Post Diploma Training in Dermatology (PDT-Dermatology) Course Details
Post Diploma Training in Dermatology. Mobile No. 01987-073965, 01797-522136. These Courses are 6 Months PDT-Dermatology, 1-Year PDT-Dermatology, and 2-Year PDT-Dermatology. 6 Month PDT Dermatology course Fee is Tk 35000/-, 1 Year PDT Dermatology Course Fee is Tk 65000/-, and 2 Years PDT Dermatology Course Fee Tk 125000/-. Each Semester of 6 Months contains 4 subjects and an exam mark of 400.

6 Month Post Diploma Training in Dermatology (PDT-Dermatology 6 Months) Course Details
6 Months Post-Diploma Training in Dermatology that is PDT-Dermatology 6 Months Course Fee 35000/-. The payment system is an Admission Fee of Tk 10000/-, Monthly Fee of Tk 4000/- and Exam Fee of Tk 1000. 6 Months PDT-Dermatology Course contains 4 subjects. You can choose any 4 of these subjects Skin Anatomy & Physiology, Dermatological Drugs, Common Skin Diseases, Fungal Infections, etc.

1 Year Post Diploma Training in Dermatology (PDT-Dermatology 1 Year) Course Details
1 Year Post-Diploma Training in Dermatology that is PDT-Dermatology 1 Year Course Fee Tk 65000/-. The payment system is an Admission Fee of Tk 15000/-, Monthly Fee of Tk 4000/- and Exam Fee of Tk 2000. 1 Year PDT-Dermatology Course contains 8 subjects. You can choose any 8 of these subjects Skin Anatomy & Physiology, Dermatological Drugs-1, Dermatological Drugs-2, Common Skin Diseases, Fungal Infections, Allergic Dermatitis, Bacterial Skin Diseases, Management of Eczema, etc.

2 Years Post Diploma Training in Dermatology (PDT-Dermatology 2 Years) Course Details
2 Years Post-Diploma Training in Dermatology that is PDT-Dermatology 2 Years Course Fee Tk 125000/-. The payment system is an Admission Fee of Tk 25000/-, a Monthly Fee of Tk 4000/-, and an Exam Fee of Tk 1000/- per Semester. 2 Years PDT-Dermatology Course contains 16 Subjects. Some subjects of PDT-Dermatology are Skin Anatomy & Physiology, Dermatological Drugs-1, Dermatological Drugs-2, Fungal Infections, Bacterial Skin Infections, Skin Biochemistry, Allergic Dermatitis, Management of Eczema, Skin Pigmentation, Skin Surgery, Pediatric Dermatology, Geriatric Dermatology, etc.
What is Dermatology?
Dermatology is the branch of medicine that focuses on the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of diseases and conditions affecting the skin, hair, nails, and mucous membranes. As the body’s largest organ, the skin serves as a protective barrier against environmental factors and reflects overall health.
চর্মরোগবিদ্যা হল চিকিৎসার একটি শাখা যা ত্বক, চুল, নখ এবং শ্লেষ্মা ঝিল্লিকে প্রভাবিত করে এমন রোগ এবং অবস্থার নির্ণয়, চিকিৎসা এবং প্রতিরোধের উপর দৃষ্টি নিবদ্ধ করে। শরীরের বৃহত্তম অঙ্গ হিসেবে, ত্বক পরিবেশগত কারণগুলির বিরুদ্ধে একটি প্রতিরক্ষামূলক বাধা হিসেবে কাজ করে এবং সামগ্রিক স্বাস্থ্যের প্রতিফলন ঘটায়।
What are the layers of Skin?
There are three layer of skin-
- Epidermis (Most outer layer or Dorsal layer)
- Dermis (Middle layer or Intermediate layer)
- Hypodermis (Inner layer or Ventral layer)
Layers of skin are discussed eleborately in Post Diploma Training in Dermatology Course.
What are the functions of skin?
Function of Skin-
1.Cover the body
2.Protect body from trauma and micro organism.
3.Maintain body temperature
4.Discharge seat from sweat gland
5. Absorbed ultra violet ray from sunlight for vitamin D Synthesis.
6.Adipose tissue in skin dermis layer is stored fat and provides energy when needed.
What are the common Bacterial Infections of the Skin?
Bacterial skin infections are caused by the invasion of bacteria into the skin and its underlying tissues, leading to various conditions that can range from mild to severe. Common bacterial skin infections include:
1. Impetigo
A highly contagious infection, impetigo primarily affects infants and young children. It presents as red sores on the face, especially around the nose and mouth, and on hands and feet. The sores rupture quickly, forming honey-colored crusts. Impetigo is commonly caused by Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes.
১. ইমপেটিগো
একটি অত্যন্ত সংক্রামক সংক্রমণ, ইমপেটিগো মূলত শিশু এবং ছোট বাচ্চাদের প্রভাবিত করে। এটি মুখে, বিশেষ করে নাক ও মুখের চারপাশে এবং হাতে ও পায়ে লাল ঘা হিসেবে দেখা দেয়। ঘাগুলি দ্রুত ফেটে যায়, মধুর রঙের ক্রাস্ট তৈরি করে। ইমপেটিগো সাধারণত স্ট্যাফিলোকক্কাস অরিয়াস এবং স্ট্রেপ্টোকক্কাস পাইওজেনেস দ্বারা সৃষ্ট হয়।
2. Cellulitis
This infection involves the deeper layers of the skin, including the dermis and subcutaneous tissue. Symptoms include redness, swelling, warmth, and pain in the affected area, often on the lower legs. If untreated, cellulitis can spread rapidly and become life-threatening. It is commonly caused by Staphylococcus and Streptococcus species.
MERCK MANUALS
২. সেলুলাইটিস
এই সংক্রমণ ত্বকের গভীর স্তরগুলিকে প্রভাবিত করে, যার মধ্যে রয়েছে ডার্মিস এবং ত্বকের নিচের টিস্যু। লক্ষণগুলির মধ্যে রয়েছে লালভাব, ফোলাভাব, উষ্ণতা এবং আক্রান্ত স্থানে ব্যথা, প্রায়শই নীচের পায়ে। যদি চিকিৎসা না করা হয়, তাহলে সেলুলাইটিস দ্রুত ছড়িয়ে পড়তে পারে এবং জীবন-হুমকির কারণ হতে পারে। এটি সাধারণত স্ট্যাফিলোকক্কাস এবং স্ট্রেপ্টোকক্কাস প্রজাতির কারণে হয়।
মার্ক ম্যানুয়াল
3. Erysipelas
A superficial form of cellulitis, erysipelas presents as a raised, clearly demarcated, red area of skin, typically on the face or legs. It is often accompanied by fever and chills. Streptococcus pyogenes is the usual causative agent.
৩. ইরিসিপেলাস
সেলুলাইটিসের একটি উপরিভাগের রূপ, ইরিসিপেলাস ত্বকের একটি উত্থিত, স্পষ্টভাবে চিহ্নিত, লাল অংশ হিসাবে উপস্থিত হয়, সাধারণত মুখ বা পায়ে। এর সাথে প্রায়শই জ্বর এবং ঠান্ডা লাগা থাকে। স্ট্রেপ্টোকক্কাস পাইজেনেস হল এর স্বাভাবিক কার্যকারক।
4. Folliculitis
An infection of the hair follicles, folliculitis appears as small, red bumps or white-headed pimples around hair follicles. It can be itchy or tender. Staphylococcus aureus is a common cause, but other bacteria, fungi, and viruses can also be responsible.
৪. ফলিকুলাইটিস
লোমকূপের সংক্রমণ, ফলিকুলাইটিস, লোমকূপের চারপাশে ছোট, লাল দাগ বা সাদা মাথার ব্রণ হিসাবে দেখা যায়। এটি চুলকানি বা ব্যথা হতে পারে। স্ট্যাফিলোকক্কাস অরিয়াস একটি সাধারণ কারণ, তবে অন্যান্য ব্যাকটেরিয়া, ছত্রাক এবং ভাইরাসও এর জন্য দায়ী হতে পারে।
5. Furuncles and Carbuncles
Furuncles, or boils, are deep folliculitis, presenting as painful, pus-filled nodules. Carbuncles are clusters of furuncles that form a connected area of infection under the skin. Both are commonly caused by Staphylococcus aureus.
৫. ফুরাঙ্কেল এবং কার্বাঙ্কেল
ফুরাঙ্কেল বা ফোঁড়া হল গভীর ফলিকুলাইটিস, যা বেদনাদায়ক, পুঁজভর্তি নোডুলস হিসেবে দেখা দেয়। কার্বাঙ্কেল হল ফুরাঙ্কেলের গুচ্ছ যা ত্বকের নীচে সংক্রমণের একটি সংযুক্ত স্থান তৈরি করে। উভয়ই সাধারণত স্ট্যাফিলোকক্কাস অরিয়াস দ্বারা সৃষ্ট হয়।
6. Abscesses
Localized collections of pus within tissues, abscesses result in swollen, red, and tender areas. They can occur anywhere on the body and are often caused by Staphylococcus aureus
৬. ফোড়া
কোষের ভেতরে পুঁজের স্থানীয় জমা, ফোড়ার ফলে ফোলা, লাল এবং কোমল জায়গা দেখা দেয়। এগুলি শরীরের যেকোনো স্থানে হতে পারে এবং প্রায়শই স্ট্যাফিলোকক্কাস অরিয়াসের কারণে হয়।
7.Necrotizing Skin Infections
These are severe infections that cause rapid tissue death. They require immediate medical attention and are often caused by Streptococcus pyogenes and Staphylococcus aureus
৭. নেক্রোটাইজিং স্কিন ইনফেকশন
এগুলি গুরুতর সংক্রমণ যা দ্রুত টিস্যুর মৃত্যু ঘটায়। এগুলির জন্য তাৎক্ষণিক চিকিৎসার প্রয়োজন এবং প্রায়শই স্ট্রেপ্টোকক্কাস পাইজেনেস এবং স্ট্যাফিলোকক্কাস অরিয়াস দ্বারা সৃষ্ট হয়।
These all infectious diseases are discussed in Post Diploma Training in Dermatology.
Subjects for Post Diploma Training In Dermatology
1st Semester Subject for Post Diploma Training In Dermatology
- Skin Anatomy & Physiology
- Drug Used In Dermatology
- Tineasis & Candidiasis
- Common Skin Disorder
These four subjects are discussed eleborately in 1st semester of Post Diploma Training in Dermatology Course.
2nd Semester Subjects For Post Diploma Training In Dermatology
- Cardiogenic Dermatology
- Neurogenic Dermatology
- Infection Skin Disorder
- Atopic Dermatitis
These four subjects are discussed eleborately in 2nd semester of Post Diploma Training in Dermatology Course.
3rd Semester Subjects For Post Diploma Training In Dermatology
- Fungal Infections
আরও বিস্তারিত জানতে আমাদের ওয়েবসাইট ভিজিট করুন ।।
পিডিটি কোর্স সমূহ জানতে ভিজিট করুন https://www.pdtms.com
ডিপ্লোমা এবং প্যারামেডিকেল কোর্স সমূহ জানতে ভিজিট করুন
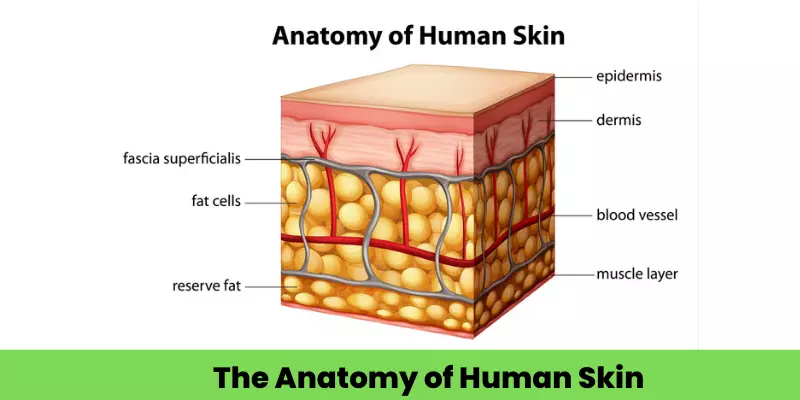
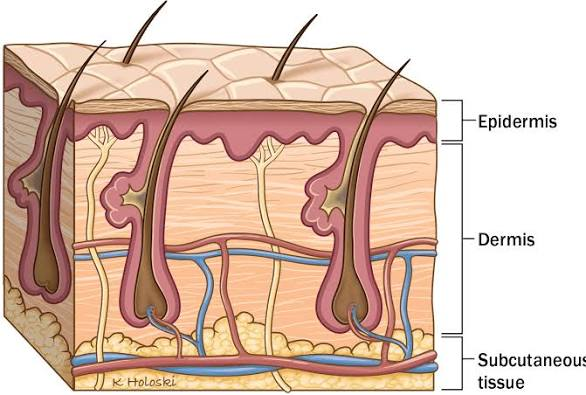
Skin Anatomy & Physiology for Dermatology
The skin is the body’s largest organ, consisting of three main layers: the epidermis (outer), dermis (middle), and hypodermis (innermost). Its primary functions include acting as a protective barrier against pathogens and injury, regulating body temperature through sweating and blood flow, and providing sensation via nerve receptors. The skin also plays a role in vitamin D synthesis and water regulation
Anatomy of the skin layers
- Epidermis: The outermost layer, it is avascular and provides a waterproof barrier. It contains melanocytes for skin tone and is made f several sub-layers, including the stratum corneum (the outermost protective layer) and the stratum basale (where new cells are made).
- Dermis: Located beneath the epidermis, this layer is thicker and contains connective tissue, blood vessels, nerves, hair follicles, and sweat glands.
- Papillary dermis: The thinner, upper layer of the dermis.
- Reticular dermis: The thicker, lower layer that contains dense connective tissue, blood vessels, and nerves.
- Hypodermis: The deepest layer, also known as subcutaneous tissue, it is composed of fat and connective tissue. Its functions include insulation and shock absorption.
Physiology and functions of the skin
- Protection: The skin forms a physical barrier against pathogens, UV radiation, and physical injury.
- Thermoregulation: It helps control body temperature through vasodilation and vasoconstriction of blood vessels and by producing sweat for evaporative cooling.
- Sensation: Nerve endings in the dermis detect pressure, pain, and temperature.
- Vitamin D synthesis: The epidermis synthesizes vitamin D when exposed to UV light.
- Water resistance: The skin prevents excessive water loss from the body through a process called transepidermal water loss (TEWL).
- Excretion: Sweat glands excrete water and small amounts of electrolytes.
Drug Used In Dermatology for Diploma Training In Dermatology
Drugs used in dermatology are categorized into topical (applied to the skin) and systemic (taken orally or by injection) forms, depending on the condition being treated. Common classes include corticosteroids, antibiotics, antifungals, retinoids, and newer targeted therapies like biologics
Common Drug Classes in Dermatology
| Drug Class | Examples | Common Conditions Treated | Administration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Corticosteroids | Hydrocortisone, clobetasol, prednisone | Eczema, psoriasis, inflammatory conditions, poison ivy rashes | Topical, Oral, Injection |
| Antibiotics | Clindamycin, doxycycline, amoxicillin, mupirocin | Acne, impetigo, bacterial skin infections | Topical, Oral |
| Antifungals | Clotrimazole, ketoconazole, terbinafine | Athlete’s foot, ringworm, fungal nail infections | Topical, Oral |
| Retinoids | Tretinoin, adapalene, isotretinoin | Acne, psoriasis, signs of aging, some skin cancers | Topical, Oral |
| Antivirals | Acyclovir, valacyclovir | Herpes simplex (cold sores), shingles | Topical, Oral |
| Immunosuppressants & Biologics | Methotrexate, azathioprine, adalimumab, dupilumab | Severe psoriasis, severe eczema, autoimmune skin diseases | Oral, Injection |
| Keratolytics | Salicylic acid, urea | Warts, acne, scaling conditions (e.g., seborrheic dermatitis) | Topical |
| Antihistamines | Diphenhydramine (oral), doxepin (topical/oral) | Itching associated with various skin conditions | Topical, Oral |
- Topical vs. Systemic: Topical treatments are often preferred for localized issues to achieve high drug concentrations in the skin with minimal systemic exposure. Systemic drugs are generally reserved for more severe, widespread, or persistent conditions that do not respond to topical therapy.
- Side Effects: All medications carry potential side effects. For instance, topical corticosteroids can lead to skin thinning with prolonged use, while oral retinoids can cause birth defects and require careful monitoring.
- Consult a Professional: It is important to consult a dermatologist or healthcare provider before starting any new treatment to ensure the correct diagnosis and appropriate medication are selected, as treatments and potential risks vary significantly between conditions and drug types. You can find a dermatologist through resources like the American Academy of Dermatology (for US-based information).
Tineasis & Candidiasis for Diploma Training In Dermatology
Tineasis (tinea infections) and candidiasis are both common fungal infections, but they are caused by different types of fungi and have distinct characteristics and treatment approaches. Tineasis is caused by dermatophytes (molds), while candidiasis is caused by yeasts, primarily the Candida species.
Tineasis (Ringworm)
Tineasis, also known as ringworm, is a group of infections caused by a type of mold called dermatophytes (Trichophyton, Epidermophyton, Microsporum genera). These fungi thrive on keratin found in the skin, hair, and nails and do not typically affect internal organs.
- Common Types & Locations: Tinea is named for the body part it affects, such as tinea pedis (athlete’s foot), tinea cruris (jock itch), tinea corporis (body ringworm), and tinea capitis (scalp ringworm).
- Symptoms: Tinea often presents as a red, scaly, dry rash, sometimes with a classic ring shape where the outer edge is raised and the center is clear.
- Transmission: It is contagious and can spread through direct contact with infected people, animals, or contaminated surfaces (e.g., clothing, shower floors).
- Treatment: Antifungal creams and powders containing ingredients like terbinafine or clotrimazole are common. For severe or persistent cases, oral antifungal medications may be prescribed.
Candidiasis (Yeast Infection)
Candidiasis is an infection caused by an overgrowth of Candida, a type of yeast that naturally lives on the body but can cause problems when an imbalance occurs. Unlike tinea, Candida can cause serious internal infections (invasive candidiasis), especially in people with weakened immune systems.
- Common Locations: It tends to occur in warm, moist, creased areas like the armpits, groin, under the breasts, and in the mouth (oral thrush) or vagina (vaginal yeast infection).
- Symptoms: Candidiasis typically presents as a bright red, moist rash with small red bumps or pustules (satellite lesions) on the periphery. Other symptoms include itching, burning, and abnormal discharge depending on the location.
- Transmission: It is not considered contagious in the same way as tinea; rather, it results from an overgrowth of yeast already present on the body, often due to factors like antibiotic use, uncontrolled diabetes, or a weakened immune system.
- Treatment: Antifungal creams (e.g., nystatin, miconazole) and oral medications (e.g., fluconazole) are used for treatment.
| Feature | Tineasis (Ringworm) | Candidiasis (Yeast Infection) |
|---|---|---|
| Causative Agent | Dermatophyte molds | Candida yeast |
| Appearance | Dry, scaly, often ring-shaped | Red, moist, satellite lesions |
| Contagion | Contagious | Generally not contagious (internal overgrowth) |
| Invasiveness | Stays on skin/hair/nails | Can become invasive (spread to organs) |
Common Skin Disorder for Diploma Training In Dermatology
The most common skin disorders include acne, eczema (atopic dermatitis), psoriasis, contact dermatitis, and fungal infections. While most are not life-threatening, they can significantly impact a person’s quality of life, self-esteem, and daily activities
Common Skin Disorders
| Condition | Symptoms | Causes | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acne | Pimples, blackheads, whiteheads, and deep cysts, often on the face, back, and chest. | Clogged pores by oil and dead skin cells, hormonal changes, bacteria, and inflammation. | Over-the-counter creams (benzoyl peroxide, salicylic acid), prescription retinoids, or oral medications in severe cases. |
| Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis) | Dry, intensely itchy, scaly, and red or discolored patches of skin, often in the creases of the elbows and knees. | Genetics, immune system dysfunction, and environmental triggers. | Moisturizers, topical steroid creams, antihistamines for itching, and avoiding triggers. |
| Psoriasis | Thick, red patches covered with silvery scales, which can be itchy or painful. | Autoimmune disorder that speeds up skin cell production. | Topical creams, light therapy, and systemic medications like biologics for severe cases. |
| Contact Dermatitis | Inflamed, itchy, and sometimes blistering or crusting rash due to contact with an irritant or allergen. | Contact with substances like poison ivy, soaps, detergents, or certain metals (e.g., nickel). | Avoiding the trigger, antihistamines, and topical steroid creams. |
| Fungal Infections | Redness, itching, and peeling skin (e.g., athlete’s foot, ringworm, jock itch). | Fungi that thrive in warm, moist areas. | Antifungal creams, sprays, or oral medications for persistent infections. |
| Rosacea | Facial redness, flushing, visible blood vessels, and sometimes acne-like bumps. | Immune system issues, vein problems, and environmental triggers. | Antibiotic creams or oral medications, beta-blockers, and laser therapy. |
When to Seek Medical Attention
While many conditions can be managed with home treatment, it is important to see a healthcare professional, such as a dermatologist, if symptoms are severe, persistent, or worsening. Prompt medical advice should be sought for:
- Rashes that spread quickly or are accompanied by a fever.
- Unexplained skin changes, especially in moles or growths (which could indicate skin cancer).
- Open sores or blisters that do not heal.
- Skin infections with severe pain, swelling, or warmth.
For further information on common skin disorders, you can visit the American Academy of Dermatology.
 HRTD Medical Institute
HRTD Medical Institute






2 comments
Pingback: Post-Diploma Training in Cardiology...........
Pingback: Best Post Diploma Training in Pediatrics (PDT-Pediatrics) Courses 1 year