক্যানেল: মেরুদণ্ডের কেন্দ্রীয় ক্যানেলেও অল্প পরিমাণে সিএসএফ প্রবাহিত হয়।
Functions:
- Cushioning and Protection: CSF acts as a shock absorber, protecting the brain and spinal cord from injury by reducing the impact of movements or blows.
- Buoyancy: It supports the weight of the brain, making it feel lighter and preventing it from crushing the skull’s base.
- Nutrient and Waste Removal: CSF transports nutrients to the brain tissue and removes waste products, maintaining a stable chemical environment.
- Homeostasis: CSF helps regulate the chemical environment of the central nervous system, maintaining stable brain pressure and temperature.
- Immune Function: CSF plays a role in the brain’s immune response by transporting immune cells and molecules.
- Signal Transduction: CSF facilitates the transport of neurotransmitters and other signaling molecules.
কুশনিং এবং সুরক্ষা: CSF একটি শক শোষক হিসেবে কাজ করে, নড়াচড়া বা আঘাতের প্রভাব কমিয়ে মস্তিষ্ক এবং মেরুদণ্ডকে আঘাত থেকে রক্ষা করে। উচ্ছ্বাস: এটি মস্তিষ্কের ওজনকে সমর্থন করে, এটিকে হালকা বোধ করে এবং মাথার খুলির গোড়া পিষে ফেলা থেকে বিরত রাখে। পুষ্টি এবং বর্জ্য অপসারণ: CSF মস্তিষ্কের টিস্যুতে পুষ্টি পরিবহন করে এবং বর্জ্য পদার্থ অপসারণ করে, একটি স্থিতিশীল রাসায়নিক পরিবেশ বজায় রাখে। হোমিওস্ট্যাসিস: CSF কেন্দ্রীয় স্নায়ুতন্ত্রের রাসায়নিক পরিবেশ নিয়ন্ত্রণ করতে সাহায্য করে, স্থিতিশীল মস্তিষ্কের চাপ এবং তাপমাত্রা বজায় রাখে। রোগ প্রতিরোধ ক্ষমতার কার্যকারিতা: CSF রোগ প্রতিরোধ কোষ এবং অণু পরিবহনের মাধ্যমে মস্তিষ্কের রোগ প্রতিরোধ ক্ষমতায় ভূমিকা পালন করে। সংকেত স্থানান্তর: CSF নিউরোট্রান্সমিটার এবং অন্যান্য সংকেত অণু পরিবহনকে সহজতর করে।
Digestive Body Fluids
Digestive fluids, like saliva, gastric juice, bile, and pancreatic juice, are crucial for breaking down food into smaller, absorbable nutrients. They are produced in various locations within the digestive system, including the salivary glands, stomach, liver, pancreas, and small intestine, each with specific roles in the digestive process.
লালা, পাকস্থলীর রস, পিত্ত এবং অগ্ন্যাশয়ের রসের মতো হজম তরল খাদ্যকে ছোট, শোষণযোগ্য পুষ্টিতে ভেঙে ফেলার জন্য অত্যন্ত গুরুত্বপূর্ণ। এগুলি পাচনতন্ত্রের বিভিন্ন স্থানে উৎপাদিত হয়, যার মধ্যে রয়েছে লালা গ্রন্থি, পাকস্থলী, লিভার, অগ্ন্যাশয় এবং ক্ষুদ্রান্ত্র, প্রতিটিরই হজম প্রক্রিয়ায় নির্দিষ্ট ভূমিকা রয়েছে।
Location and Functions:
- Salivary Glands:Located in the mouth, these glands secrete saliva, which contains the enzyme amylase that begins the digestion of carbohydrates. Saliva also moistens food for easier swallowing.
- Stomach:The stomach produces gastric juice, which contains hydrochloric acid and the enzymes pepsin and gastric lipase. Hydrochloric acid creates an acidic environment for pepsin to break down proteins and kills harmful microorganisms. Pepsin digests proteins, and gastric lipase digests fats, particularly butterfat.
- Liver:The liver produces bile, which is stored in the gallbladder and then released into the small intestine. Bile salts emulsify fats, breaking them down into smaller droplets to increase their surface area for digestion by lipase.
- Pancreas:The pancreas secretes pancreatic juice, which contains a variety of enzymes including amylase, trypsin, and lipase. These enzymes are crucial for digesting carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, respectively, in the small intestine.
- Small Intestine:The small intestine receives digestive fluids from the pancreas and bile from the liver, and it also secretes its own intestinal juices. These fluids, along with the enzymes from the pancreas, complete the digestion of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats into their simplest forms.
লালা গ্রন্থি: মুখের মধ্যে অবস্থিত, এই গ্রন্থিগুলি লালা নিঃসরণ করে, যার মধ্যে অ্যামাইলেজ নামক এনজাইম থাকে যা কার্বোহাইড্রেটের হজম শুরু করে। লালা খাবারকে সহজে গিলে ফেলার জন্য আর্দ্রতাও দেয়।
পাকস্থলী: পাকস্থলী গ্যাস্ট্রিক রস উৎপন্ন করে, যার মধ্যে হাইড্রোক্লোরিক অ্যাসিড এবং এনজাইম পেপসিন এবং গ্যাস্ট্রিক লিপেজ থাকে। হাইড্রোক্লোরিক অ্যাসিড পেপসিনের প্রোটিন ভেঙে ফেলার এবং ক্ষতিকারক অণুজীবকে মেরে ফেলার জন্য একটি অ্যাসিডিক পরিবেশ তৈরি করে। পেপসিন প্রোটিন হজম করে এবং গ্যাস্ট্রিক লিপেজ চর্বি, বিশেষ করে বাটারফ্যাট হজম করে।
লিভার: লিভার পিত্ত উৎপন্ন করে, যা পিত্তথলিতে জমা হয় এবং তারপর ক্ষুদ্রান্ত্রে নির্গত হয়। পিত্ত লবণ চর্বিগুলিকে ইমালসিফাই করে, লিপেজ দ্বারা হজমের জন্য তাদের পৃষ্ঠের ক্ষেত্রফল বৃদ্ধি করার জন্য ছোট ছোট ফোঁটায় ভেঙে দেয়।
অগ্ন্যাশয়: অগ্ন্যাশয় অগ্ন্যাশয় রস নিঃসরণ করে, যার মধ্যে অ্যামাইলেজ, ট্রিপসিন এবং লিপেজ সহ বিভিন্ন এনজাইম থাকে। এই এনজাইমগুলি ক্ষুদ্রান্ত্রে যথাক্রমে কার্বোহাইড্রেট, প্রোটিন এবং চর্বি হজম করার জন্য অত্যন্ত গুরুত্বপূর্ণ।
ক্ষুদ্রান্ত্র: ক্ষুদ্রান্ত্র অগ্ন্যাশয় থেকে হজম তরল এবং যকৃত থেকে পিত্ত গ্রহণ করে এবং এটি নিজস্ব অন্ত্রের রসও নিঃসরণ করে। এই তরলগুলি, অগ্ন্যাশয়ের এনজাইমগুলির সাথে, কার্বোহাইড্রেট, প্রোটিন এবং চর্বিগুলিকে তাদের সহজতম আকারে হজম করে।
Specific enzymes and their roles:
- Amylase: Breaks down carbohydrates (starches).
- Trypsin: Breaks down proteins.
- Lipase: Breaks down fats.
- Pepsin: Digests proteins, particularly in the stomach.
- Rennin: Curdles milk protein, aiding in digestion.
- Gastric Lipase: Digests fats, particularly in the stomach.
- Bile Salts: Emulsify fats, making them easier to digest.
অ্যামিলেজ: কার্বোহাইড্রেট (স্টার্চ) ভেঙে দেয়। ট্রিপসিন: প্রোটিন ভেঙে দেয়। লাইপেজ: চর্বি ভেঙে দেয়। পেপসিন: প্রোটিন হজম করে, বিশেষ করে পাকস্থলীতে। রেনিন: দুধের প্রোটিন দই করে, হজমে সহায়তা করে। গ্যাস্ট্রিক লিপেজ: চর্বি হজম করে, বিশেষ করে পাকস্থলীতে। পিত্ত লবণ: চর্বিকে ইমালসিফাই করে, হজম করা সহজ করে তোলে।
The digestive fluids and enzymes work together to break down food into smaller molecules that can be absorbed by the body, providing it with the necessary nutrients.
হজম তরল এবং এনজাইম একসাথে কাজ করে খাদ্যকে ছোট ছোট অণুতে ভেঙে দেয় যা শরীর দ্বারা শোষিত হতে পারে, যা প্রয়োজনীয় পুষ্টি সরবরাহ করে।
Saliva is a Digestive Body Fluid
Saliva, produced by salivary glands in the mouth, serves multiple vital functions including aiding in digestion, protecting oral health, and facilitating speech and swallowing. The major salivary glands are the parotid, submandibular, and sublingual glands.
Saliva’s functions include moistening food, initiating starch breakdown via amylase, preventing infections, maintaining pH balance, and protecting teeth.
মুখের লালা গ্রন্থি দ্বারা উৎপন্ন লালা একাধিক গুরুত্বপূর্ণ কাজ করে, যার মধ্যে রয়েছে হজমে সহায়তা করা, মুখের স্বাস্থ্য রক্ষা করা, কথা বলা এবং গিলতে সাহায্য করা। প্রধান লালা গ্রন্থিগুলি হল প্যারোটিড, সাবম্যান্ডিবুলার এবং সাবলিঙ্গুয়াল গ্রন্থি। লালার কাজগুলির মধ্যে রয়েছে খাবারকে আর্দ্র করা, অ্যামাইলেজের মাধ্যমে স্টার্চ ভাঙন শুরু করা, সংক্রমণ প্রতিরোধ করা, pH ভারসাম্য বজায় রাখা এবং দাঁত রক্ষা করা।
Location of Salivary Glands:
- Submandibular glands: Located below the jaw, on either side of the mouth.
- Sublingual glands: Located under the tongue.
- Minor salivary glands: Numerous small glands are scattered throughout the mouth, including the cheeks, lips, tongue, and palate.
সাবম্যান্ডিবুলার গ্রন্থি: চোয়ালের নীচে, মুখের উভয় পাশে অবস্থিত। সাবলিঙ্গুয়াল গ্রন্থি: জিহ্বার নীচে অবস্থিত। ক্ষুদ্র লালা গ্রন্থি: গাল, ঠোঁট, জিহ্বা এবং তালু সহ মুখ জুড়ে অসংখ্য ছোট গ্রন্থি ছড়িয়ে ছিটিয়ে থাকে।
Functions of Saliva:
- Digestion: Saliva moistens food, making it easier to chew and swallow. It also contains amylase, an enzyme that begins the chemical breakdown of starches.
- Oral Health: Saliva helps maintain a healthy oral environment by:
- Neutralizing acids: Buffering acids produced by bacteria, preventing tooth decay.
- Cleaning the mouth: Removing food debris, dead cells, and bacteria.
- Preventing infection: Containing antimicrobial substances like lysozyme and lactoferrin.
- Maintaining tooth integrity: Providing minerals for enamel remineralization.
- Speech and Swallowing: Saliva lubricates the mouth, facilitating smooth articulation of words and the passage of food down the throat.
- Taste: Saliva acts as a solvent, allowing food molecules to interact with taste buds.
- Protection: Saliva protects the oral mucosa from dryness, irritation, and potential damage.
হজম: লালা খাবারকে আর্দ্র করে, চিবানো এবং গিলতে সহজ করে তোলে। এতে অ্যামাইলেজও রয়েছে, একটি এনজাইম যা স্টার্চের রাসায়নিক ভাঙ্গন শুরু করে। মৌখিক স্বাস্থ্য: লালা একটি সুস্থ মৌখিক পরিবেশ বজায় রাখতে সাহায্য করে: অ্যাসিড নিরপেক্ষ করে: ব্যাকটেরিয়া দ্বারা উৎপাদিত অ্যাসিডগুলিকে বাফার করে, দাঁতের ক্ষয় রোধ করে। মুখ পরিষ্কার করা: খাদ্যের ধ্বংসাবশেষ, মৃত কোষ এবং ব্যাকটেরিয়া অপসারণ করে। সংক্রমণ প্রতিরোধ করা: লাইসোজাইম এবং ল্যাকটোফেরিনের মতো অ্যান্টিমাইক্রোবিয়াল পদার্থ ধারণ করে। দাঁতের অখণ্ডতা বজায় রাখা: এনামেল পুনর্খনিজকরণের জন্য খনিজ সরবরাহ করা। কথা বলা এবং গিলতে: লালা মুখকে লুব্রিকেট করে, শব্দের মসৃণ উচ্চারণ এবং গলা দিয়ে খাবারের প্রবাহকে সহজ করে। স্বাদ: লালা একটি দ্রাবক হিসাবে কাজ করে, খাদ্য অণুগুলিকে স্বাদ কুঁড়িগুলির সাথে যোগাযোগ করতে দেয়। সুরক্ষা: লালা মুখের শ্লেষ্মাকে শুষ্কতা, জ্বালা এবং সম্ভাব্য ক্ষতি থেকে রক্ষা করে।
In essence, saliva plays a crucial role in both digestive processes and maintaining the overall health of the oral cavity.
মূলত, লালা হজম প্রক্রিয়া এবং মৌখিক গহ্বরের সামগ্রিক স্বাস্থ্য বজায় রাখার ক্ষেত্রে গুরুত্বপূর্ণ ভূমিকা পালন করে।
Gastric Fluid is Digestive Body Fluid
Gastric Fluid is a kind of body fluid. Gastric fluid, also known as gastric juice, is a digestive fluid produced by glands in the stomach lining. It’s a mixture of hydrochloric acid, enzymes like pepsin, mucus, and other substances. Its primary function is to break down food, particularly proteins, and to help protect the body from harmful microorganisms.
গ্যাস্ট্রিক ফ্লুইড হল এক ধরণের দেহ তরল। গ্যাস্ট্রিক ফ্লুইড, যা গ্যাস্ট্রিক জুস নামেও পরিচিত, পাকস্থলীর আস্তরণের গ্রন্থি দ্বারা উৎপাদিত একটি পাচক তরল। এটি হাইড্রোক্লোরিক অ্যাসিড, পেপসিনের মতো এনজাইম, শ্লেষ্মা এবং অন্যান্য পদার্থের মিশ্রণ। এর প্রাথমিক কাজ হল খাদ্য, বিশেষ করে প্রোটিন ভেঙে ফেলা এবং ক্ষতিকারক অণুজীব থেকে শরীরকে রক্ষা করা।
Location:
- Gastric fluid is produced by specialized cells within the gastric glands located in the stomach lining.
- These glands are found throughout the stomach, with different types of glands (cardiac, fundic, and pyloric) producing different components of the gastric fluid.
- The stomach itself is located in the upper left quadrant of the abdomen, below the diaphragm.
পাকস্থলীর আস্তরণে অবস্থিত গ্যাস্ট্রিক গ্রন্থির মধ্যে বিশেষ কোষ দ্বারা পাকস্থলীর তরল উৎপন্ন হয়। এই গ্রন্থিগুলি পুরো পাকস্থলী জুড়ে পাওয়া যায়, বিভিন্ন ধরণের গ্রন্থি (কার্ডিয়াক, ফান্ডিক এবং পাইলোরিক) পাকস্থলীর তরলের বিভিন্ন উপাদান উৎপন্ন করে। পাকস্থলী নিজেই পেটের উপরের বাম চতুর্ভুজে, ডায়াফ্রামের নীচে অবস্থিত।
Functions:
- Digestion:The hydrochloric acid in gastric fluid denatures food proteins, making them more susceptible to digestion by enzymes.
- Enzymatic Action:Pepsin, a key enzyme in gastric juice, breaks down proteins into smaller peptides.
- Antimicrobial Action:The acidic environment created by hydrochloric acid helps kill or inhibit the growth of many harmful microorganisms ingested with food.
- Preparation for Small Intestine:Gastric fluid helps convert ingested food into a semi-liquid mixture called chyme, preparing it for further digestion and absorption in the small intestine.
- Nutrient Absorption:Gastric fluid also plays a role in the absorption of vitamin B12, with the help of intrinsic factor.
হজম: পাকস্থলীর তরলে থাকা হাইড্রোক্লোরিক অ্যাসিড খাদ্য প্রোটিনকে বিকৃত করে, এনজাইম দ্বারা হজমের জন্য তাদের আরও সংবেদনশীল করে তোলে। এনজাইম্যাটিক ক্রিয়া: গ্যাস্ট্রিক রসের একটি মূল এনজাইম পেপসিন প্রোটিনকে ছোট ছোট পেপটাইডে ভেঙে দেয়। অ্যান্টিমাইক্রোবিয়াল ক্রিয়া: হাইড্রোক্লোরিক অ্যাসিড দ্বারা সৃষ্ট অ্যাসিডিক পরিবেশ খাদ্যের সাথে গ্রহণ করা অনেক ক্ষতিকারক অণুজীবকে হত্যা বা বৃদ্ধিতে বাধা দিতে সাহায্য করে। ক্ষুদ্রান্ত্রের জন্য প্রস্তুতি: পাকস্থলীর তরল খাদ্যকে কাইম নামক একটি আধা-তরল মিশ্রণে রূপান্তর করতে সাহায্য করে, যা ক্ষুদ্রান্ত্রে আরও হজম এবং শোষণের জন্য প্রস্তুত করে। পুষ্টি শোষণ: অভ্যন্তরীণ ফ্যাক্টরের সাহায্যে গ্যাস্ট্রিক তরল ভিটামিন বি১২ শোষণেও ভূমিকা পালন করে।
Pancreatic Fluid is a Digestive Fluid
The pancreas, located behind the stomach in the abdomen, produces pancreatic fluids (also known as pancreatic juice) which are essential for digestion and blood sugar regulation. These fluids contain enzymes that break down carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, and hormones like insulin and glucagon that manage blood sugar levels.
পেটের পেছনে পেটের গহ্বরে অবস্থিত অগ্ন্যাশয় অগ্ন্যাশয় তরল (যা অগ্ন্যাশয় রস নামেও পরিচিত) উৎপন্ন করে যা হজম এবং রক্তে শর্করার মাত্রা নিয়ন্ত্রণের জন্য অপরিহার্য। এই তরলগুলিতে এমন এনজাইম থাকে যা কার্বোহাইড্রেট, প্রোটিন এবং চর্বি ভেঙে দেয় এবং ইনসুলিন এবং গ্লুকাগনের মতো হরমোন থাকে যা রক্তে শর্করার মাত্রা নিয়ন্ত্রণ করে।
The pancreatic juice travels through ducts and empties into the small intestine, specifically the duodenum, where it aids in the digestive process.
অগ্ন্যাশয়ের রস নালীর মধ্য দিয়ে ভ্রমণ করে এবং ক্ষুদ্রান্ত্রে, বিশেষ করে ডুওডেনামে, যেখানে এটি হজম প্রক্রিয়ায় সহায়তা করে।
Location:
- The pancreas is situated in the upper abdomen, tucked behind the stomach and in front of the spine.
- It extends from the duodenum (the first part of the small intestine) to the spleen.
অগ্ন্যাশয় পেটের উপরের অংশে অবস্থিত, পেটের পিছনে এবং মেরুদণ্ডের সামনে অবস্থিত। এটি ডুওডেনাম (ক্ষুদ্র অন্ত্রের প্রথম অংশ) থেকে প্লীহা পর্যন্ত বিস্তৃত।
Functions:
- Exocrine Function:The pancreas produces and releases digestive enzymes (pancreatic juice) into the small intestine.
- Amylase: Breaks down carbohydrates.
- Lipase: Breaks down fats.
- Proteases (like trypsin and chymotrypsin): Break down proteins.
- Endocrine Function:The pancreas also produces hormones like insulin and glucagon, which regulate blood sugar levels.
- Insulin: Lowers blood sugar by helping cells absorb glucose.
- Glucagon: Raises blood sugar by signaling the liver to release stored glucose.
- Neutralization of Stomach Acid:Pancreatic juice contains bicarbonate, which helps neutralize the acidic chyme (partially digested food) entering the small intestine from the stomach.
এক্সোক্রাইন ফাংশন: অগ্ন্যাশয় ক্ষুদ্রান্ত্রে পাচক এনজাইম (অগ্ন্যাশয়ের রস) তৈরি করে এবং ছেড়ে দেয়।
অ্যামিলেজ: কার্বোহাইড্রেট ভেঙে দেয়।
লিপেজ: চর্বি ভেঙে দেয়।
প্রোটিজ (যেমন ট্রিপসিন এবং কাইমোট্রিপসিন): প্রোটিন ভেঙে দেয়।
এন্ডোক্রাইন ফাংশন: অগ্ন্যাশয় ইনসুলিন এবং গ্লুকাগনের মতো হরমোনও তৈরি করে, যা রক্তে শর্করার মাত্রা নিয়ন্ত্রণ করে।
ইনসুলিন: কোষগুলিকে গ্লুকোজ শোষণে সাহায্য করে রক্তে শর্করার পরিমাণ কমায়।
গ্লুকাগন: লিভারকে সঞ্চিত গ্লুকোজ ছেড়ে দেওয়ার জন্য সংকেত দিয়ে রক্তে শর্করার পরিমাণ বাড়ায়।
পেটের অ্যাসিডের নিরপেক্ষকরণ: অগ্ন্যাশয়ের রসে বাইকার্বোনেট থাকে, যা পাকস্থলী থেকে ক্ষুদ্রান্ত্রে প্রবেশকারী অ্যাসিডিক কাইম (আংশিকভাবে হজম হওয়া খাবার) নিরপেক্ষ করতে সাহায্য করে।
Pancreatic Juice Flow:
- Pancreatic juice is produced in the acinar tissues of the pancreas and secreted into a network of ducts.
- These ducts converge into the main pancreatic duct, which joins the common bile duct from the liver.
- The combined duct, called the ampulla of Vater, opens into the duodenum.
- A muscular valve (sphincter of Oddi) controls the release of pancreatic juice and bile into the duodenum.
অগ্ন্যাশয়ের অ্যাসিনার টিস্যুতে অগ্ন্যাশয়ের রস উৎপন্ন হয় এবং নালীগুলির একটি নেটওয়ার্কে নিঃসৃত হয়। এই নালীগুলি মূল অগ্ন্যাশয়ের নালীতে একত্রিত হয়, যা লিভার থেকে সাধারণ পিত্ত নালীতে যোগ দেয়। অ্যাম্পুলা অফ ভ্যাটার নামে পরিচিত সম্মিলিত নালীটি ডুওডেনামে খোলে। একটি পেশীবহুল ভালভ (ওডির স্ফিঙ্কটার) ডুওডেনামে অগ্ন্যাশয়ের রস এবং পিত্তের নিঃসরণ নিয়ন্ত্রণ করে।
Intestinal Fluids is a Digestive Body Fluid
Intestinal fluids, including intestinal juice and mucus, are secreted throughout the small and large intestines. These fluids aid in digestion by neutralizing stomach acid, lubricating the intestinal lining, and breaking down food with enzymes.
They also play a crucial role in absorbing nutrients and electrolytes, maintaining proper fluid balance within the digestive system.
অন্ত্রের রস এবং শ্লেষ্মা সহ অন্ত্রের তরলগুলি ছোট এবং বড় অন্ত্র জুড়ে নিঃসৃত হয়। এই তরলগুলি পাকস্থলীর অ্যাসিড নিরপেক্ষ করে, অন্ত্রের আস্তরণকে তৈলাক্ত করে এবং এনজাইম দিয়ে খাদ্য ভেঙে হজমে সহায়তা করে। এগুলি পুষ্টি এবং ইলেক্ট্রোলাইট শোষণে, পাচনতন্ত্রের মধ্যে সঠিক তরল ভারসাম্য বজায় রাখতে গুরুত্বপূর্ণ ভূমিকা পালন করে।
Location of Intestinal Fluids:
- Small Intestine:Intestinal juice is secreted along the entire length of the small intestine, with the duodenum receiving secretions from the pancreas and liver (bile) in addition to its own secretions.
- Large Intestine:The large intestine also secretes mucus, primarily from goblet cells, to lubricate and protect the lining.
ক্ষুদ্রান্ত্র: ক্ষুদ্রান্ত্রের পুরো দৈর্ঘ্য জুড়ে অন্ত্রের রস নিঃসৃত হয়, ডুওডেনাম তার নিজস্ব নিঃসরণ ছাড়াও অগ্ন্যাশয় এবং যকৃত (পিত্ত) থেকে নিঃসৃত পদার্থ গ্রহণ করে। বৃহৎ অন্ত্র: বৃহৎ অন্ত্র আস্তরণকে তৈলাক্তকরণ এবং সুরক্ষার জন্য প্রাথমিকভাবে গবলেট কোষ থেকে শ্লেষ্মাও নিঃসৃত করে।
Functions of Intestinal Fluids:
- Neutralization:Intestinal juice, rich in bicarbonate, neutralizes the acidic chyme (partially digested food) coming from the stomach.
- Lubrication:Mucus secreted by the intestines lubricates the intestinal walls, preventing damage from food and digestive enzymes.
- Digestion:Intestinal juice contains various enzymes that break down remaining carbohydrates, proteins, and fats.
- Absorption:The small intestine absorbs the majority of water and nutrients from digested food, facilitated by the fluid environment.
- Fluid Balance:Intestinal fluids help maintain a proper fluid balance in the digestive tract. Absorption of water and electrolytes is crucial, and imbalances can lead to conditions like diarrhea or constipation.
- Hormone Release:Intestinal secretions also include hormones that regulate digestion and appetite.
- Waste Elimination:The large intestine absorbs water from the remaining waste material, forming stool, and facilitates its movement towards the rectum for elimination.
নিরপেক্ষকরণ: বাইকার্বোনেট সমৃদ্ধ অন্ত্রের রস পাকস্থলী থেকে আসা অ্যাসিডিক কাইম (আংশিকভাবে হজম হওয়া খাবার) কে নিরপেক্ষ করে। তৈলাক্তকরণ: অন্ত্র দ্বারা নিঃসৃত শ্লেষ্মা অন্ত্রের দেয়ালকে লুব্রিকেট করে, খাদ্য এবং হজমকারী এনজাইমগুলির ক্ষতি রোধ করে। হজম: অন্ত্রের রসে বিভিন্ন এনজাইম থাকে যা অবশিষ্ট কার্বোহাইড্রেট, প্রোটিন এবং চর্বি ভেঙে দেয়। শোষণ: ক্ষুদ্রান্ত্র তরল পরিবেশ দ্বারা সহজতর হজমকৃত খাবার থেকে বেশিরভাগ জল এবং পুষ্টি শোষণ করে। তরল ভারসাম্য: অন্ত্রের তরল পরিপাকতন্ত্রে সঠিক তরল ভারসাম্য বজায় রাখতে সাহায্য করে। জল এবং ইলেক্ট্রোলাইট শোষণ অত্যন্ত গুরুত্বপূর্ণ, এবং ভারসাম্যহীনতা ডায়রিয়া বা কোষ্ঠকাঠিন্যের মতো অবস্থার কারণ হতে পারে। হরমোন নিঃসরণ: অন্ত্রের নিঃসরণে এমন হরমোনও অন্তর্ভুক্ত থাকে যা হজম এবং ক্ষুধা নিয়ন্ত্রণ করে। বর্জ্য নির্মূল: বৃহৎ অন্ত্র অবশিষ্ট বর্জ্য পদার্থ থেকে জল শোষণ করে, মল তৈরি করে এবং নির্মূলের জন্য মলদ্বারের দিকে এর চলাচলকে সহজতর করে।
Mucus is a Moisturizing Body Fluid
Mucus is a slippery, viscous secretion that lines the moist surfaces of the body, including the respiratory, digestive, and reproductive tracts. It acts as a protective barrier, a lubricant, and a filtration system, trapping pathogens and irritants while allowing essential substances to pass through.
শ্লেষ্মা হল একটি পিচ্ছিল, সান্দ্র নিঃসরণ যা শ্বাসযন্ত্র, পরিপাকতন্ত্র এবং প্রজননতন্ত্র সহ শরীরের আর্দ্র পৃষ্ঠতলকে আবদ্ধ করে। এটি একটি প্রতিরক্ষামূলক বাধা, একটি লুব্রিকেন্ট এবং একটি পরিস্রাবণ ব্যবস্থা হিসেবে কাজ করে, রোগজীবাণু এবং জ্বালাপোড়াকে আটকে রাখে এবং প্রয়োজনীয় পদার্থগুলিকে এর মধ্য দিয়ে যেতে দেয়।
Location of Mucus:
- Respiratory Tract: Mucus lines the nasal passages, sinuses, trachea, and lungs, playing a vital role in trapping inhaled particles and pathogens.
- Digestive Tract: Mucus coats the esophagus, stomach, and intestines, protecting these organs from digestive acids, enzymes, and mechanical damage.
- Reproductive Tract: Mucus lines the vagina, cervix, and uterus, protecting these areas from infection and facilitating sperm transport.
- Other Areas: Mucus is also found in the eyes, ears, and urinary tract, serving similar protective and lubricating functions.
শ্বাস নালী: নাকের পথ, সাইনাস, শ্বাসনালী এবং ফুসফুসে শ্লেষ্মা রেখা তৈরি করে, যা শ্বাস-প্রশ্বাসের মাধ্যমে নিঃশ্বাসের মাধ্যমে গ্রহণ করা কণা এবং রোগজীবাণু আটকে রাখার ক্ষেত্রে গুরুত্বপূর্ণ ভূমিকা পালন করে। পাচন নালী: খাদ্যনালী, পাকস্থলী এবং অন্ত্রকে শ্লেষ্মা আবরণ করে, এই অঙ্গগুলিকে পাচক অ্যাসিড, এনজাইম এবং যান্ত্রিক ক্ষতি থেকে রক্ষা করে। প্রজনন নালী: শ্লেষ্মা যোনি, জরায়ু এবং জরায়ুকে রেখা তৈরি করে, এই অঞ্চলগুলিকে সংক্রমণ থেকে রক্ষা করে এবং শুক্রাণু পরিবহনকে সহজতর করে। অন্যান্য অঞ্চল: চোখ, কান এবং মূত্রনালিতেও শ্লেষ্মা পাওয়া যায়, যা একই রকম প্রতিরক্ষামূলক এবং তৈলাক্তকরণ কার্য সম্পাদন করে
Functions of Mucus:
- Protection: Mucus acts as a physical barrier, trapping pathogens like bacteria and viruses, as well as irritants like dust and allergens, preventing them from reaching and damaging underlying tissues.
- Lubrication: Mucus keeps surfaces moist and prevents tissues from drying out, which is particularly important in areas like the lungs and digestive tract.
- Filtration: Mucus in the respiratory tract traps inhaled particles, which are then removed by cilia (tiny hair-like structures) or through coughing and sneezing.
- Immunity: Mucus contains immune cells and antibodies that help fight off infections and maintain a healthy mucosal environment.
- Transport: Mucus facilitates the movement of substances, such as food through the digestive tract and sperm through the reproductive tract.
- Wound Healing: Mucus plays a role in the repair and regeneration of damaged tissues
সুরক্ষা: শ্লেষ্মা একটি শারীরিক বাধা হিসেবে কাজ করে, ব্যাকটেরিয়া এবং ভাইরাসের মতো রোগজীবাণু, সেইসাথে ধুলো এবং অ্যালার্জেনের মতো জ্বালাময় পদার্থকে আটকে রাখে, যা তাদের অন্তর্নিহিত টিস্যুতে পৌঁছাতে এবং ক্ষতি করতে বাধা দেয়।
তৈলাক্তকরণ: শ্লেষ্মা পৃষ্ঠতলকে আর্দ্র রাখে এবং টিস্যুগুলিকে শুকিয়ে যাওয়া থেকে রক্ষা করে, যা ফুসফুস এবং পরিপাকতন্ত্রের মতো অঞ্চলে বিশেষভাবে গুরুত্বপূর্ণ।
পরিস্রাবণ: শ্বাসনালীর শ্লেষ্মা শ্বাস-প্রশ্বাসের মাধ্যমে নেওয়া কণাগুলিকে আটকে রাখে, যা পরে সিলিয়া (ছোট চুলের মতো কাঠামো) দ্বারা বা কাশি এবং হাঁচির মাধ্যমে অপসারণ করা হয়।
রোগ প্রতিরোধ ক্ষমতা: শ্লেষ্মায় রোগ প্রতিরোধক কোষ এবং অ্যান্টিবডি থাকে যা সংক্রমণের বিরুদ্ধে লড়াই করতে এবং একটি সুস্থ শ্লেষ্মা পরিবেশ বজায় রাখতে সহায়তা করে।
পরিবহন: শ্লেষ্মা পদার্থের চলাচলকে সহজ করে তোলে, যেমন খাদ্য পরিপাকতন্ত্রের মাধ্যমে এবং শুক্রাণু প্রজননতন্ত্রের মাধ্যমে।
ক্ষত নিরাময়: ক্ষতিগ্রস্ত টিস্যুগুলির মেরামত এবং পুনর্জন্মে শ্লেষ্মা ভূমিকা পালন করে।
Tears is a Eye Lubricating Body Fluid
Tears are produced by the lacrimal glands, located above the eyes, and serve multiple functions including keeping the eyes lubricated, removing debris, and aiding in vision and emotional expression. They also contain antibodies that help fight infection and protect the eyes from damage.
চোখের উপরে অবস্থিত ল্যাক্রিমাল গ্রন্থি দ্বারা অশ্রু উৎপন্ন হয় এবং চোখকে তৈলাক্ত রাখা, ময়লা অপসারণ করা এবং দৃষ্টি ও আবেগ প্রকাশে সহায়তা করা সহ একাধিক কাজ করে। এগুলিতে অ্যান্টিবডিও রয়েছে যা সংক্রমণের বিরুদ্ধে লড়াই করতে এবং চোখকে ক্ষতি থেকে রক্ষা করতে সহায়তা করে।
Location:
- Lacrimal Glands: These are the primary tear-producing glands, situated above the outer corner of each eye, within the bony orbit.
- Tear Ducts: These are small channels in the inner corners of the eyelids that drain tears away from the eyes and into the nasal cavity.
- Tear Film: The tears form a thin, three-layered film (mucus, aqueous, and lipid layers) that coats the surface of the eye.
চোখের উপরে অবস্থিত ল্যাক্রিমাল গ্রন্থি দ্বারা অশ্রু উৎপন্ন হয় এবং চোখকে তৈলাক্ত রাখা, ময়লা অপসারণ করা এবং দৃষ্টি ও আবেগ প্রকাশে সহায়তা করা সহ একাধিক কাজ করে। এগুলিতে অ্যান্টিবডিও রয়েছে যা সংক্রমণের বিরুদ্ধে লড়াই করতে এবং চোখকে ক্ষতি থেকে রক্ষা করতে সহায়তা করে।
Functions:
- Lubrication and Moisture: Tears keep the eye surface moist, preventing dryness and discomfort.
- Removal of Debris: They flush out dust, dirt, and other irritants that can enter the eyes.
- Vision: Tears help maintain a smooth, clear surface on the cornea, essential for proper light refraction and clear vision.
- Immunity: They contain antibodies and enzymes that help fight off bacteria and other pathogens, protecting against infection.
- Emotional Expression: While the exact mechanism is still being studied, emotional tears may play a role in stress reduction and social bonding.
- Nutrient and Oxygen Supply: Tears deliver essential nutrients and oxygen to the cornea, which lacks its own blood supply.
তৈলাক্তকরণ এবং আর্দ্রতা: অশ্রু চোখের পৃষ্ঠকে আর্দ্র রাখে, শুষ্কতা এবং অস্বস্তি প্রতিরোধ করে। ধ্বংসাবশেষ অপসারণ: এগুলি ধুলো, ময়লা এবং অন্যান্য জ্বালাপোড়া যা চোখে প্রবেশ করতে পারে তা বের করে দেয়। দৃষ্টি: অশ্রু কর্নিয়ার উপর একটি মসৃণ, স্বচ্ছ পৃষ্ঠ বজায় রাখতে সাহায্য করে, যা সঠিক আলোর প্রতিসরণ এবং স্পষ্ট দৃষ্টিশক্তির জন্য অপরিহার্য। রোগ প্রতিরোধ ক্ষমতা: এগুলিতে অ্যান্টিবডি এবং এনজাইম থাকে যা ব্যাকটেরিয়া এবং অন্যান্য রোগজীবাণুগুলির বিরুদ্ধে লড়াই করতে সাহায্য করে, সংক্রমণ থেকে রক্ষা করে। আবেগের প্রকাশ: যদিও সঠিক প্রক্রিয়াটি এখনও অধ্যয়ন করা হচ্ছে, মানসিক অশ্রু চাপ হ্রাস এবং সামাজিক বন্ধনে ভূমিকা পালন করতে পারে। পুষ্টি এবং অক্সিজেন সরবরাহ: অশ্রু কর্নিয়ায় প্রয়োজনীয় পুষ্টি এবং অক্সিজেন সরবরাহ করে, যার নিজস্ব রক্ত সরবরাহের অভাব রয়েছে।
Sweat is a Temperature Regulatory Body Fluid
Sweat is produced by sweat glands located in the dermis (deeper layer) of the skin. Eccrine glands, found all over the body, are the primary regulators of body temperature through sweat evaporation. Apocrine glands, primarily in armpits and groin, are activated by emotions and hormonal changes.
Sweat’s main function is to cool the body down through evaporation, but it also plays a role in skin lubrication and possibly antimicrobial defense.
ত্বকের ডার্মিস (গভীর স্তর) এ অবস্থিত ঘাম গ্রন্থি দ্বারা ঘাম উৎপন্ন হয়। সারা শরীরে পাওয়া একক্রাইন গ্রন্থিগুলি ঘামের বাষ্পীভবনের মাধ্যমে শরীরের তাপমাত্রার প্রাথমিক নিয়ন্ত্রক। অ্যাপোক্রাইন গ্রন্থিগুলি, মূলত বগল এবং কুঁচকিতে, আবেগ এবং হরমোনের পরিবর্তনের দ্বারা সক্রিয় হয়।
ঘামের প্রধান কাজ হল বাষ্পীভবনের মাধ্যমে শরীরকে ঠান্ডা করা, তবে এটি ত্বকের তৈলাক্তকরণ এবং সম্ভবত অ্যান্টিমাইক্রোবিয়াল প্রতিরক্ষাতেও ভূমিকা পালন করে।
Location of Sweat Glands:
- Eccrine glands: These are the most numerous and are found throughout the body, with the highest concentrations on the palms, soles, forehead, and armpits.
- Apocrine glands: These glands are located in the armpits (axillae), groin, and around the nipples.
একক্রাইন গ্রন্থি: এগুলি সর্বাধিক অসংখ্য এবং সারা শরীরে পাওয়া যায়, যার ঘনত্ব সর্বাধিক, হাতের তালু, তলা, কপাল এবং বগলে। অ্যাপোক্রাইন গ্রন্থি: এই গ্রন্থিগুলি বগলে (অক্ষি), কুঁচকিতে এবং স্তনবৃন্তের চারপাশে অবস্থিত।
Functions of Sweat:
- Thermoregulation: The primary function of sweat, particularly from eccrine glands, is to regulate body temperature. When the body heats up, sweat glands release sweat, which evaporates from the skin’s surface, carrying away heat and cooling the body down.
- Skin Lubrication: Sweat, especially from apocrine glands, contributes to skin lubrication, particularly in areas with hair follicles.
- Waste Removal: Sweat also helps to eliminate some waste products from the body, such as urea.
- Antimicrobial Defense: Sweat, specifically a protein called dermcidin, can help to kill some bacteria and fungi on the skin.
তাপ নিয়ন্ত্রণ: ঘামের প্রাথমিক কাজ, বিশেষ করে একক্রাইন গ্রন্থি থেকে, শরীরের তাপমাত্রা নিয়ন্ত্রণ করা। যখন শরীর গরম হয়, তখন ঘাম গ্রন্থিগুলি ঘাম নির্গত করে, যা ত্বকের পৃষ্ঠ থেকে বাষ্পীভূত হয়, তাপ বহন করে এবং শরীরকে ঠান্ডা করে। ত্বকের তৈলাক্তকরণ: ঘাম, বিশেষ করে অ্যাপোক্রাইন গ্রন্থি থেকে, ত্বকের তৈলাক্তকরণে অবদান রাখে, বিশেষ করে লোমকূপযুক্ত অঞ্চলে। বর্জ্য অপসারণ: ঘাম শরীর থেকে কিছু বর্জ্য পদার্থ, যেমন ইউরিয়া অপসারণ করতেও সাহায্য করে। অ্যান্টিমাইক্রোবিয়াল প্রতিরক্ষা: ঘাম, বিশেষ করে ডার্মসিডিন নামক একটি প্রোটিন, ত্বকের কিছু ব্যাকটেরিয়া এবং ছত্রাককে মেরে ফেলতে সাহায্য করতে পারে।
In summary, sweat glands are located throughout the skin, with eccrine glands being the main temperature regulators and apocrine glands playing a role in lubrication and body odor. The primary function of sweat is thermoregulation, but it also contributes to skin lubrication and waste removal.
সংক্ষেপে, ঘাম গ্রন্থিগুলি ত্বক জুড়ে অবস্থিত, একক্রাইন গ্রন্থিগুলি প্রধান তাপমাত্রা নিয়ন্ত্রক এবং অ্যাপোক্রাইন গ্রন্থিগুলি তৈলাক্তকরণ এবং শরীরের গন্ধে ভূমিকা পালন করে। ঘামের প্রাথমিক কাজ হল তাপ নিয়ন্ত্রণ, তবে এটি ত্বকের তৈলাক্তকরণ এবং বর্জ্য অপসারণেও অবদান রাখে।
Urine is a Water Balance Body Fluid
Urine, a liquid waste product, is produced in the kidneys and stored in the bladder before being expelled from the body through the urethra. The kidneys filter waste and excess fluid from the blood, forming urine.
This urine then travels through the ureters to the bladder, where it’s stored until urination. The urethra then carries the urine out of the body.
প্রস্রাব, একটি তরল বর্জ্য পদার্থ, কিডনিতে উৎপাদিত হয় এবং মূত্রনালী দিয়ে শরীর থেকে বের করে দেওয়ার আগে মূত্রাশয়ে জমা হয়। কিডনি রক্ত থেকে বর্জ্য এবং অতিরিক্ত তরল ফিল্টার করে প্রস্রাব তৈরি করে।
Here’s a more detailed breakdown:
Location:
- Kidneys: Two bean-shaped organs located in the back of the abdominal cavity, on either side of the spine.
- Ureters: Two narrow tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder.
- Bladder: A muscular sac in the pelvis that stores urine.
- Urethra: A tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body.
কিডনি: পেটের গহ্বরের পিছনে, মেরুদণ্ডের উভয় পাশে অবস্থিত দুটি শিমের আকৃতির অঙ্গ। মূত্রনালী: দুটি সরু নল যা কিডনি থেকে মূত্রাশয়ে প্রস্রাব বহন করে। মূত্রাশয়: পেলভিসে অবস্থিত একটি পেশীবহুল থলি যা প্রস্রাব সংরক্ষণ করে। মূত্রনালী: একটি নল যা মূত্রাশয় থেকে শরীরের বাইরের দিকে প্রস্রাব বহন করে।
Functions:
- Waste Removal: The urinary system, including the kidneys, filters waste products (like urea) and excess water from the blood, forming urine.
- Fluid Balance: The kidneys regulate the body’s fluid levels by adjusting how much water is excreted in the urine.
- Electrolyte Balance: The kidneys help maintain the balance of electrolytes (like sodium and potassium) in the blood.
- Blood Pressure Regulation: The kidneys play a role in regulating blood pressure by influencing fluid and electrolyte balance.
- Blood pH Regulation: The kidneys help regulate the acidity of the blood by controlling the excretion of acids and bases.
- Hormone Production: The kidneys produce hormones like erythropoietin, which stimulates red blood cell production.
বর্জ্য অপসারণ: কিডনি সহ মূত্রতন্ত্র রক্ত থেকে বর্জ্য পদার্থ (যেমন ইউরিয়া) এবং অতিরিক্ত জল ফিল্টার করে প্রস্রাব তৈরি করে। তরল ভারসাম্য: প্রস্রাবে কত জল নির্গত হয় তা সামঞ্জস্য করে কিডনি শরীরের তরলের মাত্রা নিয়ন্ত্রণ করে। ইলেক্ট্রোলাইট ভারসাম্য: কিডনি রক্তে ইলেক্ট্রোলাইটের (যেমন সোডিয়াম এবং পটাসিয়াম) ভারসাম্য বজায় রাখতে সাহায্য করে। রক্তচাপ নিয়ন্ত্রণ: তরল এবং ইলেক্ট্রোলাইট ভারসাম্যকে প্রভাবিত করে কিডনি রক্তচাপ নিয়ন্ত্রণে ভূমিকা পালন করে। রক্তের pH নিয়ন্ত্রণ: অ্যাসিড এবং ক্ষার নির্গমন নিয়ন্ত্রণ করে কিডনি রক্তের অম্লতা নিয়ন্ত্রণে সহায়তা করে। হরমোন উৎপাদন: কিডনি এরিথ্রোপয়েটিন এর মতো হরমোন তৈরি করে, যা লোহিত রক্তকণিকা উৎপাদনকে উদ্দীপিত করে।
Semen is a Reproductive Body Fluid
Semen is a fluid produced by the male reproductive system that carries sperm and is released during ejaculation. It originates from the testes, where sperm are produced, and is mixed with fluids from the seminal vesicles, prostate gland, and bulbourethral glands before ejaculation.
The primary function of semen is to transport sperm to the female reproductive tract and facilitate fertilization.
বীর্য হল পুরুষ প্রজনন ব্যবস্থা দ্বারা উৎপাদিত একটি তরল যা শুক্রাণু বহন করে এবং বীর্যপাতের সময় নির্গত হয়। এটি অণ্ডকোষ থেকে উৎপন্ন হয়, যেখানে শুক্রাণু উৎপন্ন হয় এবং বীর্যপাতের আগে সেমিনাল ভেসিকেল, প্রোস্টেট গ্রন্থি এবং বাল্বোরেথ্রাল গ্রন্থি থেকে নির্গত তরলের সাথে মিশ্রিত হয়। বীর্যের প্রাথমিক কাজ হল শুক্রাণুকে নারীর প্রজনন নালীতে পরিবহন করা এবং নিষেককে সহজতর করা।
Location:
- Testes: The testes (or testicles) are where sperm are produced.
- Epididymis: Immature sperm are stored and mature in the epididymis, a coiled structure located on the back of each testicle.
- Seminal Vesicles: Located behind the bladder, these glands secrete a fluid rich in fructose and other substances that nourish the sperm.
- Prostate Gland: This gland, located below the bladder, adds additional fluid to the semen.
- Bulbourethral Glands: Located near the base of the penis, these glands also contribute to the seminal fluid.
- Urethra: The urethra, which carries both urine and semen, is the final pathway for ejaculation.
অণ্ডকোষ: অণ্ডকোষ (বা অণ্ডকোষ) হল সেই স্থান যেখানে শুক্রাণু উৎপন্ন হয়।
এপিডিডাইমিস: অপরিণত শুক্রাণু এপিডিডাইমিসে সঞ্চিত এবং পরিপক্ক হয়, প্রতিটি অণ্ডকোষের পিছনে অবস্থিত একটি কুণ্ডলীকৃত কাঠামো।
সেমিনাল ভেসিকেল: মূত্রাশয়ের পিছনে অবস্থিত, এই গ্রন্থিগুলি ফ্রুক্টোজ এবং অন্যান্য পদার্থ সমৃদ্ধ তরল নিঃসরণ করে যা শুক্রাণুকে পুষ্টি জোগায়।
প্রোস্টেট গ্রন্থি: মূত্রাশয়ের নীচে অবস্থিত এই গ্রন্থিটি বীর্যে অতিরিক্ত তরল যোগ করে।
বুলবোরেথ্রাল গ্রন্থি: লিঙ্গের গোড়ার কাছে অবস্থিত, এই গ্রন্থিগুলি সেমিনাল তরলেও অবদান রাখে।
মূত্রনালী: মূত্র এবং বীর্য উভয়ই বহন করে, মূত্রনালী হল বীর্যপাতের চূড়ান্ত পথ।
Functions:
- Sperm Transport: Semen provides a fluid medium for sperm to travel through the male and female reproductive tracts.
- Nourishment: The seminal vesicles and prostate gland secrete fluids that contain nutrients, such as fructose, which provide energy for sperm.
- Protection: Semen helps protect sperm from the acidic environment of the female reproductive tract.
- Fertilization: Semen facilitates the delivery of sperm to the egg, where fertilization can occur.
- Coagulation: Semen may also contain clotting factors that help it solidify in the female reproductive tract, potentially aiding in sperm retention.
- Other components: Semen also contains enzymes and other substances that play a role in sperm motility and survival.
শুক্রাণু পরিবহন: বীর্য পুরুষ ও মহিলাদের প্রজননতন্ত্রের মধ্য দিয়ে শুক্রাণু চলাচলের জন্য একটি তরল মাধ্যম প্রদান করে।
Vaginal Fluid is a Reproductive Body Fluid
Vaginal fluids, or discharge, serve multiple essential functions within the female reproductive system. These include lubrication during sexual arousal, protection against infection through its acidic pH and local flora, and facilitating the transport of sperm and, during childbirth, the passage of the baby.
Vaginal fluids are also crucial for maintaining a healthy vaginal environment and can vary in consistency and appearance throughout the menstrual cycle.
যোনি তরল, বা স্রাব, নারী প্রজনন ব্যবস্থার মধ্যে একাধিক গুরুত্বপূর্ণ কাজ করে। এর মধ্যে রয়েছে যৌন উত্তেজনার সময় তৈলাক্তকরণ, এর অ্যাসিডিক pH এবং স্থানীয় উদ্ভিদের মাধ্যমে সংক্রমণের বিরুদ্ধে সুরক্ষা, এবং শুক্রাণু পরিবহন এবং প্রসবের সময় শিশুর উত্তরণকে সহজতর করা। যোনি তরল একটি সুস্থ যোনি পরিবেশ বজায় রাখার জন্যও অত্যন্ত গুরুত্বপূর্ণ এবং মাসিক চক্র জুড়ে ধারাবাহিকতা এবং চেহারা ভিন্ন হতে পারে।
Location:
- Vaginal fluids are produced by various glands within the vulva and vagina, including the Bartholin’s and Skene’s glands, as well as the vaginal walls themselves.
- The cervix, which is the opening to the uterus, also contributes to vaginal secretions, particularly during ovulation.
- These secretions are expelled through the vaginal opening.
যোনিপথের তরল পদার্থ যোনিপথ এবং যোনির ভেতরের বিভিন্ন গ্রন্থি দ্বারা উৎপন্ন হয়, যার মধ্যে রয়েছে বার্থোলিন এবং স্কিন গ্রন্থি, এবং যোনির দেয়ালও। জরায়ুর প্রবেশপথ, যা জরায়ুর প্রবেশপথ, যোনিপথ থেকে স্রাব নিঃসরণেও অবদান রাখে, বিশেষ করে ডিম্বস্ফোটনের সময়। এই স্রাবগুলি যোনিপথের মাধ্যমে নির্গত হয়।
Functions:
- Lubrication:During sexual arousal, vaginal fluids increase significantly, facilitating comfortable intercourse and enhancing sexual pleasure.
- Immune Defense:The acidic pH of vaginal fluid, along with the presence of beneficial bacteria (local flora), helps to protect against infections by inhibiting the growth of harmful pathogens.
- Reproduction:Vaginal fluids provide a moist environment that supports sperm survival and transport to the egg for fertilization. They also act as a lubricant and canal during childbirth.
- Normal Vaginal Environment:Vaginal fluids help to maintain a healthy balance of moisture and lubrication within the vagina, which is essential for overall vaginal health.
- Menstrual Flow:During menstruation, vaginal fluids help to carry menstrual blood and tissue out of the uterus and vagina.
তৈলাক্তকরণ: যৌন উত্তেজনার সময়, যোনি তরল উল্লেখযোগ্যভাবে বৃদ্ধি পায়, আরামদায়ক সহবাসকে সহজতর করে এবং যৌন আনন্দ বৃদ্ধি করে। রোগ প্রতিরোধ ক্ষমতা: যোনি তরলের অ্যাসিডিক pH, উপকারী ব্যাকটেরিয়া (স্থানীয় উদ্ভিদ) এর উপস্থিতির সাথে, ক্ষতিকারক রোগজীবাণুগুলির বৃদ্ধিকে বাধা দিয়ে সংক্রমণ থেকে রক্ষা করতে সাহায্য করে। প্রজনন: যোনি তরল একটি আর্দ্র পরিবেশ প্রদান করে যা শুক্রাণু বেঁচে থাকার এবং নিষেকের জন্য ডিম্বাণুতে পরিবহনকে সমর্থন করে। এগুলি প্রসবের সময় লুব্রিকেন্ট এবং খাল হিসাবেও কাজ করে। স্বাভাবিক যোনি পরিবেশ: যোনি তরল যোনির ভিতরে আর্দ্রতা এবং তৈলাক্তকরণের একটি সুস্থ ভারসাম্য বজায় রাখতে সাহায্য করে, যা সামগ্রিক যোনি স্বাস্থ্যের জন্য অপরিহার্য। মাসিক প্রবাহ: ঋতুস্রাবের সময়, যোনি তরল জরায়ু এবং যোনি থেকে মাসিকের রক্ত এবং টিস্যু বহন করতে সাহায্য করে।
Changes throughout the menstrual cycle:
- Vaginal discharge can vary in consistency and appearance throughout the menstrual cycle.
- During ovulation, the discharge may become clear, slippery, and stretchy, resembling egg white, to facilitate sperm transport.
- Before menstruation, the discharge may become thicker and stickier, and may appear white or yellow.
- Changes in vaginal discharge, especially if accompanied by other symptoms like itching, pain, or a foul odor, should be evaluated by a healthcare professional to rule out any potential infections or other health issues.
মাসিক চক্র জুড়ে যোনি স্রাবের ধারাবাহিকতা এবং চেহারা ভিন্ন হতে পারে। ডিম্বস্ফোটনের সময়, স্রাব পরিষ্কার, পিচ্ছিল এবং প্রসারিত হতে পারে, ডিমের সাদা অংশের মতো, যা শুক্রাণু পরিবহনকে সহজতর করে। ঋতুস্রাবের আগে, স্রাব ঘন এবং আঠালো হতে পারে এবং সাদা বা হলুদ দেখাতে পারে। যোনি স্রাবের পরিবর্তন, বিশেষ করে যদি চুলকানি, ব্যথা বা দুর্গন্ধের মতো অন্যান্য লক্ষণগুলির সাথে থাকে, তাহলে সম্ভাব্য সংক্রমণ বা অন্যান্য স্বাস্থ্য সমস্যা বাতিল করার জন্য একজন স্বাস্থ্যসেবা পেশাদার দ্বারা মূল্যায়ন করা উচিত।
Serous Fluids are Lubricant Body Fluid
Serous fluids are clear, pale yellow liquids found in the body’s serous cavities. These fluids are located between serous membranes that line the cavities and cover organs, acting as a lubricant to reduce friction between moving organs.
Key locations include the pericardial cavity around the heart, the pleural cavities surrounding the lungs, and the peritoneal cavity within the abdomen.
সিরাস তরল হল স্বচ্ছ, ফ্যাকাশে হলুদ তরল যা শরীরের সিরাস গহ্বরে পাওয়া যায়। এই তরলগুলি সিরাস ঝিল্লির মধ্যে অবস্থিত যা গহ্বরগুলিকে রেখাযুক্ত করে এবং অঙ্গগুলিকে আবৃত করে, যা চলমান অঙ্গগুলির মধ্যে ঘর্ষণ কমাতে লুব্রিকেন্ট হিসাবে কাজ করে। মূল অবস্থানগুলির মধ্যে রয়েছে হৃৎপিণ্ডের চারপাশে পেরিকার্ডিয়াল গহ্বর, ফুসফুসকে ঘিরে থাকা প্লুরাল গহ্বর এবং পেটের ভিতরে পেরিটোনিয়াল গহ্বর।
Functions of Serous Fluids:
- Lubrication:Serous fluids allow organs to move smoothly against each other and against the body wall without causing friction or irritation.
- Cushioning:They also provide a cushioning effect, protecting organs from mechanical trauma.
- Nutrient and Waste Transport:Serous fluids facilitate the transport of nutrients and waste products to and from cells within these cavities.
- Immune Response:They can also play a role in the body’s immune response by acting as a medium for immune cells.
- Fluid Balance:They help maintain fluid balance within the cavities and can also contribute to blood pressure regulation.
তৈলাক্তকরণ: সিক্রেট তরল অঙ্গগুলিকে একে অপরের বিরুদ্ধে এবং শরীরের প্রাচীরের বিরুদ্ধে মসৃণভাবে চলাচল করতে দেয়, ঘর্ষণ বা জ্বালা ছাড়াই। কুশনিং: এগুলি একটি কুশনিং প্রভাবও প্রদান করে, অঙ্গগুলিকে যান্ত্রিক আঘাত থেকে রক্ষা করে। পুষ্টি এবং বর্জ্য পরিবহন: সিক্রেট তরলগুলি এই গহ্বরের মধ্যে কোষগুলিতে এবং সেখান থেকে পুষ্টি এবং বর্জ্য পদার্থ পরিবহনকে সহজতর করে। রোগ প্রতিরোধ প্রতিক্রিয়া: এগুলি রোগ প্রতিরোধ কোষের জন্য একটি মাধ্যম হিসেবে কাজ করে শরীরের রোগ প্রতিরোধ প্রতিক্রিয়াতেও ভূমিকা পালন করতে পারে। তরল ভারসাম্য: এগুলি গহ্বরের মধ্যে তরল ভারসাম্য বজায় রাখতে সাহায্য করে এবং রক্তচাপ নিয়ন্ত্রণেও অবদান রাখতে পারে।
Specific Locations and Examples:
- Pericardial Cavity:Serous fluid in this cavity surrounds the heart, preventing friction as the heart beats.
- Pleural Cavities:These cavities contain serous fluid that surrounds the lungs, allowing them to expand and contract during breathing.
- Peritoneal Cavity:Serous fluid here lubricates the abdominal organs, allowing them to move freely within the abdominal cavity.
পেরিকার্ডিয়াল ক্যাভিটি: এই গহ্বরের সিরাস তরল হৃৎপিণ্ডকে ঘিরে থাকে, হৃৎপিণ্ড স্পন্দনের সময় ঘর্ষণ প্রতিরোধ করে। প্লিউরাল ক্যাভিটি: এই গহ্বরগুলিতে সিরাস তরল থাকে যা ফুসফুসকে ঘিরে থাকে, যা শ্বাস-প্রশ্বাসের সময় ফুসফুসকে প্রসারিত এবং সংকুচিত হতে দেয়। পেরিটোনিয়াল ক্যাভিটি: এখানে সিরাস তরল পেটের অঙ্গগুলিকে লুব্রিকেট করে, যা পেটের গহ্বরের মধ্যে অবাধে চলাচল করতে দেয়।
Bile is a Digestive Body Fluid
Bile is a digestive fluid produced by the liver and stored in the gallbladder. Its primary function is to help digest fats by breaking them down into fatty acids, which can be absorbed by the body. Bile also plays a role in eliminating waste products like bilirubin.
পিত্ত হল একটি হজমকারী তরল যা লিভার দ্বারা উৎপাদিত হয় এবং পিত্তথলিতে জমা হয়। এর প্রাথমিক কাজ হল চর্বিগুলিকে ফ্যাটি অ্যাসিডে ভেঙে হজম করতে সাহায্য করা, যা শরীর দ্বারা শোষিত হতে পারে। পিত্ত বিলিরুবিনের মতো বর্জ্য পদার্থ অপসারণেও ভূমিকা পালন করে।
Location:
- Liver: Bile is synthesized in the liver’s hepatocytes.
- Gallbladder: Bile is then stored and concentrated in the gallbladder, a small, pear-shaped organ located beneath the liver.
- Bile ducts: Bile travels from the liver and gallbladder through a network of ducts, eventually reaching the small intestine.
- Duodenum: The bile duct empties into the duodenum, the first part of the small intestine, where it aids in digestion.
লিভার: পিত্ত যকৃতের হেপাটোসাইটে সংশ্লেষিত হয়।
পিত্তথলি: পিত্ত তারপর পিত্তথলিতে জমা হয় এবং ঘনীভূত হয়, যা লিভারের নীচে অবস্থিত একটি ছোট, নাশপাতি আকৃতির অঙ্গ।
পিত্তনালী: পিত্ত যকৃত এবং পিত্তথলি থেকে নালীগুলির একটি নেটওয়ার্কের মাধ্যমে ভ্রমণ করে, অবশেষে ক্ষুদ্রান্ত্রে পৌঁছায়।
ডুওডেনাম: পিত্তনালী ক্ষুদ্রান্ত্রে প্রথম অংশ, ডুওডেনামে খালি হয়, যেখানে এটি হজমে সহায়তা করে।
Functions:
- Fat Digestion: Bile contains bile salts, which emulsify fats, breaking them down into smaller droplets, increasing the surface area for digestive enzymes to act upon.
- Absorption: Bile facilitates the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K) and other fats from the intestine.
- Waste Removal: Bile carries waste products, including bilirubin (a byproduct of red blood cell breakdown), from the liver to the intestine for elimination from the body.
- Neutralization: Bile helps neutralize stomach acid as it enters the duodenum.
- Lubrication:Bile contains mucin, which lubricates the intestinal walls, aiding in smooth digestion.
চর্বি হজম: পিত্তে পিত্ত লবণ থাকে, যা চর্বিকে ইমালসিফাই করে, ছোট ছোট ফোঁটায় ভেঙে দেয়, যার ফলে পাচক এনজাইমগুলির উপরিভাগের ক্ষেত্রফল বৃদ্ধি পায়। শোষণ: পিত্ত অন্ত্র থেকে চর্বি-দ্রবণীয় ভিটামিন (A, D, E, এবং K) এবং অন্যান্য চর্বি শোষণকে সহজ করে। বর্জ্য অপসারণ: পিত্ত শরীর থেকে নির্মূলের জন্য লিভার থেকে অন্ত্রে বিলিরুবিন (লোহিত রক্তকণিকা ভাঙনের উপজাত) সহ বর্জ্য পদার্থ বহন করে। নিরপেক্ষকরণ: পিত্ত পাকস্থলীর অ্যাসিডকে ডুডেনামে প্রবেশের সময় নিরপেক্ষ করতে সাহায্য করে। তৈলাক্তকরণ: পিত্তে মিউসিন থাকে, যা অন্ত্রের দেয়ালকে লুব্রিকেট করে, মসৃণ হজমে সহায়তা করে।
Interstitial Fluid is a Transporting Body Fluid
Interstitial fluid is located in the spaces surrounding cells throughout the body, filling the gaps between tissues. Its primary function is to transport oxygen and nutrients to cells while also removing waste products.
This fluid is essentially plasma that has leaked from capillaries and bathes the cells, facilitating vital cellular processes.
শরীরের বিভিন্ন কোষের চারপাশের ফাঁকা স্থানে ইন্টারস্টিশিয়াল ফ্লুইড থাকে, যা টিস্যুর মধ্যে ফাঁক পূরণ করে। এর প্রাথমিক কাজ হল কোষে অক্সিজেন এবং পুষ্টি পরিবহন করা এবং একই সাথে বর্জ্য পদার্থ অপসারণ করা। এই তরলটি মূলত প্লাজমা যা কৈশিক থেকে বেরিয়ে আসে এবং কোষগুলিকে স্নান করে, গুরুত্বপূর্ণ কোষীয় প্রক্রিয়াগুলিকে সহজতর করে।
Location:
- Interstitial fluid is found in the spaces between cells in various tissues and organs throughout the body.
- It’s a component of the extracellular fluid (ECF), which also includes plasma and lymph.
- It fills the spaces within the interstitium, the area between cells and blood and lymphatic vessels.
শরীরের বিভিন্ন টিস্যু এবং অঙ্গের কোষের মধ্যবর্তী স্থানে ইন্টারস্টিশিয়াল তরল পাওয়া যায়। এটি বহির্কোষীয় তরল (ECF) এর একটি উপাদান, যার মধ্যে প্লাজমা এবং লিম্ফও রয়েছে। এটি ইন্টারস্টিশিয়ামের মধ্যে, কোষ এবং রক্ত এবং লিম্ফ্যাটিক জাহাজের মধ্যবর্তী স্থান পূরণ করে।
Functions:
- Nutrient and Waste Exchange: Interstitial fluid acts as a medium for the exchange of oxygen, nutrients, and waste products between blood capillaries and cells.
- Cellular Support: It bathes cells, providing a suitable environment for their function and survival.
- Lymphatic System Connection: Interstitial fluid is returned to the bloodstream via the lymphatic system, playing a role in immune response and fluid balance.
- Mechanical Support: Interstitial fluid flow also provides mechanical support and influences cell behavior, including migration and interaction.
- Waste Removal: It helps transport metabolic waste products away from cells and towards the lymphatic system for removal from the body.
পুষ্টি এবং বর্জ্য বিনিময়: আন্তঃস্থায়ী তরল রক্তকৈশিক এবং কোষের মধ্যে অক্সিজেন, পুষ্টি এবং বর্জ্য পদার্থের বিনিময়ের মাধ্যম হিসেবে কাজ করে। কোষীয় সহায়তা: এটি কোষগুলিকে স্নান করায়, তাদের কার্যকারিতা এবং বেঁচে থাকার জন্য একটি উপযুক্ত পরিবেশ প্রদান করে। লিম্ফ্যাটিক সিস্টেম সংযোগ: আন্তঃস্থায়ী তরল লিম্ফ্যাটিক সিস্টেমের মাধ্যমে রক্তপ্রবাহে ফিরে আসে, যা রোগ প্রতিরোধ ক্ষমতা এবং তরল ভারসাম্যে ভূমিকা পালন করে। যান্ত্রিক সহায়তা: আন্তঃস্থায়ী তরল প্রবাহ যান্ত্রিক সহায়তাও প্রদান করে এবং কোষের আচরণকে প্রভাবিত করে, যার মধ্যে স্থানান্তর এবং মিথস্ক্রিয়া অন্তর্ভুক্ত। বর্জ্য অপসারণ: এটি বিপাকীয় বর্জ্য পদার্থগুলিকে কোষ থেকে দূরে এবং শরীর থেকে অপসারণের জন্য লিম্ফ্যাটিক সিস্টেমের দিকে পরিবহনে সহায়তা করে।
Intracellular Fluid is a Body Fluid
Intracellular fluid (ICF) is the fluid found inside the cells of the body, making up about two-thirds of the body’s total water. It’s the principal component of the cytoplasm and cytosol, where many critical cellular processes take place.
ইন্ট্রাসেলুলার ফ্লুইড (ICF) হল শরীরের কোষের ভিতরে পাওয়া তরল, যা শরীরের মোট পানির প্রায় দুই-তৃতীয়াংশ তৈরি করে। এটি সাইটোপ্লাজম এবং সাইটোসোলের প্রধান উপাদান, যেখানে অনেক গুরুত্বপূর্ণ কোষীয় প্রক্রিয়া সংঘটিত হয়।
ICF is vital for maintaining cell structure and function, facilitating metabolic reactions, and regulating the movement of substances in and out of the cell.
কোষের গঠন এবং কার্যকারিতা বজায় রাখার জন্য, বিপাকীয় বিক্রিয়া সহজতর করার জন্য এবং কোষের ভেতরে এবং বাইরে পদার্থের চলাচল নিয়ন্ত্রণের জন্য ICF অত্যন্ত গুরুত্বপূর্ণ।
Location:
- ICF resides within the cell, encompassing the cytoplasm and nucleoplasm (fluid within the nucleus).
- It is distinct from extracellular fluid (ECF), which is found outside the cells, in the blood, lymph, and interstitial spaces.
- The cell membrane acts as the barrier separating ICF from ECF.
ICF কোষের ভেতরে থাকে, যা সাইটোপ্লাজম এবং নিউক্লিওপ্লাজম (নিউক্লিয়াসের ভেতরের তরল) কে ঘিরে থাকে। এটি কোষের বাইরে, রক্ত, লিম্ফ এবং ইন্টারস্টিশিয়াল স্পেসে পাওয়া যায় এমন বহির্কোষীয় তরল (ECF) থেকে আলাদা। কোষের পর্দা ICF কে ECF থেকে পৃথককারী বাধা হিসেবে কাজ করে।
Functions:
- Medium for cellular processes:ICF serves as the medium for various metabolic reactions, enzymatic reactions, and other cellular processes to occur.
- Transport of substances:It facilitates the transport of gases, nutrients, and other molecules necessary for cell function.
- Regulation of cell volume and pressure:ICF helps maintain the cell’s internal environment and ensures proper cell volume and pressure, preventing cells from swelling or shrinking.
- Ion balance and nerve signaling:The high concentration of potassium and other electrolytes in ICF is crucial for muscle contraction, nerve signaling, and other cellular functions.
- Protein synthesis:ICF provides the environment for protein synthesis and other cellular activities.
- Cellular communication:ICF plays a role in cell signaling and communication.
- Homeostasis:It contributes to maintaining the internal balance of the cell and overall bodily homeostasis.
কোষীয় প্রক্রিয়ার জন্য মাধ্যম: ICF বিভিন্ন বিপাকীয় বিক্রিয়া, এনজাইমেটিক বিক্রিয়া এবং অন্যান্য কোষীয় প্রক্রিয়ার জন্য মাধ্যম হিসেবে কাজ করে। পদার্থ পরিবহন: এটি কোষের কার্যকারিতার জন্য প্রয়োজনীয় গ্যাস, পুষ্টি এবং অন্যান্য অণু পরিবহনকে সহজতর করে। কোষের আয়তন এবং চাপ নিয়ন্ত্রণ: ICF কোষের অভ্যন্তরীণ পরিবেশ বজায় রাখতে সাহায্য করে এবং সঠিক কোষের আয়তন এবং চাপ নিশ্চিত করে, কোষগুলিকে ফুলে যাওয়া বা সঙ্কুচিত হওয়া থেকে রক্ষা করে। আয়ন ভারসাম্য এবং স্নায়ু সংকেত: ICF-তে পটাসিয়াম এবং অন্যান্য ইলেক্ট্রোলাইটের উচ্চ ঘনত্ব পেশী সংকোচন, স্নায়ু সংকেত এবং অন্যান্য কোষীয় ক্রিয়াকলাপের জন্য অত্যন্ত গুরুত্বপূর্ণ। প্রোটিন সংশ্লেষণ: ICF প্রোটিন সংশ্লেষণ এবং অন্যান্য কোষীয় ক্রিয়াকলাপের জন্য পরিবেশ প্রদান করে। কোষীয় যোগাযোগ: ICF কোষ সংকেত এবং যোগাযোগে ভূমিকা পালন করে। হোমিওস্ট্যাসিস: এটি কোষের অভ্যন্তরীণ ভারসাম্য এবং সামগ্রিক শারীরিক হোমিওস্ট্যাসিস বজায় রাখতে অবদান রাখে।
Synovial Fluid is a Bone Joint Body Fluid
Synovial fluid is a thick liquid found within the cavities of synovial joints, which are freely movable joints like the knees, hips, and shoulders. Its primary function is to reduce friction between cartilage surfaces during movement, acting as a lubricant and shock absorber. It also nourishes the cartilage and surrounding tissues through diffusion.
সাইনোভিয়াল ফ্লুইড হল সাইনোভিয়াল জয়েন্টের গহ্বরের মধ্যে পাওয়া একটি ঘন তরল, যা হাঁটু, নিতম্ব এবং কাঁধের মতো অবাধে চলমান জয়েন্ট। এর প্রাথমিক কাজ হল নড়াচড়ার সময় তরুণাস্থির পৃষ্ঠের মধ্যে ঘর্ষণ কমানো, লুব্রিকেন্ট এবং শক শোষক হিসেবে কাজ করা। এটি ছড়িয়ে পড়ার মাধ্যমে তরুণাস্থি এবং আশেপাশের টিস্যুগুলিকেও পুষ্টি জোগায়।
Location:
- Synovial fluid is located within the joint cavity of synovial joints.
- It’s produced by the synovial membrane, which lines the inner surface of the joint capsule.
- This membrane also secretes other components of the fluid.
সাইনোভিয়াল তরল সাইনোভিয়াল জয়েন্টের জয়েন্ট গহ্বরের মধ্যে অবস্থিত। এটি সাইনোভিয়াল ঝিল্লি দ্বারা উৎপাদিত হয়, যা জয়েন্ট ক্যাপসুলের ভেতরের পৃষ্ঠকে রেখাযুক্ত করে। এই ঝিল্লি তরলের অন্যান্য উপাদানও নিঃসরণ করে।
Functions:
- Lubrication: Synovial fluid reduces friction between the articular cartilage surfaces of bones during movement, allowing for smooth and painless motion.
- Shock Absorption: The fluid helps cushion the joint and absorb impact, protecting the bones and cartilage from damage.
- Nutrient Supply: Synovial fluid acts as a medium for the exchange of nutrients and waste products between the blood and the avascular cartilage.
- Phagocytosis: Synovial fluid contains cells that remove debris and foreign particles from the joint, maintaining a healthy environment.
- Reduction of inflammation: By removing debris and providing lubrication, synovial fluid helps reduce inflammation and pain within the joint.
In essence, synovial fluid is a vital component for maintaining the health and proper function of synovial joints, allowing for smooth, pain-free movement and protecting the joint from damage.
তৈলাক্তকরণ: সাইনোভিয়াল তরল নড়াচড়ার সময় হাড়ের আর্টিকুলার কার্টিলেজ পৃষ্ঠের মধ্যে ঘর্ষণ কমায়, যা মসৃণ এবং ব্যথাহীন গতির অনুমতি দেয়।
শক অ্যাবসর্পশন: তরলটি জয়েন্টকে কুশন করতে এবং প্রভাব শোষণ করতে সাহায্য করে, হাড় এবং কার্টিলেজকে ক্ষতি থেকে রক্ষা করে।
পুষ্টির সরবরাহ: সাইনোভিয়াল তরল রক্ত এবং অ্যাভাস্কুলার কার্টিলেজের মধ্যে পুষ্টি এবং বর্জ্য পদার্থের বিনিময়ের জন্য একটি মাধ্যম হিসেবে কাজ করে।
ফ্যাগোসাইটোসিস: সাইনোভিয়াল তরলে এমন কোষ থাকে যা জয়েন্ট থেকে ধ্বংসাবশেষ এবং বিদেশী কণা অপসারণ করে, একটি সুস্থ পরিবেশ বজায় রাখে।
প্রদাহ হ্রাস: ধ্বংসাবশেষ অপসারণ এবং তৈলাক্তকরণ প্রদানের মাধ্যমে, সাইনোভিয়াল তরল জয়েন্টের মধ্যে প্রদাহ এবং ব্যথা কমাতে সাহায্য করে।
মূলত, সাইনোভিয়াল তরল সাইনোভিয়াল জয়েন্টগুলির স্বাস্থ্য এবং সঠিক কার্যকারিতা বজায় রাখার জন্য একটি গুরুত্বপূর্ণ উপাদান, যা মসৃণ, ব্যথামুক্ত চলাচলের অনুমতি দেয় এবং জয়েন্টকে ক্ষতির হাত থেকে রক্ষা করে।
Breast Milk is a Body Fluid
Breast fluid, primarily referring to milk in lactating women, is produced within the mammary glands, specifically the lobules, and travels through ducts to the nipple for secretion. Its main function is to provide nourishment and immunological protection to a newborn through breastfeeding.
স্তন্যদানকারী মহিলাদের ক্ষেত্রে স্তন তরল, যা মূলত দুধকে বোঝায়, স্তন গ্রন্থিগুলির মধ্যে উৎপন্ন হয়, বিশেষ করে লোবিউলগুলিতে, এবং স্রাবের জন্য নালীগুলির মাধ্যমে স্তনবৃন্তে যায়। এর প্রধান কাজ হল বুকের দুধ খাওয়ানোর মাধ্যমে নবজাতককে পুষ্টি এবং রোগ প্রতিরোধ ক্ষমতার সুরক্ষা প্রদান করা।
Here’s a more detailed breakdown:
Location:
- Lobules: These are the milk-producing glands within the breast, clustered together to form lobes.
- Ducts: Tiny tubes that connect the lobules to the nipple, carrying milk produced in the lobules.
- Nipple:The central point of the breast where milk is secreted.
- Areola:The dark-colored area surrounding the nipple, which has sensitive nerve endings that play a role in milk release.
লোবিউলস: এগুলি স্তনের মধ্যে দুধ উৎপাদনকারী গ্রন্থি, যা একত্রিত হয়ে লোব তৈরি করে।
নালী: ক্ষুদ্র নল যা স্তনবৃন্তের সাথে লোবিউলগুলিকে সংযুক্ত করে, লোবিউলে উৎপাদিত দুধ বহন করে।
স্তনবৃন্ত: স্তনের কেন্দ্রীয় বিন্দু যেখানে দুধ নিঃসৃত হয়।
অ্যারিওলা: স্তনবৃন্তের চারপাশের গাঢ় রঙের অংশ, যার সংবেদনশীল স্নায়ু প্রান্ত রয়েছে যা দুধ নিঃসরণে ভূমিকা পালন করে।
Functions:
- Lactation (Milk Production and Secretion):In lactating women, the primary function is to produce, store, and secrete milk to nourish a newborn.
- Nutrient Delivery:Breast milk provides essential nutrients, antibodies, and growth factors to the infant.
- Immunological Protection:Breast milk contains antibodies that help protect the infant from infections and illnesses.
- Bonding:Breastfeeding also releases hormones that promote bonding between the mother and child.
স্তন্যদান (দুধ উৎপাদন এবং নিঃসরণ): স্তন্যদানকারী মহিলাদের প্রাথমিক কাজ হল নবজাতকের পুষ্টির জন্য দুধ উৎপাদন, সঞ্চয় এবং নিঃসরণ করা। পুষ্টিকর উপাদান সরবরাহ: বুকের দুধ শিশুকে প্রয়োজনীয় পুষ্টি, অ্যান্টিবডি এবং বৃদ্ধির কারণ সরবরাহ করে। রোগ প্রতিরোধ ক্ষমতা সুরক্ষা: বুকের দুধে অ্যান্টিবডি থাকে যা শিশুকে সংক্রমণ এবং অসুস্থতা থেকে রক্ষা করতে সাহায্য করে। বন্ধন: বুকের দুধ খাওয়ানোর ফলে এমন হরমোনও নিঃসৃত হয় যা মা এবং শিশুর মধ্যে বন্ধন তৈরিতে সহায়তা করে।
Other Important Considerations:
- Nipple Discharge:Fluid other than milk can sometimes leak from the nipple (nipple discharge), which may be normal or indicate an underlying issue that requires medical evaluation.
- Lymphatic System:The breast’s lymphatic system plays a role in fluid balance and the spread of some diseases, including breast cancer.
- Male Breasts:While present in males, the mammary glands are not developed and don’t produce milk.
স্তনবৃন্ত থেকে দুধ ছাড়া অন্য তরল পদার্থ বের হতে পারে (স্তনবৃন্ত থেকে তরল পদার্থ বের হতে পারে), যা স্বাভাবিক হতে পারে অথবা এমন কোনও অন্তর্নিহিত সমস্যা নির্দেশ করতে পারে যার জন্য চিকিৎসা মূল্যায়ন প্রয়োজন। লিম্ফ্যাটিক সিস্টেম: স্তনের লিম্ফ্যাটিক সিস্টেম তরল ভারসাম্য এবং স্তন ক্যান্সার সহ কিছু রোগের বিস্তারে ভূমিকা পালন করে। পুরুষ স্তন: পুরুষদের মধ্যে উপস্থিত থাকাকালীন, স্তন্যপায়ী গ্রন্থিগুলি বিকশিত হয় না এবং দুধ উৎপাদন করে না।
Amniotic Fluid is a Reproductive Body Fluid
Amniotic fluid is a clear, slightly yellowish liquid that surrounds the fetus inside the amniotic sac within the uterus during pregnancy. It acts as a protective cushion, allowing for fetal movement and development, and also plays a role in lung and digestive system development.
অ্যামনিওটিক তরল হল একটি স্বচ্ছ, সামান্য হলুদাভ তরল যা গর্ভাবস্থায় জরায়ুর ভিতরে অ্যামনিওটিক থলির ভিতরে ভ্রূণকে ঘিরে রাখে। এটি একটি প্রতিরক্ষামূলক কুশন হিসেবে কাজ করে, যা ভ্রূণের নড়াচড়া এবং বিকাশের অনুমতি দেয় এবং ফুসফুস এবং পাচনতন্ত্রের বিকাশেও ভূমিকা পালন করে।
Location:
- Amniotic fluid is found within the amniotic sac, a thin membrane that surrounds the developing fetus in the uterus.
- The amniotic sac is filled with this fluid, providing a protective and supportive environment for the fetus.
অ্যামনিওটিক তরল অ্যামনিওটিক থলির মধ্যে পাওয়া যায়, এটি একটি পাতলা পর্দা যা জরায়ুতে বিকাশমান ভ্রূণকে ঘিরে থাকে। অ্যামনিওটিক থলি এই তরল দিয়ে পূর্ণ থাকে, যা ভ্রূণের জন্য একটি প্রতিরক্ষামূলক এবং সহায়ক পরিবেশ প্রদান করে।
Functions:
- Protection:Amniotic fluid acts as a shock absorber, protecting the fetus from injury caused by external impacts or movements. It also cushions the umbilical cord, preventing it from being compressed between the fetus and the uterine wall.
- Fetal Development:
- Musculoskeletal: The fluid allows the fetus to move freely, which is essential for the development of muscles and bones.
- Lung: The fetus breathes in and out amniotic fluid, which helps the lungs to develop properly.
- Digestive: The fetus swallows amniotic fluid, which aids in the development of the digestive system.
- Temperature Regulation: Amniotic fluid helps to maintain a stable temperature for the fetus.
- Nutrient and Waste Exchange:Amniotic fluid contains nutrients, hormones, and antibodies that are beneficial for the fetus. It also serves as a reservoir for fetal waste products.
- Parturition:Amniotic fluid, particularly the rupture of the amniotic sac, can signal the start of labor.
- Diagnostic Tool: Amniotic fluid can be sampled via amniocentesis and analyzed to assess fetal health and detect certain genetic abnormalities.
সুরক্ষা: অ্যামনিওটিক তরল একটি শক শোষক হিসেবে কাজ করে, ভ্রূণকে বাইরের আঘাত বা নড়াচড়ার কারণে সৃষ্ট আঘাত থেকে রক্ষা করে। এটি নাভির কর্ডকেও সুরক্ষিত রাখে, এটি ভ্রূণ এবং জরায়ুর প্রাচীরের মধ্যে সংকুচিত হতে বাধা দেয়। ভ্রূণের বিকাশ: পেশীকঙ্কাল: এই তরল ভ্রূণকে অবাধে চলাচল করতে দেয়, যা পেশী এবং হাড়ের বিকাশের জন্য অপরিহার্য। ফুসফুস: ভ্রূণ অ্যামনিওটিক তরল গ্রহণ করে এবং বের করে দেয়, যা ফুসফুসকে সঠিকভাবে বিকাশে সহায়তা করে। পাচন: ভ্রূণ অ্যামনিওটিক তরল গ্রহণ করে, যা পাচনতন্ত্রের বিকাশে সহায়তা করে। তাপমাত্রা নিয়ন্ত্রণ: অ্যামনিওটিক তরল ভ্রূণের জন্য একটি স্থিতিশীল তাপমাত্রা বজায় রাখতে সাহায্য করে। পুষ্টি এবং বর্জ্য বিনিময়: অ্যামনিওটিক তরলে পুষ্টি, হরমোন এবং অ্যান্টিবডি থাকে যা ভ্রূণের জন্য উপকারী। এটি ভ্রূণের বর্জ্য পদার্থের জন্য একটি আধার হিসেবেও কাজ করে। প্রসব: অ্যামনিওটিক তরল, বিশেষ করে অ্যামনিওটিক থলির ফেটে যাওয়া, প্রসব শুরু হওয়ার সংকেত দিতে পারে। রোগ নির্ণয়ের সরঞ্জাম: অ্যামনিওসেন্টেসিসের মাধ্যমে অ্যামনিওটিক তরল নমুনা নেওয়া যেতে পারে এবং ভ্রূণের স্বাস্থ্য মূল্যায়ন এবং কিছু জিনগত অস্বাভাবিকতা সনাক্ত করার জন্য বিশ্লেষণ করা যেতে পারে।
 HRTD Medical Institute
HRTD Medical Institute




