Best Cardiology Course in Dhaka
Best Cardiology Course in Dhaka. Mobile No.01969947171, 01987-073965, 01797-522136. PDT Cardiology 6 Months, PDT Cardiology 1 Year, PDT Cardiology 2 Years, PGT Cardiology 6 Months, PGT Cardiology 1 Year. The meaning of PDT is Post Diploma Training and the meaning of PGT is Post Graduation Training.

Qualification for Admission to PDT Cardiology
Qualification for Admission to PDT Cardiology. Mobile No. 01969947171, 01987-073965, 01797-522136. Medical Diploma 4 Years, Or, Short Medical Diploma with a Bachelor of Science Background like B Pharm, M Pharm, BSc in Biochemistry, MSc in Biochemistry, or BSc in Chemistry/Botany/ Zoology.
Qualification for Admission to PGT Cardiology
Qualification for Admission to PGT Cardiology. Mobile No. 01987-073965, 01797-522136. MBBS (Bachelor of Medicine & Bachelor of Surgery ) for Any Medical College of the World.
PDT Cardiology Course Fee in Dhaka, Bangladesh
PDT Cardiology Course Fee in Dhaka. Mobile No. 01969947171, 01987-073965, 01797-522136. PDT Cardiology 6 Months Tk 35000/-, PDT Cardiology 1 Year Tk 70500/-, PDT Cardiology 2 Years Tk 130500/-.
PGT Cardiology Course Fee in Dhaka, Bangladesh
PGT Cardiology Course Fee in Dhaka. Mobile No. 01969947171, 01987-073965, 01797-522136. PGT Cardiology 6 Months Course Fee Tk 60,000/-, PGT Cardiology 1 Year Course Fee Tk 110,000/-
Cardiology Course Location in Dhaka, Bangladesh
Cardiology Course Location in Dhaka. Mobile No. 01969947171, 01987-073965, 01797-522136. HRTD Medical Institue, Abdul Ali Madbor Mansion, Section-6, Block-Kha, Road-1, Plot-11, Metro Rail Piller No. 249, Dhaka-1216.
What is Cardiology?
Definition of Cardiology. Briefly speaking, The study of the heart is called Cardiology. Broadly speaking, The Study of the Anatomy, Physiology, Biochemistry, Pathology, Pharmacology, Disease, Clinical Features of Disease, Treatment, and Complication of Heart Disease, is called Cardiology. If you want to complete your Cardiology Course in Dhaka please contact us.
Cardiovascular Subjects
Cardiovascular Subjects. Mobile No. Cardiovascular Anatomy & Physiology, Cardiovascular Drugs & Medicine, Cardiovascular Biochemistry, Cardiovascular Neurology, Cardiovascular Diseases, Cardiovascular Pathology, Cardiovascular Endocrinology, Types of Heart Blocks, ECG for Medical Practice, Echo & ETT.
Stages of Heart Failure
The Stages of Heart Failure are:
Stage A: High Risk of Heart Failure No Structural Heart Disease or Symptoms of Heart Failure.
Stage B: Structural Heart Disease but No Symptoms of Heart Failure.
Stage C: Structural Heart Disease and Symptoms of Heart Failure.
Stage D: Refractory Heart Failure Requiring Specialized Interventions.
Coronary Heart Block and Conductive Heart Block
Coronary Heart Block
Coronary Block:
A coronary block, also known as a coronary artery blockage or coronary artery disease (CAD), refers to the narrowing or blockage of one or more of the coronary arteries that supply oxygen-rich blood to the heart muscle. This blockage is often caused by the buildup of fatty deposits, cholesterol, and other substances, collectively known as plaque, on the inner walls of the coronary arteries. Over time, this plaque buildup can restrict blood flow to the heart muscle, leading to various cardiovascular issues.
When blood flow to the heart muscle is significantly reduced due to a coronary block, it can result in chest pain (angina) or even a heart attack (myocardial infarction), where a portion of the heart muscle doesn’t receive adequate oxygen and nutrients, potentially causing permanent damage.
Treatment for coronary blockages can involve lifestyle changes, medications, and medical procedures such as angioplasty, stent placement, or coronary artery bypass surgery, depending on the severity of the blockage.
Conductive Heart Block
Conductive Block:
A conductive block, in the context of the cardiovascular system, generally refers to a disruption in the normal electrical conduction pathway of the heart. The heart relies on a coordinated electrical system to regulate its rhythm and ensure efficient pumping of blood. The electrical signals that control the heartbeat originate in the sinoatrial (SA) node and travel through specific pathways to reach the different parts of the heart.
A conductive block can occur when these electrical signals are obstructed or slowed down as they travel through the heart’s conduction system. This can lead to irregular heart rhythms or arrhythmias. Types of conductive blocks include:
Atrioventricular Block/AV Block
Atrioventricular (AV) Block: This type of block occurs between the atria (upper chambers) and ventricles (lower chambers) of the heart. It can be categorized into three degrees of severity, ranging from mild delays in conduction to complete blockage of the signals between the atria and ventricles.
Bundle Branch Block: This occurs when there’s a delay or blockage in one of the pathways (bundle branches) that carry the electrical signals down the ventricles of the heart. It can cause a delay in ventricular contraction.
Heart Block: This is a general term that encompasses various types of conduction abnormalities in the heart’s electrical system.
The treatment for conductive blocks depends on the severity and type of blockage. Some cases may require medication to regulate the heart’s rhythm, while more serious cases might need interventions such as pacemaker implantation to ensure proper electrical signaling and maintain a regular heartbeat.
Remember, both coronary blocks and conductive blocks are important aspects of cardiovascular health, and any concerns should be discussed with a medical professional for accurate diagnosis and appropriate management.
Subjects for Cardiology Course in Dhaka, Bangladesh
Cardiovascular Anatomy & Physiology
Cardiovascular Drugs & Pharmacology
Management of Hypertension & Hypotension
Coronary Circulation & Conductive System
Cardiovascular Anatomy & Physiology for Cardiology Course in Bangladesh
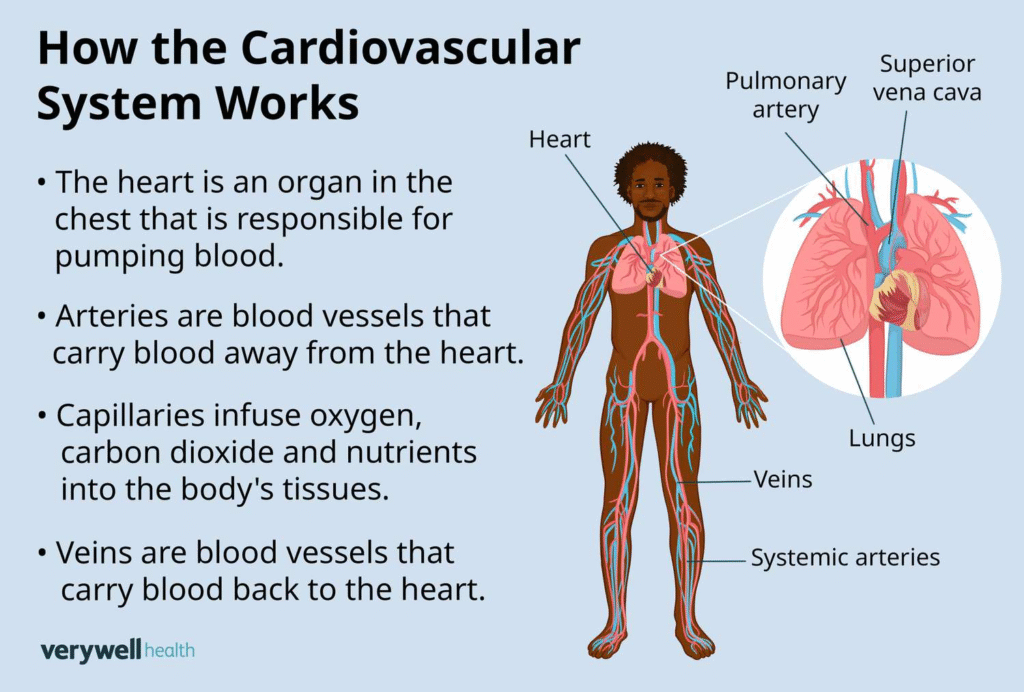
The cardiovascular system is a closed transport system composed of the heart, a muscular pump, and a network of blood vessels (arteries, capillaries, and veins) that circulate blood throughout the body. Its primary function is to deliver oxygen and nutrients to tissues and remove waste products.
The Heart
The heart is a four-chambered, muscular organ located in the chest. It has upper chambers called atria and lower chambers called ventricles, separated by a wall called the septum. Four valves control blood flow within the heart and prevent backflow: the tricuspid, pulmonary, mitral, and aortic valves. The heart wall consists of three layers: the endocardium (inner), myocardium (muscular middle), and epicardium (outer).
Blood Vessels
Blood vessels include arteries, capillaries, and veins.
Arteries: Carry blood away from the heart, generally oxygenated (except pulmonary arteries). They have thick, elastic walls.
Capillaries: Tiny vessels where exchange of oxygen, nutrients, and waste occurs between blood and tissues.
Veins: Carry blood back to the heart, generally deoxygenated (except pulmonary veins). They have thinner walls and contain valves
Blood Flow and Circulation
Blood circulates through two main pathways.
- Pulmonary Circulation: Deoxygenated blood travels from the right side of the heart to the lungs and returns oxygenated to the left side.
- Systemic Circulation: Oxygenated blood is pumped from the left side of the heart to the body and returns deoxygenated to the right side.
The heart muscle itself is supplied with blood by the coronary arteries.
Electrical Conduction System
The heart’s electrical system, driven by the sinoatrial (SA) node, regulates its pumping rhythm.
Cardiovascular Drugs & Pharmacology for Cardiology Course in Bangladesh
Cardiovascular drugs are a wide range of medications used to treat conditions affecting the heart and blood vessels, such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, heart failure, and arrhythmias. They work by various mechanisms, including altering heart rate and force of contraction, dilating blood vessels, and preventing blood clots.
| Drug Class | Mechanism of Action | Common Examples | Used to Treat |
|---|---|---|---|
| ACE Inhibitors | Block the formation of angiotensin II (a potent vasoconstrictor) to relax blood vessels and reduce blood pressure. | Lisinopril, Ramipril, Enalapril, Captopril | Hypertension, heart failure, preventing complications after heart attack |
| Angiotensin Receptor Blockers (ARBs) | Block the action of angiotensin II at its receptors, causing blood vessels to widen and blood pressure to fall. | Losartan, Valsartan, Candesartan, Irbesartan | Hypertension, heart failure (often used as an alternative to ACE inhibitors) |
| Beta-Blockers | Block the effects of adrenaline, making the heart beat slower and with less force, reducing its workload and oxygen demand. | Metoprolol, Carvedilol, Bisoprolol, Atenolol | Hypertension, angina, arrhythmias, heart failure, reducing risk after heart attack |
| Calcium Channel Blockers | Prevent calcium from entering heart muscle cells and the walls of arteries, causing blood vessels to relax and open, lowering blood pressure and heart rate. | Amlodipine, Diltiazem, Nifedipine, Verapamil | Hypertension, angina, arrhythmias |
| Diuretics | Help the body eliminate excess water and sodium (salt) through increased urination, reducing blood volume and fluid buildup in the body. | Furosemide, Bumetanide, Hydrochlorothiazide | Hypertension, edema (swelling) due to heart failure or kidney disease |
| Statins | Lower cholesterol by blocking an enzyme the liver needs to produce it. This reduces levels of “bad” cholesterol (LDL) and slows plaque formation in arteries. | Atorvastatin, Rosuvastatin, Simvastatin | High cholesterol, prevention of heart attacks and strokes |
| Anticoagulants | Prevent blood clots from forming or growing larger by interrupting the clotting cascade. | Warfarin, Heparin, Apixaban, Rivaroxaban | Atrial fibrillation, deep vein thrombosis (DVT), pulmonary embolism (PE), post-surgery clot prevention |
| Antiplatelets | Prevent blood platelets from sticking together to form clots. | Aspirin, Clopidogrel, Ticagrelor | Preventing heart attacks and strokes |
| Vasodilators | Relax muscles in blood vessels, causing them to widen and blood to flow more easily. | Nitroglycerin, Hydralazine | Angina pectoris, heart failure, hypertension |

Cardiovascular Disease & Treatment for Cardiology Course in Bangladesh
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a general term for conditions that affect the heart or blood vessels. It is the leading cause of death globally, primarily resulting from atherosclerosis, the buildup of fatty deposits (plaque) that narrow arteries and restrict blood flow.
Types of Cardiovascular Disease
CVD encompasses a range of conditions, including:
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD): Narrowed or blocked blood vessels supplying the heart muscle, which can lead to angina (chest pain), heart attacks, and heart failure.
Cerebrovascular Disease: Conditions affecting the blood vessels supplying the brain, such as stroke (blood supply cut off) and transient ischemic attack (TIA, or “mini-stroke”).
Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD): Narrowing of arteries supplying the legs, arms, or abdominal organs, causing pain or cramps in the limbs.
- Heart Failure: The heart’s inability to pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs, leading to fluid buildup and shortness of breath.
- Arrhythmias: Problems with the heart’s electrical system, resulting in abnormal heart rates or rhythms.
- Heart Valve Disease: Issues with the heart valves not opening fully (stenosis) or closing tightly (regurgitation).
- Congenital Heart Disease: Heart defects present at birth.
Common Symptoms
Often, there are no symptoms of the underlying disease until a major event like a heart attack or stroke occurs. When symptoms do appear, they depend on the specific condition but can include:
- Chest pain, pressure, tightness, or discomfort (angina)
- Shortness of breath
- Pain or discomfort in the arms, left shoulder, jaw, back, or neck
- Dizziness, lightheadedness, or fainting
- Fatigue or exhaustion
- Swelling in the legs, ankles, or feet
- Irregular heartbeats (palpitations)
- Cold sweats or nausea
Causes and Risk Factors
The primary cause of many CVDs is atherosclerosis. Risk factors fall into modifiable (changeable) and non-modifiable categories:
| Modifiable Risk Factors | Non-Modifiable Risk Factors |
|---|---|
| High blood pressure | Age (risk increases with age) |
| High cholesterol | Sex (men generally at higher risk earlier in life) |
| Tobacco use (smoking, vaping, secondhand smoke) | Family history of heart disease |
| Diabetes (Type 2) | Ethnicity |
| Physical inactivity | Genetic factors |
| Obesity or excess weight |
Prevention and Treatment
Many CVDs can be largely prevented by adopting a healthy lifestyle. Prevention strategies include:
- Avoiding all tobacco products
- Eating a heart-healthy diet (low in salt, saturated fat, and sugar; high in fruits and vegetables)
- Getting regular physical activity (at least 30-60 minutes on most days)
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Managing stress and other health conditions like high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes
Treatment options vary by condition and severity and may include lifestyle changes, medications, or surgical procedures like stents or bypass surgery. Early detection and working with a healthcare provider are crucial for effective management and prevention of serious complications.
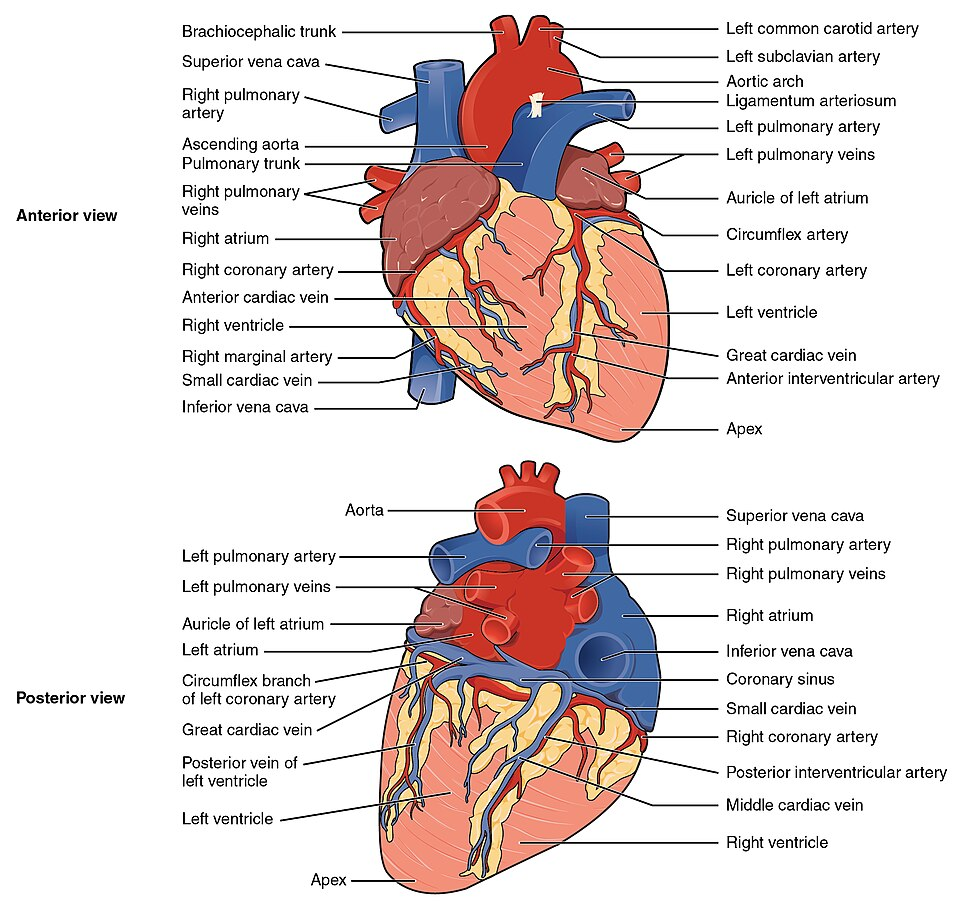
Coronary Circulation & Conductive System for Cardiology Course in Bangladesh
In Bangladesh, postgraduate cardiology curricula, such as the MD in Cardiology and Diploma in Medical Technology (Cardiac Perfusion), focus heavily on the anatomical and physiological basis of heart function.
1. Coronary Circulation
The heart’s blood supply is provided by the coronary arteries, which are the first branches of the ascending aorta.
- Right Coronary Artery (RCA): Arises from the anterior aortic sinus and travels in the right atrioventricular groove.
- Major Branches: Sinoatrial (SA) nodal artery (in ~60% of people), right marginal artery, and the Posterior Descending Artery (PDA).
- Supply Area: Right atrium, right ventricle, SA node, and Atrioventricular (AV) node (in ~80%–90% of people).
- Left Main Coronary Artery (LMCA): Arises from the left posterior aortic sinus and bifurcates quickly.
- Left Anterior Descending (LAD): Supplies the anterior 2/3 of the interventricular septum, the bundle of His, and the anterior wall of the left ventricle.
- Left Circumflex (LCx): Supplies the left atrium and the lateral/posterior walls of the left ventricle.
- Venous Drainage: Most deoxygenated blood is collected by the coronary sinus, which empties directly into the right atrium.
2. Cardiac Conduction System
This specialized network of cells initiates and coordinates the rhythmic contraction of the heart muscle.
- Sinoatrial (SA) Node: The “natural pacemaker” located at the junction of the superior vena cava and right atrium. It initiates impulses at a rate of 60–100 bpm.
- Internodal Pathways: Three pathways (anterior, middle, posterior) that transmit signals from the SA node to the AV node.
- Atrioventricular (AV) Node: Located in the Triangle of Koch. It delays the signal (~120ms) to allow the ventricles to fill with blood before contracting.
- Bundle of His & Branches: The electrical bridge between atria and ventricles. It divides into the Right and Left Bundle Branches, carrying the signal down the interventricular septum.
- Purkinje Fibers: Fast-conducting terminal fibers in the subendocardium that cause the ventricles to contract synchronously from the apex upward.
3. Clinical Correlation (ECG & Infarction)
Postgraduate courses in Bangladesh emphasize correlating anatomy with ECG findings:
- P Wave: Represents atrial depolarization (SA node/atria).
- PR Interval: Reflects the delay at the AV node.
- QRS Complex: Represents ventricular depolarization (Purkinje system).
- Infarction Patterns: An anterior wall MI (ST elevation in V1-V4) usually involves the LAD, while an inferior wall MI (ST elevation in II, III, aVF) typically involves the RCA.
Would you like a detailed breakdown of the coronary artery dominance variations commonly seen in clinical practice?
Coronary Circulation এর কাজ কি ?
করোনারি সার্কুলেশন (Coronary Circulation) হৃৎপিণ্ডের পেশীতে (মায়োকার্ডিয়াম) অক্সিজেন ও পুষ্টিসমৃদ্ধ রক্ত সরবরাহ করে এবং কার্বন ডাই অক্সাইডসহ বর্জ্য পদার্থ অপসারণ করে। এটি হৃৎপিণ্ডের পেশীগুলোর অবিরাম কাজ করার জন্য প্রয়োজনীয় শক্তি নিশ্চিত করে, যা সারা শরীরে রক্ত পাম্প করতে সাহায্য করে।
করোনারি সার্কুলেশনের প্রধান কাজগুলো হলো:
- অক্সিজেন ও পুষ্টি সরবরাহ: করোনারি ধমনীর মাধ্যমে হৃৎপিণ্ডের পেশীতে অক্সিজেন এবং পুষ্টি পৌছে দেওয়া [৩, ৫]।
- বর্জ্য পদার্থ অপসারণ: বিপাকীয় বর্জ্য এবং কার্বন ডাই অক্সাইড সরিয়ে ফেলা ।
- ডায়াস্টোলিক পারফিউশন: হৃৎপিণ্ড যখন সংকুচিত না হয়ে শিথিল থাকে (ডায়াস্টোল), তখন রক্ত প্রবাহের মাধ্যমে হৃদপেশীকে পুষ্টি দেওয়া [১, ৮]।
- হার্ট অ্যাটাক প্রতিরোধ: অবরুদ্ধ বা সরু ধমনীর মাধ্যমে রক্ত প্রবাহ কমিয়ে হার্ট ফেইলিউর বা হার্ট অ্যাটাক হওয়ার ঝুঁকি কমানো [৭, ১০, ১৫]।
সহজ কথায়, করোনারি সার্কুলেশন হলো হৃৎপিণ্ডের নিজস্ব রক্ত সরবরাহ ব্যবস্থা, যা হার্টকে নিরবচ্ছিন্নভাবে কাজ করতে সাহায্য করে।
করোনারি ধমনি রক্ত সংবহন করে কোথায়?
করোনারি ধমনি (Coronary arteries) হৃৎপিণ্ডের পেশীতে (myocardium) অক্সিজেন ও পুষ্টিসমৃদ্ধ রক্ত সংবহন করে। এই ধমনিগুলো অওর্টা বা মহাধমনি থেকে উৎপন্ন হয়ে হৃৎপিণ্ডের বাইরে চাদরের মতো জড়িয়ে থেকে হৃৎপিণ্ডের পেশীকোষগুলোকে সচল ও সুস্থ রাখে।
মূল তথ্য:
- কোথায় রক্ত দেয়: সরাসরি হৃৎপিণ্ডের পেশী বা মায়োকার্ডিয়ামে ।
- রক্তের ধরণ: অক্সিজেন ও পুষ্টিসমৃদ্ধ (Oxygenated) রক্ত ।
- ধমনির ধরণ: প্রধান দুটি ধমনি—বাম এবং ডান করোনারি ধমনি।
সংক্ষেপে, হৃৎপিণ্ডের নিজস্ব রক্ত সরবরাহের মাধ্যম হলো এই করোনারি ধমনি
করোনারি হৃদরোগের পূর্ব লক্ষণ কোনটি?
করোনারি হৃদরোগের (Coronary Artery Disease) প্রধান পূর্ব লক্ষণ বা প্রাথমিক সতর্কবার্তা হলো বুকে ব্যথা বা অস্বস্তি, যাকে চিকিৎসাবিজ্ঞানে এনজাইনা (Angina) বলা হয় । এটি বুকের মাঝখানে বা বাম দিকে চাপ, ভারী ভাব, মোচড় দেওয়া বা প্রচণ্ড ব্যথার মতো অনুভূত হতে পারে, যা অনেক সময় কাঁধ, বাহু, ঘাড় বা চোয়ালে ছড়িয়ে পড়ে ।
অন্যান্য সাধারণ পূর্ব লক্ষণসমূহ:
- শ্বাসকষ্ট: সামান্য পরিশ্রমেই বা হাঁটাচলায় দম ফুরিয়ে আসা ।
- অতিরিক্ত ক্লান্তি: কোনো বিশেষ কারণ ছাড়াই বা অল্প পরিশ্রমে প্রচণ্ড দুর্বল লাগা ।
- বুক ধড়ফড় করা: হৃদস্পন্দন অস্বাভাবিক বা দ্রুত অনুভূত হওয়া ।
- বমি বমি ভাব বা বদহজম: পেটে অস্বস্তি বা বুক জ্বালাপোড়া ।
- ঘাম হওয়া: হঠাৎ শরীর ঘেমে যাওয়া, বিশেষ করে বুকের ব্যথার সাথে
নারীদের ক্ষেত্রে লক্ষণ: নারীদের ক্ষেত্রে অনেক সময় বুকে ব্যথার চেয়েও হঠাৎ অতিরিক্ত ক্লান্তি, শ্বাসকষ্ট, ঘাড় বা চোয়ালে ব্যথা এবং বমি বমি ভাবের মতো লক্ষণ বেশি দেখা যায় ।
এই লক্ষণগুলো দেখলে দ্রুত চিকিৎসকের পরামর্শ নেওয়া প্রয়োজন।
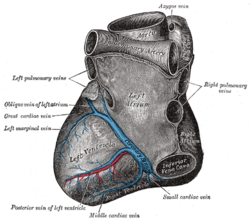
Coronary circulation
Coronary circulation is the circulation of blood in the arteries and veins that supply the heart muscle (myocardium). Coronary arteries supply oxygenated blood to the heart muscle. Cardiac veins then drain away the blood after it has been deoxygenated. Because the rest of the body, and most especially the brain, needs a steady supply of oxygenated blood that is free of all but the slightest interruptions, the heart is required to function continuously. Therefore its circulation is of major importance not only to its own tissues but to the entire body and even the level of consciousness of the brain from moment to moment. Interruptions of coronary circulation quickly cause heart attacks (myocardial infarctions), in which the heart muscle is damaged by oxygen starvation. Such interruptions are usually caused by coronary ischemia linked to coronary artery disease, and sometimes to embolism from other causes like obstruction in blood flow through vessels.
Coronary arteries
Coronary arteries supply blood to the myocardium and other components of the heart. Two coronary arteries originate from the left side of the heart at the beginning (root) left ventricle. There are three aortic sinuses (dilations) in the wall of the aorta just superior to the aortic semilunar valve. Two of these, the left posterior aortic sinus and anterior aortic sinus, give rise to the left and right coronary arteries, respectively. The third sinus, the right posterior aortic sinus, typically does not give rise to a vessel. Coronary vessel branches that remain on the surface of the heart and follow the sulci of the heart are called epicardial coronary arteries.
The left coronary artery distributes blood to the left side of the heart, the left atrium and ventricle, and the interventricular septum. The circumflex artery arises from the left coronary artery and follows the coronary sulcus to the left. Eventually, it will fuse with the small branches of the right coronary artery. The larger left anterior descending artery (LAD), is the second major branch arising from the left coronary artery. It follows the anterior interventricular sulcus around the pulmonary trunk. Along the way it gives rise to numerous smaller branches that interconnect with the branches of the posterior interventricular artery, forming anastomoses. An anastomosis is an area where vessels unite to form interconnections that normally allow blood to circulate to a region even if there may be partial blockage in another branch. The anastomoses in the heart are very small. Therefore, this ability is somewhat restricted in the heart so a coronary artery blockage often results in myocardial infarction causing death of the cells supplied by the particular vessel.
The right coronary artery proceeds along the coronary sulcus and distributes blood to the right atrium, portions of both ventricles, and the heart conduction system. Normally, one or more marginal arteries arise from the right coronary artery inferior to the right atrium. The marginal arteries supply blood to the superficial portions of the right ventricle. On the posterior surface of the heart, the right coronary artery gives rise to the posterior interventricular artery, also known as the posterior descending artery. It runs along the posterior portion of the interventricular sulcus toward the apex of the heart, giving rise to branches that supply the interventricular septum and portions of both ventricles.
Cardiac veins
The vessels that remove the deoxygenated blood from the heart muscle are the cardiac veins. These include the great cardiac vein, the middle cardiac vein, the small cardiac vein, the smallest cardiac veins, and the anterior cardiac veins. Cardiac veins carry blood with a poor level of oxygen, from the myocardium to the right atrium. Most of the blood of the coronary veins returns through the coronary sinus. The anatomy of the veins of the heart is very variable, but generally it is formed by the following veins: heart veins that go into the coronary sinus: the great cardiac vein, the middle cardiac vein, the small cardiac vein, the posterior vein of the left ventricle, and the oblique vein of Marshall. Heart veins that go directly to the right atrium: the anterior cardiac veins, the smallest cardiac veins (Thebesian veins).
Anastomoses
There are some anastomoses between branches of the two coronary arteries. However the coronary arteries are functionally end arteries and so these meetings are referred to as potential anastomoses, which lack function, as opposed to true anastomoses like that in the palm of the hand. This is because blockage of one coronary artery generally results in death of the heart tissue due to lack of sufficient blood supply from the other branch. When two arteries or their branches join, the area of the myocardium receives dual blood supply. These junctions are called anastomoses. If one coronary artery is obstructed by an atheroma, the second artery is still able to supply oxygenated blood to the myocardium. However, this can only occur if the atheroma progresses slowly, giving the anastomoses a chance to proliferate.
Under the most common configuration of coronary arteries, there are three areas of anastomoses. Small branches of the LAD (left anterior descending/anterior interventricular) branch of the left coronary join with branches of the posterior interventricular branch of the right coronary in the interventricular sulcus (groove). More superiorly, there is an anastomosis between the circumflex artery (a branch of the left coronary artery) and the right coronary artery in the atrioventricular groove. There is also an anastomosis between the septal branches of the two coronary arteries in the interventricular septum. The photograph shows area of heart supplied by the right and the left coronary arteries.
Variation
The left and right coronary arteries occasionally arise by a common trunk, or their number may be increased to three; the additional branch being the posterior coronary artery (which is smaller in size). In rare cases, a person will have the third coronary artery run around the root of the aorta.
Occasionally, a coronary artery will exist as a double structure (i.e. there are two arteries, parallel to each other, where ordinarily there would be one).
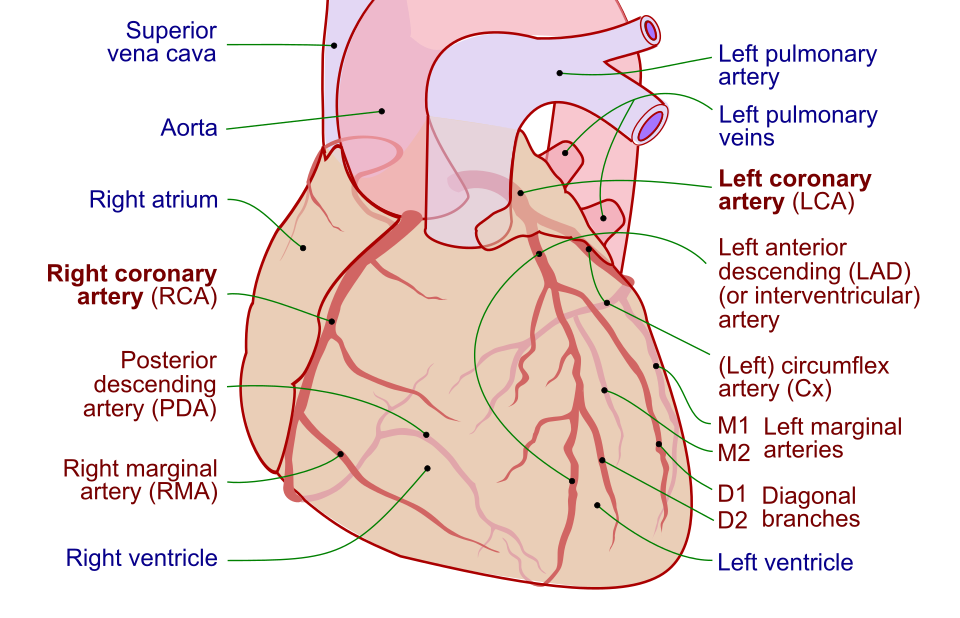
Coronary artery dominance
The artery that supplies the posterior third of the interventricular septum – the posterior descending artery (PDA) determines the coronary dominance.
- If the posterior descending artery is supplied by the right coronary artery (RCA), then the coronary circulation can be classified as “right-dominant.”
- If the posterior descending artery is supplied by the circumflex artery (CX), a branch of the left artery, then the coronary circulation can be classified as “left-dominant.”
- If the posterior descending artery is supplied by both the right coronary artery and the circumflex artery, then the coronary circulation can be classified as “co-dominant.”
Approximately 70% of the general population are right-dominant, 20% are co-dominant, and 10% are left-dominant. A precise anatomic definition of dominance would be the artery which gives off supply to the AV node i.e. the AV nodal artery. Most of the time this is the right coronary artery.
Management of Hypertension & Hypotension for Cardiology Course in Bangladesh
Management of both hypertension (high blood pressure) and hypotension (low blood pressure) typically involves a combination of lifestyle modifications and, in many cases, medication tailored to the underlying cause and the individual’s overall health.
The goal of hypertension management is to lower blood pressure to a healthy range (often a goal of less than 130/80 mm Hg for most adults with risk factors) to reduce the risk of heart disease, stroke, and kidney disease.
হাইপারটেনশন কেন হয় এবং ঝুঁকির কারণ কী?
বেশিরভাগ ক্ষেত্রে, উচ্চ রক্তচাপের কোনো নির্দিষ্ট কারণ থাকে না (প্রাইমারি বা এসেনশিয়াল হাইপারটেনশন)। তবে, কিছু কারণ এবং জীবনযাত্রার অভ্যাস এই ঝুঁকি বাড়িয়ে দেয়:
- অস্বাস্থ্যকর খাদ্যাভ্যাস: অতিরিক্ত লবণ খাওয়া, চর্বিযুক্ত খাবার এবং ফলমূল-শাকসবজি কম খাওয়া।
- শারীরিক পরিশ্রমের অভাব: নিয়মিত ব্যায়াম না করা।
- স্থূলতা বা অতিরিক্ত ওজন।
- ধূমপান ও তামাক ব্যবহার: তামাক রক্তনালীকে ক্ষতিগ্রস্ত করে এবং সরু করে দেয়।
- অতিরিক্ত অ্যালকোহল সেবন।
- বয়স: বয়স বাড়ার সাথে সাথে ঝুঁকি বাড়ে।
- পারিবারিক ইতিহাস বা জেনেটিক কারণ।
- দীর্ঘস্থায়ী মানসিক চাপ।
কিছু ক্ষেত্রে, কিডনি রোগ বা হরমোনজনিত সমস্যার মতো অন্য কোনো স্বাস্থ্যের অবস্থার কারণেও উচ্চ রক্তচাপ হতে পারে (সেকেন্ডারি হাইপারটেনশন)।
উপসর্গ
উচ্চ রক্তচাপকে প্রায়শই “নীরব ঘাতক” বলা হয়, কারণ সাধারণত এর কোনো স্পষ্ট উপসর্গ থাকে না। আক্রান্ত ব্যক্তিরা বছরের পর বছর ধরে এটি নিয়ে বসবাস করতে পারে কোনো লক্ষণ ছাড়াই।
তবে, যখন রক্তচাপ খুব বেশি বেড়ে যায়, তখন কিছু উপসর্গ দেখা দিতে পারে, যেমন:
- তীব্র মাথা ব্যথা
- মাথা ঘোরা বা অজ্ঞান হয়ে যাওয়া
- বুক ধড়ফড় করা
- শ্বাসকষ্ট
- ক্লান্তি
- নাকে রক্ত পড়া (বিরল ক্ষেত্রে)
চিকিৎসা ও নিয়ন্ত্রণ
উচ্চ রক্তচাপ নিয়ন্ত্রণ করা অত্যন্ত গুরুত্বপূর্ণ। এর ব্যবস্থাপনার মধ্যে সাধারণত জীবনযাত্রার পরিবর্তন এবং প্রয়োজনে ওষুধ ব্যবহার অন্তর্ভুক্ত থাকে:
- স্বাস্থ্যকর খাদ্যাভ্যাস: কম লবণের DASH eating plan (ড্যাশ ডায়েট) অনুসরণ করা।
- নিয়মিত ব্যায়াম: প্রতিদিন অন্তত ৩০ মিনিট মাঝারি ধরনের শারীরিক কার্যকলাপ করা।
- ওজন নিয়ন্ত্রণ: সুস্থ ওজন বজায় রাখা।
- ধূমপান ত্যাগ করা এবং অ্যালকোহল সেবন সীমিত করা।
- মানসিক চাপ কমানো।
যদি জীবনযাত্রার পরিবর্তনে কাজ না হয়, তবে ডাক্তার রক্তচাপ কমানোর জন্য ওষুধ লিখে দিতে পারেন, যেমন: ডাইউরেটিকস, এসিই ইনহিবিটরস, ক্যালসিয়াম চ্যানেল ব্লকার ইত্যাদি।
উচ্চ রক্তচাপ নির্ণয় এবং উপযুক্ত চিকিৎসা পরিকল্পনার জন্য একজন ডাক্তারের সাথে পরামর্শ করা অপরিহার্য।
Hypotension Management
Management of hypotension (low blood pressure with symptoms like dizziness or fainting) focuses on identifying and treating the underlying cause
হাইপোটেনশন (Hypotension) বা নিম্ন রক্তচাপ হলো এমন একটি অবস্থা যখন একজন ব্যক্তির রক্তচাপ স্বাভাবিক মাত্রার (স্বাভাবিক রক্তচাপ সাধারণত ১২০/৮০ মিমি পারদ ধরা হয়) চেয়ে বেশ নিচে নেমে যায়। যদিও সুনির্দিষ্ট কোনো সার্বজনীন কাট-অফ পয়েন্ট নেই, তবে সাধারণত সিস্টোলিক রক্তচাপ (উপরের মান) ৯০ মিমি পারদ বা তার কম এবং ডায়াস্টোলিক রক্তচাপ (নিচের মান) ৬০ মিমি পারদ বা তার কম হলে তাকে নিম্ন রক্তচাপ বা হাইপোটেনশন বলা হয়।
নিম্ন রক্তচাপের প্রকারভেদ
নিম্ন রক্তচাপ বিভিন্ন ধরনের হতে পারে:
- অর্থোস্ট্যাটিক হাইপোটেনশন (Orthostatic Hypotension): এটি সবচেয়ে সাধারণ ধরন। যখন কেউ বসে থাকা বা শুয়ে থাকা অবস্থা থেকে হঠাৎ উঠে দাঁড়ায়, তখন মাধ্যাকর্ষণের কারণে রক্ত পায়ের দিকে চলে যায়। শরীর দ্রুত রক্তচাপ সামঞ্জস্য করতে না পারলে এই ধরনের নিম্ন রক্তচাপ হয়, যার ফলে মাথা ঘোরায়।
- পোস্টপ্র্যান্ডিয়াল হাইপোটেনশন (Postprandial Hypotension): এটি সাধারণত বয়স্কদের মধ্যে দেখা যায়, যখন রক্তচাপ খাওয়ার পরপরই কমে যায়। এটি ঘটে কারণ হজমের জন্য পরিপাকতন্ত্রে রক্ত প্রবাহ বেড়ে যায়।
- নিউরালি মেডিয়েটেড হাইপোটেনশন (Neurally Mediated Hypotension – NMH): এটি সাধারণত দীর্ঘ সময় ধরে দাঁড়িয়ে থাকার ফলে হয়। মস্তিষ্কের সাথে হৃদপিণ্ডের যোগাযোগের ত্রুটির কারণে রক্তচাপ কমে যায়।
- গুরুতর হাইপোটেনশন (Severe Hypotension): এটি মূলত “শক” (shock) অবস্থার সাথে সম্পর্কিত, যা মারাত্মক হতে পারে।
নিম্ন রক্তচাপের কারণ
নিম্ন রক্তচাপের অনেক কারণ থাকতে পারে, যার মধ্যে রয়েছে:
- রক্তের পরিমাণ কমে যাওয়া: পানিশূন্যতা (dehydration), রক্তপাত বা গুরুতর আঘাতের কারণে রক্তের পরিমাণ কমে যেতে পারে।
- হৃদরোগ: হার্ট ফেইলিউর বা হার্ট অ্যাটাকের মতো সমস্যা হলে হৃদপিণ্ড পর্যাপ্ত রক্ত পাম্প করতে পারে না।
- হরমোনজনিত সমস্যা: থাইরয়েড সমস্যা বা ডায়াবেটিস।
- গর্ভাবস্থা: গর্ভাবস্থায় রক্তচাপ স্বাভাবিকভাবেই কিছুটা কমে যেতে পারে।
- ওষুধের পার্শ্বপ্রতিক্রিয়া: উচ্চ রক্তচাপ, হৃদরোগ বা বিষণ্ণতার চিকিৎসার জন্য ব্যবহৃত কিছু ওষুধ রক্তচাপ কমাতে পারে।
- রক্তনালীর প্রসারণ: গুরুতর সংক্রমণ (সেপসিস) বা অ্যালার্জিক প্রতিক্রিয়ার (অ্যানাফাইল্যাক্সিস) কারণে রক্তনালী হঠাৎ প্রসারিত হতে পারে।
নিম্ন রক্তচাপের উপসর্গ
নিম্ন রক্তচাপ সবসময় সমস্যার কারণ হয় না। যাদের স্বাভাবিকভাবেই রক্তচাপ কম থাকে, তারা সাধারণত ভালো থাকে। তবে, যখন রক্তচাপ বিপজ্জনক মাত্রায় কমে যায় বা হঠাৎ করে কমে যায়, তখন নিম্নলিখিত উপসর্গগুলো দেখা দিতে পারে:
- মাথা ঘোরা বা হালকা মাথা অনুভব করা
- অজ্ঞান হয়ে যাওয়া (সিনকোপ)
- দৃষ্টিশক্তি ঝাপসা হয়ে যাওয়া
- দুর্বলতা বা ক্লান্তি
- বমি বমি ভাব
- মনোযোগের অভাব
- ঠান্ডা, ভেজা ত্বক
- দ্রুত, অগভীর শ্বাস-প্রশ্বাস (গুরুতর ক্ষেত্রে)
চিকিৎসা ও ব্যবস্থাপনা
নিম্ন রক্তচাপের চিকিৎসা নির্ভর করে এর অন্তর্নিহিত কারণ এবং উপসর্গের তীব্রতার উপর। যদি কোনো উপসর্গ না থাকে, তবে সাধারণত চিকিৎসার প্রয়োজন হয় না।
ব্যবস্থাপনার উপায়গুলির মধ্যে রয়েছে:
- কারণ শনাক্ত করা: যদি ওষুধ বা অন্য কোনো স্বাস্থ্যের অবস্থার কারণে নিম্ন রক্তচাপ হয়, তবে সেই কারণের চিকিৎসা করা হয়।
- পানিশূন্যতা প্রতিরোধ: প্রচুর পরিমাণে পানি এবং তরল পান করা।
- লবণ গ্রহণ: ডাক্তারের পরামর্শ অনুযায়ী লবণ খাওয়া বাড়ানো যেতে পারে।
- জীবনযাত্রার পরিবর্তন: ধীরে ধীরে দাঁড়ানো, ছোট ও ঘন ঘন খাবার খাওয়া এবং কম্প্রেশন স্টকিংস (Compression Stockings) ব্যবহার করা।
- ওষুধ: কিছু নির্দিষ্ট ক্ষেত্রে, যেমন অর্থোস্ট্যাটিক হাইপোটেনশন, ডাক্তার রক্তচাপ বাড়ানোর জন্য ওষুধ (যেমন ফ্লুড্রোকর্টিসোন বা মিডোডরিন) লিখে দিতে পারেন।
গুরুতর হাইপোটেনশন বা শক একটি মেডিকেল ইমার্জেন্সি এবং এর জন্য তাৎক্ষণিক হাসপাতালের চিকিৎসা প্রয়োজন।
The coronary circulation supplies the heart muscle (myocardium) with oxygenated blood and removes deoxygenated blood, while the cardiac conduction system is the heart’s intrinsic electrical network that coordinates its rhythmic beating
Coronary Circulation & Conductive System
The coronary circulation supplies the heart muscle (myocardium) with oxygenated blood and removes deoxygenated blood, while the cardiac conduction system is the heart’s intrinsic electrical network that coordinates its rhythmic beating.
Coronary Circulation
The heart requires a continuous supply of oxygen and nutrients, which is provided by the coronary circulation because the heart’s walls are too thick for diffusion from the blood within its chambers.
- Coronary Arteries: Oxygenated blood from the aorta flows into the left coronary artery (LCA) and the right coronary artery (RCA). The LCA branches into the left anterior descending artery and the circumflex artery, supplying the left atrium, left ventricle, and interventricular septum. The RCA supplies the right atrium, right ventricle, and parts of the SA and AV nodes.
- Capillaries and Veins: Within the myocardium, arteries lead to capillaries for gas exchange. Cardiac veins collect deoxygenated blood and merge into the coronary sinus, which drains directly into the right atrium.
- Key Feature: Coronary blood flow is greatest during diastole (relaxation), not systole (contraction), due to compression of vessels by the contracting muscle.
Cardiac Conduction System
This system of specialized muscle cells generates and transmits electrical impulses for coordinated heart contractions. The electrical signal follows this path:
- SA Node: The sinoatrial node, the heart’s pacemaker in the right atrium, generates the initial impulse.
- AV Node: The signal travels to the atrioventricular node between the atria and ventricles. A brief delay here allows atrial emptying.
- Bundle of His and Branches: The signal moves to the bundle of His and divides into left and right bundle branches.
- Purkinje Fibers: These fibers spread through the ventricular walls, delivering the signal for ventricular contraction.
This process results in the coordinated pumping of blood, visible on an EKG as the P wave (atrial contraction) and QRS complex (ventricular contraction
হৃদপিণ্ডের পরিবহন ব্যবস্থা (Cardiac Conduction System) হলো এক ধরনের বিশেষায়িত পেশী কোষের নেটওয়ার্ক, যা বৈদ্যুতিক সংকেত তৈরি করে এবং পরিবহন করে হৃদপিণ্ডের ছন্দবদ্ধ স্পন্দন বা সংকোচন-প্রসারণ নিয়ন্ত্রণ করে। এই ব্যবস্থাটি নিশ্চিত করে যে হৃদপিণ্ডের উপরের প্রকোষ্ঠগুলো (অ্যাট্রিয়া) প্রথমে এবং নিচের প্রকোষ্ঠগুলো (ভেন্ট্রিকল) পরে সংকুচিত হবে, যার ফলে রক্ত পাম্প করার কাজটি দক্ষতার সাথে সম্পন্ন হয়।
এই বৈদ্যুতিক সংকেত হৃদপিণ্ডের মধ্য দিয়ে একটি নির্দিষ্ট পথ অনুসরণ করে:
- এসএ নোড (Sinoatrial Node): এটি হৃদপিণ্ডের ডান অ্যাট্রিয়ামের প্রাচীরে অবস্থিত এবং এটি হলো হৃদপিণ্ডের প্রাকৃতিক পেসমেকার (pacemaker)। এটি স্বয়ংক্রিয়ভাবে এবং ছন্দবদ্ধভাবে বৈদ্যুতিক স্পন্দন তৈরি করে।
- এভি নোড (Atrioventricular Node): সংকেত এসএ নোড থেকে অ্যাট্রিয়া হয়ে এভি নোডে পৌঁছায়, যা অ্যাট্রিয়া এবং ভেন্ট্রিকলের মাঝখানে অবস্থিত। এখানে সংকেতটি সামান্য দেরি করে পৌঁছায়, যা ভেন্ট্রিকল সংকোচনের আগে অ্যাট্রিয়াকে রক্ত দিয়ে সম্পূর্ণরূপে পূর্ণ হওয়ার সময় দেয়।
- বান্ডল অফ হিজ ও বান্ডল ব্রাঞ্চ (Bundle of His and Bundle Branches): এভি নোড থেকে সংকেত বান্ডল অফ হিজ-এ যায় এবং তারপর বাম ও ডান বান্ডল শাখায় বিভক্ত হয়ে ইন্টারভেন্ট্রিকুলার সেপ্টাম (হৃদপিণ্ডের দুই ভেন্ট্রিকলের মাঝখানের দেয়াল) দিয়ে নিচের দিকে নামে।
- পারকিনজি ফাইবার (Purkinje Fibers): এই বিশেষ তন্তুগুলো ভেন্ট্রিকলের প্রাচীর জুড়ে ছড়িয়ে পড়ে এবং দ্রুত বৈদ্যুতিক সংকেত হৃদপেশী কোষগুলিতে পৌঁছে দেয়, যা ভেন্ট্রিকলের সমন্বিত সংকোচন শুরু করে।
এই বৈদ্যুতিক কার্যকলাপ একটি ইলেক্ট্রোকার্ডিওগ্রাম (EKG বা ECG) ব্যবহার করে পরিমাপ করা যায়, যেখানে পি ওয়েভ (অ্যাট্রিয়াল সংকোচন) এবং কিউআরএস কমপ্লেক্স (ভেন্ট্রিকুলার সংকোচন) হিসাবে এই ঘটনাগুলো দেখা যায়।
 HRTD Medical Institute
HRTD Medical Institute