Diploma Dental Assistant (DDA 2 Years):
Diploma Dental Assistant (DDA 2 Years): Mobile No. 01987-073965, 01941-123488, 01797-522136. A Diploma Dental Assistant Course of 2 years duration is a medium type of dental diploma course in Bangladesh. This course contains 18 subjects in 4 semesters. The 1st semester contains 5 subjects and 2nd semester contains 5 subjects. 3rd Semester contains 4 subjects & 4th Semester contains 4 subjects.
Subjects of 1st and 2nd semesters:
Subjects of 1st semester are Human Anatomy & Physiology-1, Chemistry & Pharmacology-1, First Aid & Treatment, Hematology & Pathology, and Study of OTC Drugs. 2nd Semester contains Anatomy of the Head and Neck, Neuro anatmy & Physiology, Dental Anatomy & Physiology-1, Dental Pathology & Dental Caries-1, Conservative Dentistry & Dental Surgery-1.

Subjects of 3rd and 4th semesters:
3rd Semester contains Orthopedic Anatomy & Physiology, Cardiovascular Anatomy & Physiology, Microbiology & Antimicrobial Drugs, And Dental Sterilization. The 4th semester contains Dental Anatomy & Physiology-2, Dental Pharmacology, Conservative Dentistry & Dental Surgery-2, And Clinical Practice in Dental Surgery-1.
Location of Diploma Dental Assistant Course in Dhaka
Location of Diploma Dental Assistant Training Center. Mobile No. 01987-073965. HRTD Medical Institute, Abdul Ali Madbor Mansion, Section-6, Block-Kha, Road-1, Plot-11, Mirpur-10 Golchattar, Metro Rail Piller No. 249, Dhaka-1216.
Course Fee Summary:
Total Course Fee Tk 92,500 including Admission Fee, Monthly Fee, and Exam Fee.
Admission Fee Tk 16500, Monthly Fee Tk 3000×24=Tk 72,000, Exam Fee Tk 1000×4 =Tk 4000.
Our YouTube Videos of Dental at HRTD Medical Institute, Mirpur 10, Dhaka-1216
Our Others Course:
Pharmacy Course, Dental Course, Nursing Course, Pathology Course, Homeopathy Course, Veterinary Course, Village Doctor Course, PDT( Post Diploma Training) Course, PPT, LMAF Training Course, LMAFP Course, Poultry Course, DMA ( Diploma Medical Assistant), Diploma in Medicine and Surgery (DMDS).
Job Opportunities After Completed Diploma Dental Assistant (DDA) Course
Jobs are available in Bangladesh and many other countries as dental assistants, dental technicians, or dental technologists. Each and every busy dental surgeon needs at least 2 to 3 dental technicians or Dental Assistant for the proper surgical treatment in his/her chamber or dental clinic.
Practical Class For Diploma Dental Assistant (DDA) Course
- Blood Pressure
- Hypertension & Hypotension
- Heart beat ,Heart rate, Heart Sound, Pulse
- Tooth Anatomy
- Headneck Anatomy
- Instrument Identify
- Scaling
- Diagnosis Procedure
- Filling Materials
- Root Canal Treatment
- Canal Shaping
- Obturation Sealing
- Children root canal treatment
- X-ray taking Procedure
- Crown Preparation for cap
- RPD Making (denture)
- Stitching
- Extraction Procedure
- Impress & Model making
- First Aid Box
- Auscultation
- Inhaler,Rotahaler
- Diabetes
- Injection I/V & I/M
Teachers for Diploma Dental Assistant Course
Dr. Sanjana Bite Ahmed, BDS, MPH
Dr. Sakulur Rahman, MBBS, CCD (BIRDEM)
Dr. Nurunnahar Keya, BDS,
Dr. Nazmun Nahar Juthi, BDS, PGT
Dr. Kamrunnahar Keya, BDS, PGT
Dr. Suhana, MBBS, PGT
Dr. Layla, MBBS, PGT
Dr. Lamia, MBBS
Dr. Disha, MBBS, FCPS (FP)
Dr. Afrin, MBBS, PGT
Dr. Tisha, MBBS, PGT
Dr. Danial Haque, MBBS, CCD
Dr. Turzo, MBBS, FCPS (FP)
Dr. Benzir, MBBS, FCPS (FP)
Dr. Trisha, MBBS, PGT
Dr. Farhana, MBBS, PGT
Dr. Jannatul Aman, MBBS, PGT
Dr. Mahinul Islam, MBBS
Dr. Amena Afroze Anu, MBBS, PGT

What is Dental Scaling?
Dental scaling is dental cleaning by a caller dental machine. This is routinely performed to help patients with gum disease and excessive plaque buildup. While a standard cleaning will address the surface of the tooth, scaling goes much deeper. If your dentist suggests dental scaling and root planing for your teeth, you should do this otherwise your teeth may be damaged day after day.
What is Dental Filling?
A dental filling is the fill-up of a small dental hole or cavity. To repair a cavity, a dentist removes the decayed tooth tissue and then fills the space with a filling material. The filling materials are of various types. Some are long-lasting and some are shot-lasting.
Causes of dental filling
When decay-causing bacteria come into contact with sugars and starches from foods and drinks, they form an acid. This acid can attack the tooth’s surface (enamel), causing it to lose minerals.
When a tooth is repeatedly exposed to acid, such as when you frequently consume food or drink high in sugar and starches, the enamel continues to lose minerals. A white spot may appear where minerals have been lost. This is a sign of early decay.
Tooth decay can be stopped or reversed at this point. Enamel can repair itself by using minerals from saliva and fluoride from toothpaste or through the application of fluoride by a dentist or dental hygienist. If more minerals are lost than can be restored, the enamel weakens and eventually breaks down, forming a cavity.
More severe decay can cause a large hole or even destruction of the entire tooth. If tooth decay is not treated, it can cause pain, infection, and even tooth loss. So dental filling treatment is very essential for a cavity patient.
What are the 5 dental problems?
Dentistry is one of the oldest fields of medicine, and it is vitally important to our overall health and well-being. That said, it is also one of the most commonly neglected aspects of health care, with many people failing to receive regular dental checkups and cleanings.
Unfortunately, this opens the door to a wide range of dental problems, all of which can have serious consequences if left untreated. Here are five of the most common dental problems:
1. Tooth Decay: Tooth decay is one of the most common dental problems and is caused by a buildup of plaque and bacteria on the teeth. Over time, this buildup can lead to cavities and tooth decay, which can cause serious pain and discomfort.
2. Gum Disease: Gum disease is caused by bacteria and plaque that accumulates at the gum line. If left untreated, it can lead to gum recession, tooth loss, and even bone loss.
3. Tooth Sensitivity: Tooth sensitivity is caused by a thinning of the enamel, which is the outer layer of the tooth. This can lead to pain when consuming hot or cold foods and drinks.
4. Tooth Abrasion: Tooth abrasion is caused by improper brushing techniques and can lead to the erosion of the enamel. Over time, this can cause the teeth to become more sensitive and can even lead to tooth loss.
5. Malocclusion: Malocclusion is the misalignment of the teeth, either due to genetics or other factors. This can lead to difficulty speaking and eating, as well as a higher risk of tooth decay and gum disease.
These five dental problems are just some of the many that can occur if proper oral hygiene is not maintained. Regular visits to the dentist for checkups and cleanings can help to prevent and address these issues and is essential for maintaining a healthy smile.
Class Time for Diploma Dental Assistant (DDA) Course
Weekly Class 3 hours. For Regular Students Friday 1 hour, Saturday 1 hour, and Monday 1 hour. For Job holders, Friday is 3 hours, or Monday is 3 hours. Morning Shift 9:00 am to 12:00 pm, and Evening Shift 3:00 pm to 6:00 pm.
Total Subjects for Diploma Dental Assistant (DDA) Course
DDA 1st year Subjects-
- Chemistry & Pharmacology,
- Human Anatomy & Physiology,
- First Aid & Treatment,
- Hematology & Pathology,
- Study of OTC Drugs,
- Anatomy of the Head and Neck,
- Neuro Anatomy & Physiology,
- Dental Anatomy & Physiology,
- Dental Pathology & Dental Caries,
- Conservative Dentistry & Dental Surgery.
DDA 2nd Year Subjects:
- Orthopedic Anatomy & Physiology,
- Cardiovascular Anatomy & Physiology,
- Microbiology & Antimicrobial Drugs,
- Dental Sterilization,
- Dental Anatomy & Physiology-2,
- Dental Pharmacology,
- Conservative Dentistry and Dental Surgery-2,

Human Anatomy and Physiology for Diploma Dental Assistant (DDA) Course
The study of the Body Structure and its functions is Anatomy and Physiology. Here we discuss the systems of the Human Body and its Organs, Tissues, and Cells. The systems of the Human Body are the Digestive System, Respiratory System, Cardiovascular System, Skeletal System, Muscular System, Nervous System, Endocrine System, Immune System, Lymphatic System, Integumentary System, and Urinary System.
Anatomy (অ্যানাটমি) কী?
Anatomy হচ্ছে মানবদেহের গঠন বা কাঠামো সম্পর্কিত বিজ্ঞান। এটি জানায় দেহের অঙ্গপ্রত্যঙ্গ কোথায় থাকে, তাদের আকার, অবস্থান ও সম্পর্ক কেমন।
উদাহরণ:
হৃদপিণ্ড (Heart) কোথায় অবস্থিত
কঙ্কাল (Skeleton), স্নায়ু (Nerves), পেশি (Muscles) এর গঠন
হাড়, মাংসপেশি, অঙ্গপ্রত্যঙ্গ কীভাবে যুক্ত
Physiology (ফিজিওলজি) কী?
Physiology হচ্ছে দেহের অঙ্গপ্রত্যঙ্গ কিভাবে কাজ করে তা নিয়ে আলোচনা। এটা বলে শরীরের ভেতরে কীভাবে কাজ হয় এবং কিভাবে শরীর সুস্থ থাকে।
উদাহরণ:
- হৃদপিণ্ড কিভাবে রক্ত পাম্প করে
- ফুসফুস কিভাবে অক্সিজেন নেয়
- পরিপাকতন্ত্র (Digestive system) কিভাবে খাবার হজম করে
মানবদেহের প্রধান ১১টি সিস্টেম (Human Body Systems):
| সিস্টেমের নাম (বাংলা) | ইংরেজি নাম | কাজ |
|---|---|---|
| ১. অস্থি তন্ত্র | Skeletal System | শরীরের কাঠামো তৈরি করে |
| ২. পেশি তন্ত্র | Muscular System | চলাফেরা ও গতি নিয়ন্ত্রণ |
| ৩. স্নায়ুতন্ত্র | Nervous System | তথ্য আদান-প্রদান ও নিয়ন্ত্রণ |
| ৪. শ্বাসতন্ত্র | Respiratory System | শ্বাস গ্রহণ ও কার্বন ডাই-অক্সাইড বের করা |
| ৫. রক্ত সংবহন তন্ত্র | Circulatory System | রক্ত ও পুষ্টি পরিবহন |
| ৬. পরিপাক তন্ত্র | Digestive System | খাবার হজম ও পুষ্টি গ্রহণ |
| ৭. বর্জ্য নিষ্কাশন তন্ত্র | Excretory System | দেহের বর্জ্য অপসারণ |
| ৮. প্রজনন তন্ত্র | Reproductive System | সন্তান উৎপাদন |
| ৯. অন্তঃস্রাব তন্ত্র | Endocrine System | হরমোন নিঃসরণ ও নিয়ন্ত্রণ |
| ১০. ত্বক/চর্ম তন্ত্র | Integumentary System | ত্বক, চুল, নখ সুরক্ষা প্রদান |
| ১১. রোগ প্রতিরোধ তন্ত্র | Immune System | রোগ থেকে রক্ষা |
Digestive System in Bangla (পরিপাকতন্ত্র)
পরিপাকতন্ত্র কী?
পরিপাকতন্ত্র হলো একগুচ্ছ অঙ্গপ্রত্যঙ্গের সমন্বয়ে গঠিত একটি তন্ত্র, যা খাবার হজম করে, পুষ্টি শোষণ করে এবং বর্জ্য পদার্থ শরীর থেকে বের করে দেয়।
🧾 পরিপাকতন্ত্রের প্রধান অঙ্গসমূহ ও তাদের কাজ:
| অঙ্গের নাম | কাজ |
|---|---|
| ১. মুখ (Mouth) | চিবিয়ে খাবার ছোট ছোট অংশে পরিণত করা, লালা দিয়ে নরম করা |
| ২. গ্রাসনালী (Esophagus) | মুখ থেকে পাকস্থলীতে খাবার সরবরাহ করা |
| ৩. পাকস্থলী (Stomach) | এসিড ও এনজাইম দিয়ে খাবার গলানো ও প্রাথমিক হজম |
| ৪. ক্ষুদ্রান্ত্র (Small Intestine) | এনজাইম দ্বারা খাবার হজম সম্পূর্ণ ও পুষ্টি শোষণ |
| ৫. বৃহদান্ত্র (Large Intestine) | পানি শোষণ করে মল তৈরি করা |
| ৬. রেকটাম ও মলদ্বার (Rectum & Anus) | মল সংরক্ষণ ও দেহ থেকে অপসারণ |
Respiratory System in Bangla (শ্বাসতন্ত্র)
📌 শ্বাসতন্ত্র কী?
শ্বাসতন্ত্র হলো এমন একটি অঙ্গতন্ত্র, যার মাধ্যমে আমরা অক্সিজেন গ্রহণ করি এবং কার্বন ডাই-অক্সাইড বের করে দেই। এটি আমাদের শরীরে অক্সিজেন সরবরাহ করে, যা জীবিত থাকার জন্য অত্যন্ত প্রয়োজনীয়।
🫁 শ্বাসতন্ত্রের প্রধান অঙ্গসমূহ:
| অঙ্গের নাম (বাংলা) | অঙ্গের নাম (ইংরেজি) | কাজ |
|---|---|---|
| নাক | Nose | বাতাস প্রবেশ করে, ধুলাবালি ও জীবাণু ছেঁকে ফেলে |
| গলা / ফ্যারিংস | Pharynx | নাক ও মুখ থেকে বাতাস শ্বাসনালীতে পৌঁছে দেয় |
| কণ্ঠনালী / ল্যারিংস | Larynx | শ্বাস ও স্বর নিয়ন্ত্রণ করে (এখানে কণ্ঠস্বর তৈরি হয়) |
| শ্বাসনালী | Trachea | ফুসফুসে বাতাস প্রবাহিত করে |
| ব্রঙ্কাস | Bronchi | শ্বাসনালীর দুটি শাখা, যা দুই ফুসফুসে বাতাস পাঠায় |
| ব্রঙ্কিওলস | Bronchioles | ব্রঙ্কাস থেকে আরও ছোট শাখা, যা ফুসফুসের ভেতরে ছড়িয়ে থাকে |
| অ্যালভিওলি | Alveoli | ক্ষুদ্র বায়ুথলি, যেখানে গ্যাসের বিনিময় হয় |
| ফুসফুস | Lungs | শ্বাসতন্ত্রের মূল অঙ্গ, গ্যাস বিনিময় করে |
| ডায়াফ্রাম | Diaphragm | পেশি যা শ্বাস-প্রশ্বাসে সাহায্য করে |
Pharmacology-1 for Diploma Dental Assistant (DDA) Course
The study of Drugs and Medicine is called Pharmacology. Here we discuss group-wise drugs and their medicines in Pharmacology-1. Common Groups of Drugs are Pain Killer Drugs, Anti Ulcer Drugs, Anti Vomiting Drugs, Laxative Drugs, Motility Drugs, Antimotility Drugs, Bronchodilator Drugs, Antibiotic Drugs, Anti Fungal Drugs, Anti Protozoal Drugs, Anti Viral Drugs, Anthelmintic Drugs, Anti Hypertensive Drugs, Beta Blocker Drugs, Calcium Channel Blocker Drugs, ACE Inhibitor Drugs, Hemostatic Drugs, Analgesic Drugs, Antipyretic Drugs, Anti Thrombotic Drugs, etc.
Pharmacology (ফার্মাকোলজি or ঔষধবিজ্ঞান) is the scientific study of drugs (ওষুধ) and their interactions with living systems. It explores what drugs do to the body and what the body does to the drugs. This subject is crucial in medical and dental education in Bangladesh, taught in both English and Bengali to ensure a comprehensive understanding
The study of pharmacology is divided into two main areas:
- Pharmacokinetics (ফার্মাকোকাইনেটিক্স or ঔষধসঞ্চরণবিজ্ঞান): This branch studies what the body does to the drug. It involves the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) of a chemical compound within the body.
- Example: How quickly a painkiller is absorbed into the bloodstream (রক্তপ্রবাহে শোষিত হওয়া) and how the liver breaks it down (যকৃতে বিপাক).
- Pharmacodynamics (ফার্মাকোডাইনামিক্স or ঔষধক্রিয়াবিজ্ঞান): This branch studies what the drug does to the body. It explores the mechanism of drug action, where drugs bind to target molecules (like receptors or enzymes) to produce a therapeutic effect or side effects.
- Example: How a local anesthetic blocks nerve signals (স্নায়ু সংকেত বন্ধ করা) to numb an area during a dental procedure.
Terminology in English and Bengali
| English Term | Bengali Translation | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Drug/Medicine | ওষুধ / ঔষধ | A substance used to diagnose, prevent, or treat a disease. |
| Dose | মাত্রা | The specific amount of a drug to be administered. |
| Side Effect | পার্শ্বপ্রতিক্রিয়া | An unintended effect of a drug that occurs at a normal dose. |
| Mechanism of Action | কার্যপ্রণালী | How a drug produces its effect in the body. |
| Prescription | প্রেসক্রিপশন | An order for medication issued by a licensed medical practitioner. |
| Antibiotic | অ্যান্টিবায়োটিক | A medicine that kills or inhibits the growth of bacteria. |
Significance in Dental Courses
For dental students, pharmacology focuses on Dental Therapeutics (ডেন্টাল থেরাপিউটিক্স) and includes:
- Local anesthetics (স্থানীয় অবেদনিক).
- Analgesics (ব্যথা উপশমকারী).
- Antibiotics (অ্যান্টিবায়োটিক) used for oral infections.
- Understanding drug interactions and how certain systemic drugs (e.g., blood thinners) affect dental procedures.
First Aid for Diploma Dental Assistant Course (DDA)
First Aid is an important subject for Medical Courses including Diploma in Dental, Diploma in Medicine& Surgery Course, RMP Courses, LMAF Courses, Paramedical Courses, DMA Courses, DMS Courses, Nursing Courses, Dental Courses, Pathology Courses, Physiotherapy Courses, Caregiver Courses, etc. Here we discuss Shock, Classification Shock, Causes of Shock, Stages of Shock, Clinical Features of Shock, Hypovolemic Shock, Cardiogenic Shock, Neurogenic Shock, Traumatic Shock, Burn Shock, Electric Shock, Psychogenic Shock, Anaphylactic Shock, First Aid of Shock, First Aid of Cut, First of Snake Bite, First Aid of Accidental Injury, etc.
First aid for a dental course focuses on managing medical emergencies that might arise within a dental clinic setting, as well as providing immediate care for acute traumatic dental injuries. The training goes beyond general first aid to cover specific scenarios faced by dental professionals.
Medical Emergencies in a Dental Setting
Dental professionals are trained to prevent, recognize, and manage a range of medical crises, as these can happen to any patient, regardless of their medical history. The most common emergencies include:
- Syncope (Fainting): The most frequent emergency in a dental office, often caused by anxiety or pain. Management involves positioning the patient in the Trendelenburg (supine with feet elevated) position and ensuring an open airway.
- Hyperventilation (Panic Attack): Usually anxiety-induced rapid breathing, managed by calming the patient and having them breathe into a paper bag or cupped hands to restore
CO2 levels.
- Allergic Reactions/Anaphylaxis: Ranging from minor skin rashes to life-threatening anaphylactic shock. Management includes administering antihistamines for mild cases and epinephrine (adrenaline) via intramuscular injection immediately for anaphylaxis.
- Asthma Attack: Helping the patient use their own bronchodilator inhaler (e.g., salbutamol) and administering oxygen if necessary.
- Hypoglycemia (Low Blood Sugar): A diabetic emergency. If the patient is conscious, oral glucose (e.g., orange juice, sugar packets) is administered. If unconscious, glucagon injection is used.
- Chest Pain (Angina/Heart Attack): Involves stopping treatment, positioning the patient comfortably, administering aspirin, and calling emergency services.
- Seizures (Epileptic Fits): Protecting the patient from injury, not putting anything in their mouth, and placing them in the recovery position after the seizure subsides.
- Airway Obstruction: Due to the supine position and use of small instruments, choking on materials is a risk. Dental staff are trained in the Heimlich maneuver (abdominal thrusts) and CPR.
First Aid কি?
First Aid হলো—কোনো আঘাত, ব্যথা বা জরুরি অবস্থায় তৎক্ষণাৎ দেওয়া মৌলিক চিকিৎসা, যাতে রোগীর অবস্থা খারাপ না হয় এবং সঠিক চিকিৎসা না পাওয়া পর্যন্ত রোগীকে স্থিতিশীল রাখা যায়।
Dental First Aid মানে হলো দাঁত-মুখের যেকোনো ক্ষত, ব্যথা বা emergency অবস্থায় দ্রুত দেওয়া সেই মৌলিক চিকিৎসা, যা bleeding নিয়ন্ত্রণ, ব্যথা কমানো এবং সংক্রমণ রোধ করতে সাহায্য করে।”
Dental First Aid-এর উদ্দেশ্য
- ব্যথা বা bleeding কমানো
- সংক্রমণ রোধ করা
- রোগীকে শান্ত ও স্থিতিশীল রাখা
- হাসপাতালে নেওয়ার আগ পর্যন্ত সহায়তা দেওয়া
Dental Clinic-এ সাধারণ জরুরি অবস্থা
Toothache (দাঁতের ব্যথা)
First Aid:
- উষ্ণ লবণ পানি দিয়ে কুলি
- খাবার আটকে থাকলে ফ্লস করে পরিষ্কার
- ঠান্ডা compress গালে লাগানো
- OTC painkiller (যেমন Paracetamol) দেওয়া যেতে পারে
- গরম পানির সেক বা aspirin দাঁতে লাগানো যাবে না
Bleeding After Extraction (উপড়ে ফেলার পর রক্তপাত)
First Aid:
- গজ বা টি ব্যাগ দাঁতের জায়গায় চেপে ধরতে হবে 20–30 মিনিট
- মাথা উঁচু করে বসে থাকতে হবে
- থুথু ফেলা বা কুলি করা যাবে না
- bleeding বন্ধ না হলে dentist-এর কাছে পাঠাতে হবে
Soft Tissue Injury (ঠোঁট/গাম কেটে যাওয়া)
First Aid:
- জায়গা ঠান্ডা পানিতে ধোয়া
- গজ দিয়ে চাপ দিয়ে রক্ত থামানো
- ঠান্ডা compress লাগানো
- গভীর কাটা হলে হাসপাতালে পাঠাতে হবে
Broken Tooth / Fractured Tooth (দাঁত ভেঙে যাওয়া)
First Aid:
- ভাঙা অংশ থাকলে দুধ বা স্যালাইনে রেখে dentist-এর কাছে নিয়ে যেতে হবে
- রক্তপাত থাকলে গজ চেপে ধরা
- ঠান্ডা compress
Dental First Aid Box-এ যা থাকা উচিত
- Sterile gauze
- Cotton rolls
- Saline
- Gloves
- Cold pack
- Tongue depressor
- OTC painkillers (Paracetamol/Ibuprofen)
- Antiseptic mouth rinse
- Epinephrine auto-injector (Emergency)
- Blood pressure machine
- Oxygen cylinder (Emergency setup)
Study of OTC Drugs for Diploma Dental Assistant (DDA) Course
OTC Drugs are important for Diploma in Dental Course, Diploma Dental Assistant Course, all Medical Assistant Courses, Diploma Medical Courses, LMAF Courses, and RMP Courses. It is also important for the Diploma in Medicine & Diploma in Surgery Course. These OTC Drugs can be sold or purchased without any prescription from Registered MBBS Doctors. These Drugs are Emergency and Safe for the patients. The study of OTC Drugs improves the quality of practice. Some OTC Drugs are Albendazole, Ascorbic Acid, Calcium, Multivitamins, Vitamin B Complex, Omeprazole, Oral Rehydration Salt, Salbutamol, etc.
OTC Drug কী?
OTC (Over-the-Counter) Drug হলো এমন ওষুধ যা ডাক্তারের প্রেসক্রিপশন ছাড়াই সাধারণ ফার্মেসি থেকে কেনা যায়।
এগুলো সাধারণত নিরাপদ, ডোজ সহজ, এবং ছোটখাটো সমস্যা সামলাতে ব্যবহৃত হয়।
Dental Course-এ কেন OTC Drug পড়ানো হয়?
কারণ রোগীরা সবচেয়ে বেশি দাঁতের ব্যথা, মাড়ির সমস্যা, মুখের দুর্গন্ধ, আলসার ইত্যাদিতে প্রথমেই OTC ওষুধ ব্যবহার করে।
Dental student হিসেবে এগুলো জানা দরকার যাতে—
- সঠিক পরামর্শ দেওয়া যায়
- ক্ষতিকর ব্যবহার এড়ানো যায়
- patient counseling করা যায়
OTC Drug-এর সাধারণ বৈশিষ্ট্য
- প্রেসক্রিপশন লাগে না
- নিরাপত্তা লেভেল বেশি
- সহজ ডোজ
- পার্শ্বপ্রতিক্রিয়া কম
- বাড়িতে ব্যবহারের জন্য সুবিধাজনক
OTC Drug-এর গুরুত্ব (Dental Perspective)
OTC ওষুধ helps in:
- Dental pain
- Mucosal irritation
- Mouth ulcers
- Bad breath
- Gum sensitivity
- Minor gingivitis
- Oral hygiene maintenance
OTC Drugs—Classification (Dental Use অনুযায়ী)
1️⃣ Analgesics (ব্যথানাশক)
ব্যবহার: দাঁতের ব্যথা, swelling
- Paracetamol
- Ibuprofen
- Aspirin (দাঁতে লাগানো যাবে না)
2️⃣ Oral Antiseptics (মুখের জীবাণুনাশক)
- Chlorhexidine Mouthwash (0.12% বা 0.2%)
- Listerine বা অন্যান্য antiseptic rinse
3️⃣ Topical Oral Anesthetics (লোকাল অবশ জেল)
ব্যবহার: মাউথ আলসার, minor wound pain
- Benzocaine gel
- Lidocaine gel (OTC strength)
4️⃣ Toothpaste & Oral Care Products
- Fluoride toothpaste
- Sensitivity toothpaste (Potassium Nitrate)
- Whitening products
- Ulcer healing gel (Hyaluronic acid gel)
5️⃣ Antihistamines (অ্যালার্জি নিয়ন্ত্রণ)
ব্যবহার: oral allergy, swelling
- Cetirizine
- Loratadine
6️⃣ Gastrointestinal OTC (Dental pain mimic cases)
- Antacids (Gelusil)
- OTC PPI (low dose)
OTC Dose (General Idea)
(শুধু অধ্যয়নের জন্য, clinical ব্যবহার নয়)
- Paracetamol: 500–1000 mg (6 ঘণ্টা পর)
- Ibuprofen: 200–400 mg (8 ঘণ্টা পর)
- Mouthwash: দিনে 2 বার কুলি
- Topical gel: দিনে 3–4 বার সামান্য করে
OTC Drug ব্যবহার করার সময় সতর্কতা
- অতিরিক্ত ডোজ liver/kidney ক্ষতি করতে পারে
- mouthwash বেশি ব্যবহার করলে staining
- অনেক gel শিশুদের ক্ষেত্রে ঝুঁকিপূর্ণ
- allergic reaction হতে পারে
OTC-এর সুবিধা
- সহজলভ্য
- কম দাম
- ছোট সমস্যা দ্রুত নিয়ন্ত্রণ
- বাড়িতে ব্যবহারযোগ্য
OTC-এর সীমাবদ্ধতা
- বড় সমস্যা ঠিক করতে পারে না
- infection পুরোপুরি সারাতে পারে না
- ভুল ব্যবহার → complication
- দীর্ঘদিন ব্যবহার করলে side effect
Practice of medicine for Diploma Dental Assistant(DDA) Course
Practice of Medicine” in dentistry helps future dentists understand medical conditions that affect dental treatment. Dentists often encounter patients with systemic diseases, so this subject prepares you for safe, informed, and holistic patient care.
The study of Disease and Treatment is called the Practice of Medicine. This subject is important for Diploma in Dental, Dental Practitioners, Diploma Medical Practitioner, Diploma Medical Assistant, and Rural Medical Practitioner. This subject discusses some common diseases. The discussion points for the Practice of Medicine are the Definition of Disease, Causes of Disease, Clinical Features of Disease ( Symptoms and Signs), Investigation of Disease, Treatment of Disease, Complication of Disease, and Advice for the Patients.
ডেন্টিস্ট্রিতে Practice of Medicine কেন প্রয়োজন?
ডেন্টাল ছাত্রদের জন্য Practice of Medicine (POM) জরুরি কারণ—
- অনেক ডেন্টাল রোগীর শরীরে অন্য রোগ থাকে
যেমন: ডায়াবেটিস, হাইপারটেনশন, হার্টের সমস্যা, অ্যাজমা ইত্যাদি।
এগুলো বুঝতে না পারলে নিরাপদ ডেন্টাল চিকিৎসা দেওয়া যায় না। - অনেক সিস্টেমিক রোগের লক্ষণ মুখের ভেতর দেখা যায়
যেমন:- অ্যানিমিয়া → ফ্যাকাসে মিউকোসা
- ডায়াবেটিস → মাড়ির রোগ ও সংক্রমণ
তাই দাঁতের ডাক্তারকে এসব চিনতে জানতে হয়।
- রোগীর মেডিকেল কন্ডিশন অনুযায়ী ডেন্টাল ট্রিটমেন্ট বদলাতে হয়
যেমন:- কোন ওষুধ দেওয়া যাবে/যাবে না
- কতটা অ্যানাস্থেশিয়া দেওয়া যাবে
- অ্যাপয়েন্টমেন্টের সময়
তাই মেডিসিন না জানলে ট্রিটমেন্ট ভুল হতে পারে।
- ডেন্টাল চেয়ারে মেডিকেল ইমার্জেন্সি হতে পারে
যেমন:- অচেতন হয়ে যাওয়া
- সিজার
- অ্যাজমা অ্যাটাক
- হার্ট অ্যাটাক
এসব সামলাতে মেডিসিনের জ্ঞান দরকার।
- ডেন্টাল ওষুধের সাথে মেডিকেল ওষুধের ইন্টারঅ্যাকশন হতে পারে
সঠিকভাবে প্রেসক্রাইব করতে মেডিসিন জানা জরুরি। - লিগ্যাল ও এথিক্যাল দায়িত্ব
রোগী ঝুঁকিতে থাকলে ডেন্টিস্টকে সঠিকভাবে চিনে প্রয়োজন হলে চিকিৎসকের কাছে পাঠাতে হয়। - সার্বিক (holistic) রোগী ব্যবস্থাপনা
দাঁত শরীর থেকে আলাদা নয়। রোগীকে পুরো মানুষ হিসাবে বুঝতে মেডিসিনের প্রয়োজন।
Hematology and Pathology for Diploma Dental Assistant(DDA) Course
The study of Blood and Blood Disease is called Hematology and the Study of Pathos and Process of Disease Creation and Diagnosis is called Pathology. In Hematology and Pathology, we discuss blood cells, their structure and functions, Blood Diseases, Common Pathos and their pathogenesis, Atrophy, Hypertrophy, Metaplasia, Gangrene, Pathological Tests like TC, DC, ESR, Hemoglobin Percentage, etc.
Hematology কী?
Hematology হলো রক্ত, রক্তের কোষগুলো, এবং রক্তের রোগসমূহ নিয়ে অধ্যয়ন।
ডেন্টিস্টদের জন্য হেমাটোলজি খুব গুরুত্বপূর্ণ, কারণ—রোগীর রক্তক্ষরণ (bleeding), অ্যানিমিয়া, সংক্রমণ, রক্ত জমাট বাঁধার সমস্যা ইত্যাদি দাঁত তোলার সময় বা সার্জারিতে প্রভাব ফেলে।
Dental Students-এর জন্য Hematology কেন গুরুত্বপূর্ণ?
- Extraction বা surgery-তে রক্তপাত কেন বেশি হচ্ছে তা বোঝা
- Hemophilia বা platelet কম থাকা রোগীকে কিভাবে manage করতে হবে তা জানা
- Oral infection এ white blood cell-এর ভূমিকা
- Oral manifestation of blood diseases চেনা
- Antibiotic বা anesthesia দেওয়ার আগে patient evaluation
রক্তের প্রধান উপাদান (Components of Blood)
1️⃣ Plasma (৫৫%)
- পানি
- Protein (Albumin, Globulin, Fibrinogen)
- Electrolytes
- Hormones
Dental point: Fibrinogen → clotting factor → extraction-এর সময় খুব গুরুত্বপূর্ণ।
2️⃣ Formed Elements (৪৫%)
a. RBC (Red Blood Cell)
- কাজ: Oxygen বহন করা
- মাত্রা কম হলে: Anemia
Oral signs:
- মৌখিক শুষ্কতা
- মুখের কোণে ফাটল (Angular cheilitis)
- জিহ্বা ফ্যাকাশে
b. WBC (White Blood Cell)
কাজ: Infection থেকে রক্ষা করা
প্রকার:
- Neutrophil
- Lymphocyte
- Monocyte
- Eosinophil
- Basophil
Dental point:
- Oral abscess, gingivitis, periodontitis WBC বৃদ্ধি করে
- Neutropenia রোগীর infection risk বেশি
c. Platelet (থ্রোম্বোসাইট)
কাজ: রক্ত জমাট বাঁধা (clot formation)
- স্বাভাবিক: 1.5–4 লাখ/µL
Dental significance:
- Platelet কম হলে দাঁত তোলার সময় uncontrolled bleeding হতে পারে।
Important Hematological Tests in Dentistry
- CBC (Complete Blood Count)
- RBC, WBC, Platelet সব দেখা হয়
- Bleeding Time (BT)
- রক্তপাত কতক্ষণ চলে
- Clotting Time (CT)
- clot তৈরি হতে কত সময় লাগে
- PT, aPTT
- Coagulation factors ঠিক আছে কি না
- Surgery-এর আগে খুব গুরুত্বপূর্ণ
- Hemoglobin (Hb%)
- অ্যানিমিয়া আছে কি না
Hematology সম্পর্কিত Disease এবং Dental Importance
1️⃣ Anemia (রক্তশূন্যতা)
Oral features:
- Glossitis (জিহ্বা লাল ও জ্বলজ্বল)
- Ulcer
- Angular cheilitis
Dental concern:
- Local anesthesia কম কাজ করতে পারে
- Infection chance বাড়ে
2️⃣ Leukemia (রক্তের ক্যান্সার)
Oral signs:
- Gums swelling
- Bleeding
- Ulcer
- Infection
3️⃣ Hemophilia
রক্ত জমাট বাঁধার গুরুতর সমস্যা
Dental concerns:
- Extraction করা বিপজ্জনক
- Surgery-এর আগে factor replacement লাগবে
4️⃣ Thrombocytopenia (Platelet কম)
Oral signs:
- Petechiae (ছোট লাল দাগ)
- Purpura
- Gum bleeding
Dental concern:
- কোনো surgical procedure করার আগে platelet count চেক করা জরুরি
Blood Coagulation (রক্ত জমাট বাঁধা প্রক্রিয়া)
3 ধাপ:
- Vasoconstriction – রক্তপাত কমে
- Platelet plug formation
- Coagulation cascade → Fibrin clot
Dental relevance: Extraction বা surgery-এর পর bleeding control এ সাহায্য করে।
Oral Manifestations of Hematological Disorders (Dental Viva Favorite)
- Pale mucosa
- Bleeding gums
- Ulcer
- Petechiae
- Delayed healing
- Infections
Microbiology and Antimicrobial Drugs for Diploma Dental Assistant (DDA) Course
The Study of Microorganisms is called Microbiology. The Drugs that are used for the treatment of Infectious Diseases are Antimicrobial Drugs. Microorganisms are Bacteria, Protozoa, Fungus, and Virus. Antimicrobial Drugs are Antibiotic Drugs ( Antibacterial Drugs), Anti Protozoal Drugs, Anti Fungal Drugs, and Anti Viral Drugs. Antibacterial Drugs are Azithromycin, Erythromycin, Clarithromycin, Cefaclor, Cefixime, Cefuroxime, Ceftriaxone, Ciprofloxacin, Moxifloxacin, Doxicicline, Gentamycin, Neomycin, Flucloxacillin, Amoxicillin, Clindamycin, etc. Antiprotozoal Drugs are Metronidazole, Secnidazole, Tinidazole, Ornidazole, Nitazoxanide, etc. Antifungal Drugs are Fluconazole, Ketoconazole, Itraconazole, Econazole, Miconazole, Terbinafine, etc.
Microbiology কী?
Microbiology হলো ক্ষুদ্রজীব (microorganisms)—ব্যাকটেরিয়া, ভাইরাস, ফাংগাস, প্রোটোজোয়া—এবং তাদের দ্বারা সৃষ্ট রোগসমূহ নিয়ে অধ্যয়ন।
ডেন্টিস্টদের জন্য এটি খুব গুরুত্বপূর্ণ, কারণ মুখগহ্বর ব্যাকটেরিয়ার সবচেয়ে বড় ঘর।
Dental Student-এর জন্য Microbiology কেন জরুরি?
- Dental caries (দাঁতের ক্ষয়)
- Periodontal disease (মাড়ির রোগ)
- Oral infections
- Sterilization ও infection control
- Antibiotic ব্যবহার
- Cross-infection prevent
- Oral microbiome বোঝা
Types of Microorganisms (মাইক্রোবের ধরন)
1️⃣ Bacteria
মুখে সবচেয়ে বেশি পাওয়া যায়
- Streptococcus mutans → Dental caries
- Lactobacillus → deep caries
- Actinomyces → root caries
- Porphyromonas gingivalis → Periodontitis
2️⃣ Virus (ভাইরাস)
- Herpes simplex virus → cold sore
- Human papilloma virus (HPV) → oral lesions
- HIV → oral candidiasis ও ulcer বাড়ায়
- Hepatitis B → ডেন্টাল সেটআপে অত্যন্ত ঝুঁকিপূর্ণ
3️⃣ Fungi (ছত্রাক)
সবচেয়ে গুরুত্বপূর্ণ ফাংগাস—
- Candida albicans
→ Oral thrush (সাদা দাগ), denture stomatitis
4️⃣ Protozoa
- Entamoeba gingivalis
- Trichomonas tenax
→ মাড়ির রোগে ভূমিকা
Oral Microflora (মুখের স্বাভাবিক জীবাণু)
মুখে প্রায় ৭০০+ ধরনের ব্যাকটেরিয়া থাকে।
Normal flora-এর কাজ:
- infection প্রতিরোধ করে
- immunity বাড়ায়
- খাবার ভাঙতে সাহায্য করে
কিন্তু ভারসাম্য নষ্ট হলে disease হয়।
Cardiovascular Anatomy & Physiology for Diploma Dental Assistant (DDA) Course
Cardiovascular Anatomy is a branch of Anatomy, and Cardiovascular Physiology is a branch of Physiology. These two subjects are related to cardiology. Cardiovascular Anatomy and Physiology are being studied in a single subject for Diploma Medical Courses, Paramedical Courses, and All Short Medical Courses.
We discuss here the Anatomy of the Heart, Cardiac Chambers, Cardiac Valves, Cardiac Wall, Cardiac Septum, Right Heart, Left Heat, Function of Right Heat, Functions of Left Heart, Aorta, Venecava, Artery, Vein, Capillary, Pulmonary Blood Circulation, Cerebral Blood Circulation, Renal Blood Circulation, Hepatic Blood Circulation, Portal Vein and Portal Circulation, Heart Beat, Pulse, Pulse Rate, Tachycardia, Bradycardia, Blood Pressure, Normal Blood Pressure, Hypertension, Hypotension, Stroke Volume, Cardiac Output, Heart Failure, etc. This Subject is the most essential for the Diploma in Medicine and Diploma in Surgery Course.
Dental Anatomy for Diploma Dental Assistant (DDA) Course
Dental Anatomy is an important subject for the Diploma in Dental 4 Years Course. Dental Anatomy describes the structure of every tooth and its parts. Dental parts are Enamel, Dentin, Dental Neck, Pulp Cavity or Pulp Chamber, Dental Pulp, Dental Root, Cementum etc. After studying Dental Anatomy we can understand clearly the structure of the above dental parts.
INTRODUCTION TO DENTAL ANATOMY
Dental Anatomy অন্তর্ভুক্ত করে—
- Tooth morphology
- Tooth numbering & identification
- Tooth development
- Dental arches
- Occlusion
- Supporting structures
FUNCTIONS OF TEETH
- Mastication – খাবার চিবানো
- Esthetics – মুখের সৌন্দর্য
- Speech / Phonetics –
- Protection of oral tissues
- Supporting facial muscles
TYPES OF TEETH (হিউম্যান ডেন্টিশন)
A. Primary / Deciduous Teeth (দুধ দাঁত) – ২০টি
- Incisors – 8
- Canines – 4
- Molars – 8
B. Permanent Teeth – ৩২টি
- Incisors – 8
- Canines – 4
- Premolars – 8
- Molars – 12
Dentition Periods
- 0–6 yrs → Primary dentition
- 6–12 yrs → Mixed dentition
- 12+ yrs → Permanent dentition
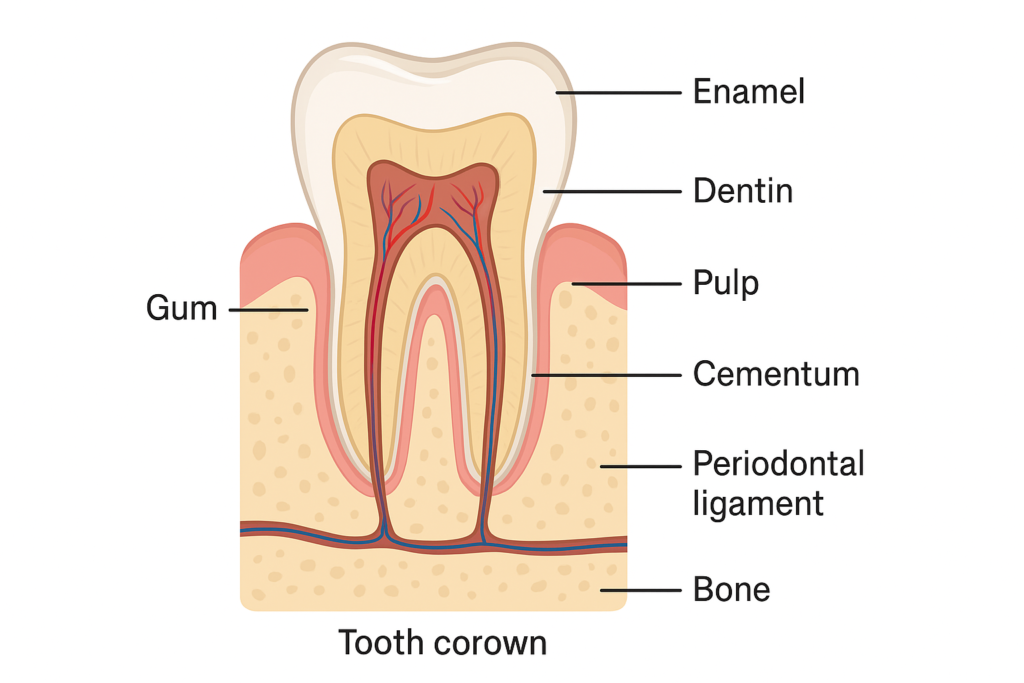
TOOTH MORPHOLOGY (দাঁতের আকৃতি ও বৈশিষ্ট্য)
1. Incisors
- Cutting food
- Sharp incisal edge
- Maxillary central incisor = সবচেয়ে বড় anterior tooth
- Mandibular incisors = smallest permanent teeth
2. Canines
- Strongest tooth
- Longest root
- Tearing of food
- Cornerstone of arch
3. Premolars
- 2 cusps (bicuspids)
- Grinding function
- Maxillary 1st premolar: usually 2 roots
4. Molars
- 4–5 cusps
- Strongest chewing teeth
- Maxillary molars → 3 roots
- Mandibular molars → 2 roots
- 3rd molars show maximum variation
TOOTH STRUCTURE (HISTOLOGY)
A tooth has 2 main parts:
1. Crown (দাঁতের মাথা)
2. Root (দাঁতের মূলে)
Layers of the Tooth:
1. Enamel
- Hardest tissue in human body
- 96% inorganic (hydroxyapatite)
- Covers crown
- Avascular (নালীবিহীন)
- Cannot regenerate
2. Dentin
- 70% inorganic
- Yellowish & softer than enamel
- Contains dentinal tubules → sensitivity
- Types: primary, secondary, tertiary
3. Pulp
- Soft tissue
- Contains nerves, blood vessels
- Functions: nourishment, sensation, defense
4. Cementum
- Covers root
- Attachment to PDL
- Types: acellular & cellular
PERIODONTIUM (Periodontal Tissue)
দাঁতকে হাড়ের সাথে যুক্ত ও সাপোর্ট করে।
Components
- Gingiva – মাড়ি
- Periodontal ligament (PDL)
- Cementum
- Alveolar bone
PDL Functions
- Shock absorption
- Sensory function
- Tooth movement during orthodontics
TOOTH DEVELOPMENT (Odontogenesis)
Stages of tooth development:
- Initiation (Bud stage)
- Cap stage
- Bell stage
- Apposition
- Maturation
- Eruption
Developmental tissues
- Enamel → ectoderm
- Dentin & Pulp → mesenchyme
ERUPTION OF TEETH
Primary Teeth Eruption Chart
| Tooth | Age |
|---|---|
| Central incisor | 6–10 months |
| Lateral incisor | 10–16 months |
| Canine | 17–23 months |
| 1st Molar | 14–18 months |
| 2nd Molar | 23–31 months |
Permanent Teeth
| Tooth | Age |
|---|---|
| 1st molar | 6 yrs |
| Central incisor | 6–7 yrs |
| Lateral incisor | 7–8 yrs |
| Canine | 11–12 yrs |
| Premolars | 10–12 yrs |
| 2nd molar | 12–13 yrs |
| 3rd molar | 17–25 yrs |
TOOTH NUMBERING SYSTEMS
Most Common: FDI System
- Upper right: 11–18
- Upper left: 21–28
- Lower left: 31–38
- Lower right: 41–48
Other Systems
- Universal
- Palmer notation
DENTAL ARCHES
Maxillary Arch
- Larger, fixed
- Teeth overlap the mandibular arch
Mandibular Arch
- Movable (TMJ)
- Slightly smaller
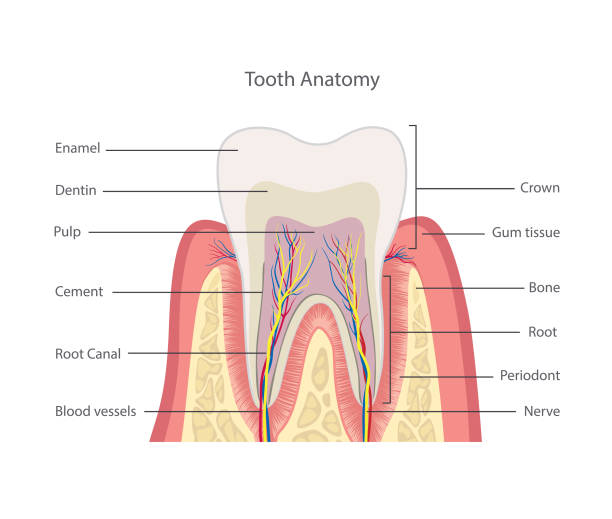
Dental Physiology for Diploma Dental Assistant (DDA) Course
Dental Physiology is an important subject for the Diploma in Dental 4 Years Course. Dental Physiology describes the functions of every tooth and its parts. After studying Dental Physiology we can understand clearly the functions of Enamel, Dentin, Dental Pulp, Dental Root, Pulp Chamber, Cementum, etc.

Anatomy of Head Neck for Diploma Dental Assistant (DDA) Course
Head & Neck Anatomy = মুখমণ্ডল, খুলিঃ (skull), ঘাড়, মাংসপেশি, স্নায়ু, রক্তনালী, লালাগ্রন্থি, দাঁত-supporting structures ইত্যাদি নিয়ে আলোচনা।
Dental students-এর জন্য important কারণ—
- Local anesthesia
- Tooth extraction
- Oral surgery
- Infection spread
- Muscles of mastication
- Nerve supply of teeth
Head-Neck bone
- Cranial bone-8
- Facial bone-14
- Middle ear bone-6
- Hyoid bone(Neck)-1
Total Bone-29
Brain :Brain হচ্ছে Nervous system এর সবচেয়ে গুরুত্বপূর্ণ অংশ যা মাথার খুলির ভিতরে অবস্থিত।
Cranial Nerves: যে সকল Nerve brain থেকে উৎপত্তি হয়েছে তাদেরকে Cranial nerve বলে। Cranial Nerve 12 জোড়া ।
Cranial Nerve গুলি brain থেকে উৎপত্তি হয়ে brain এর আশেপাশের বিভিন্ন tissue তে মিলিত হয়েছে।
Dental Head & Neck Anatomy হলো সেই শাখা যেখানে মাথা ও ঘাড়ের সকল গঠন (হাড়, মাংসপেশি, স্নায়ু, রক্তনালী, লালাগ্রন্থি, মুখগহ্বর, দাঁত ও আশেপাশের টিস্যু) বিস্তারিতভাবে অধ্যয়ন করা হয়, যা দাঁতের চিকিৎসা, অ্যানেস্থেসিয়া এবং ওরাল সার্জারির জন্য অত্যন্ত গুরুত্বপূর্ণ।
Skull (খুলি) মোট হাড় = ২২টি
Skull দুটি ভাগে বিভক্ত:
1️⃣ Cranium (মস্তিষ্ক আবরণের হাড়)
- Frontal
- Parietal (২টি)
- Temporal (২টি)
- Occipital
- Sphenoid
- Ethmoid
Cranial Bones (মস্তিষ্ক আবরণের হাড়) – ৮টি
| Bone Name | Number | বাংলা নাম |
|---|---|---|
| Frontal | 1 | কপালের হাড় |
| Parietal | 2 | মাথার পার্শ্ব হাড় |
| Temporal | 2 | কর্ণের পাশে |
| Occipital | 1 | মাথার পেছনে |
| Sphenoid | 1 | প্রজাপতি-আকৃতির হাড় |
| Ethmoid | 1 | নাক ও চোখের মাঝখানে |
2️⃣ Facial Bones (মুখমণ্ডলের হাড় – 14টি)
- Maxilla (২টি)
- Mandible
- Zygomatic (২টি)
- Nasal (২টি)
- Lacrimal (২টি)
- Palatine (২টি)
- Inferior nasal concha (২টি)
- Vomer
Facial Bones (মুখমণ্ডলের হাড়) – ১৪টি
| Bone Name | Number | বাংলা নাম |
|---|---|---|
| Maxilla | 2 | উপরের চোয়াল |
| Mandible | 1 | নিচের চোয়াল |
| Zygomatic | 2 | গালের হাড় |
| Nasal | 2 | নাকের হাড় |
| Lacrimal | 2 | অশ্রু গ্রন্থির হাড় |
| Palatine | 2 | মুখের ছাদের পিছনে |
| Inferior Nasal Concha | 2 | নাকের ভেতরের পাতলা হাড় |
| Vomer | 1 | নাকের মধ্যবর্তী বিভাজক |
Ear Bones (Auditory Ossicles – ৬টি)
| Bone | Number |
|---|---|
| Malleus | 2 |
| Incus | 2 |
| Stapes | 2 |
Hyoid Bone – ১টি
| Bone | Number | Note |
|---|---|---|
| Hyoid | 1 | ঘাড়ে ঝুলন্ত হাড়, অন্য হাড়ের সাথে যুক্ত না |
Dental Microbiology for Diploma Dental Assistant (DDA) course
Dental Microbiology is the subject that describe the pathogenic microorganisms that create dental infections. Pathogenic Microorganisms are bacteria, Virus, Fungus, and Protozoa. Common Dental Infectious Diseases are being studied in Dental Microbiology.
Dental Surgery for Diploma Dental Assistant (DDA) Course
Dental Surgery is a very vital subject for the Diploma in Dental 4 Years Course. Some common Dental Surgeries are Scaling, Polishing, Whitening, Filling, Root Canal Treatment, Fixed Denture, etc. Every Surgical Procedure should be known by the students of the Diploma in Dental 4 Years Course.
Preservative Dentistry for Diploma Dental Assistant (DDA) Course
Preservative Dentistry is a subject that describes the technique for survival of the teeth. This subject is described broadly in this Dental Diploma Course of 4 Years so that the theeth of patient can be survived.
Dental Pathology for Diploma Dental Assistant (DDA) Course
Dental Pathology is an essential subject for dental students. Dental Pathology describes the process of formation of abnormal teeth. Pathology is related to pathogens. Pathogens are the substances that create disease.
Dental Filling Materials for Diploma Dental Assistant (DDA) Course
Filling materials are those materials which are used for restoration purposes in dentistry. They vary in composition properties and manipulation.
Common Filling Materials are-
- Zinc oxide
- Zinc oxy phosphate cement
- Silver cement
- Copper cement
- Calcium hydroxide
- Glass ionomer cement
- Composite
- Gutta percha
Neuro Anatomy for Diploma Dental Assistant (DDA)Course
দেহের যে system দ্বারা Monitoring & Coordination এর কাজ সম্পাদিত হয় তাকে Nervous system বলে। এর দুইটি অংশ । 1.Central Nervous system(CNS) 2.Peripheral Nervous system (PNS)
CNS এর অংশ সমুহ -1.Brain 2. Spinal Cord
PNS এর অংশ সমুহ -1. Cranial Nerves12 জোড়া 2. Spinal Nerves 31 জোড়া
Nervous system এর কোষ গুলিকে Neuron বলে। Neuron 3 প্রকার .
1.Sensory Nerve 2. Motor Nerve 3.Internucial Neuron

Neuroanatomy is the study of the structure and organization of the nervous system, including the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves.
নিউরোঅ্যানাটমি হলো স্নায়ুতন্ত্রের গঠন, বিন্যাস ও বিভিন্ন অংশের (যেমন—মস্তিষ্ক, মেরুদণ্ড, ক্রেনিয়াল নার্ভ, পেরিফেরাল নার্ভ) কাঠামোগত অধ্যয়ন।
Nervous system দুই ভাগে ভাগ:
A. Central Nervous System (CNS)
- Brain (মস্তিষ্ক)
- Spinal Cord (মেরুদণ্ড)
B. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
- Cranial Nerves (১২ জোড়া)
- Spinal Nerves
Dentistry-তে সবচেয়ে গুরুত্বপূর্ণ: Cranial Nerves
Brain-এর প্রধান অংশ
1. Cerebrum (বড় মস্তিষ্ক)
- চিন্তা, স্মৃতি, মুভমেন্ট নিয়ন্ত্রণ করে।
2. Cerebellum
- Balance ও coordination।
3. Brainstem
- Midbrain
- Pons
- Medulla
Dental importance: PONS = Trigeminal nerve (CN V) origin
Cranial Nerves – Dental এর জন্য সবচেয়ে Important
CN V – Trigeminal Nerve
Face, teeth, gums, oral mucosa এর sensation দেয়
Chewing muscle (mastication muscle) control করে
ট্রাইজেমিনাল নার্ভের ৩টি শাখা:
- Ophthalmic (V1) – চোখের উপরের অংশ
- Maxillary (V2) – Upper jaw (maxilla) এর অনুভূতি
- Upper teeth
- Maxillary sinus
- Upper lip
- Mandibular (V3) – Lower jaw (mandible) এর অনুভূতি ও chewing movement
- Lower teeth
- Tongue anterior 2/3 sensation
- Mastication muscles (masseter, temporalis, pterygoids)
Cranial Nerves কী?
Cranial nerves হলো ১২ জোড়া স্নায়ু, যেগুলো brain থেকে সরাসরি বের হয় এবং
head, face, oral cavity, teeth, tongue, salivary gland, eyes, nose, neck–এর কাজ নিয়ন্ত্রণ করে।
এদেরকে “brain-এর special nerves” বলা যায়।
Number of Cranial Nerves
মোট ১২ জোড়া cranial nerve আছে:
I → XII পর্যন্ত নাম্বার দেওয়া থাকে।
নীচে প্রতিটি cranial nerve-এর নাম + কাজ (Bangla-friendly short notes):
I. Olfactory Nerve
- কাজ → Smell (ঘ্রাণ)
II. Optic Nerve
- কাজ → Vision (দৃষ্টি/দেখা)
III. Oculomotor Nerve
- চোখের নড়াচড়া
- চোখের pupil ছোট করা
IV. Trochlear Nerve
- চোখের নির্দিষ্ট muscle (superior oblique) কে চালায়
V. Trigeminal Nerve → MOST IMPORTANT for Dentistry
Face, teeth, gums, oral cavity এর sensation দেয়
এছাড়াও chewing muscle (mastication muscle) চালায়
শাখা:
- V1 → Ophthalmic
- V2 → Maxillary (upper teeth sensation)
- V3 → Mandibular (lower teeth sensation + chewing muscles)
VI. Abducens Nerve
- চোখের lateral movement (side দিকে)
VII. Facial Nerve
- Facial expression (হাসা, রাগ করা)
- Taste (tongue anterior 2/3)
- Salivary gland (submandibular, sublingual)
VIII. Vestibulocochlear Nerve
- Hearing (শোনা)
- Balance (ভারসাম্য)
IX. Glossopharyngeal Nerve
- Taste (posterior 1/3 tongue)
- Parotid gland secretion
- Gag reflex
X. Vagus Nerve
- Heart, lungs, digestive organs নিয়ন্ত্রণ
- Speech ও swallowing-এ ভূমিকা
XI. Accessory Nerve
- Neck muscle (sternocleidomastoid, trapezius) চালায়
XII. Hypoglossal Nerve
- Tongue movement (জিভ নড়াচড়া)
Cranial Nerves Chart
| No. | Name | Type | Main Function (Bangla) |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | Olfactory | Sensory | Smell (ঘ্রাণ) |
| II | Optic | Sensory | Vision (দেখা) |
| III | Oculomotor | Motor | চোখের নড়াচড়া, pupil control |
| IV | Trochlear | Motor | চোখের superior oblique muscle চালায় |
| V | Trigeminal | Both | Face sensation, teeth sensation, chewing muscles |
| VI | Abducens | Motor | চোখকে side-এ নড়ায় |
| VII | Facial | Both | Facial expression, taste (front 2/3 tongue), saliva |
| VIII | Vestibulocochlear | Sensory | Hearing & balance |
| IX | Glossopharyngeal | Both | Taste (back 1/3), gag reflex, parotid gland |
| X | Vagus | Both | Speech, swallowing, heart & digestive control |
| XI | Accessory | Motor | Neck muscles (SCM, trapezius) |
| XII | Hypoglossal | Motor | Tongue movement |
Extra Dental-Focused Short Chart
| Nerve | Dental Importance |
|---|---|
| V (Trigeminal) | Upper & lower teeth sensation, local anesthesia |
| VII (Facial) | Saliva, taste, facial movement |
| IX (Glossopharyngeal) | Gag reflex, posterior tongue sensation |
| XII (Hypoglossal) | Tongue movement, speech |
Trigeminal Nerve For Dental Training Course In Bangladesh
The Trigeminal nerve (Cranial Nerve V) is the largest cranial nerve that provides sensation to the face, oral cavity, teeth, and anterior scalp, and controls the muscles of mastication.
ট্রাইজেমিনাল নার্ভ (Cranial Nerve V) হলো সবচেয়ে বড় ক্রেনিয়াল নার্ভ, যা মুখ, দাঁত, জিহ্বা, ঠোঁট এবং সামনের ত্বকের সংবেদন দেয় এবং চিবানোর মাংসপেশি নিয়ন্ত্রণ করে।
Type (ধরন):
- Both (Sensory + Motor)
- Sensory: মুখ ও মুখগহ্বরের সমস্ত সংবেদন
- Motor: Mastication muscles (চিবানোর মাংসপেশি)
Origin (উৎপত্তি):
- Sensory root: Trigeminal ganglion থেকে আসে
- Motor root: Pons থেকে আসে (brainstem-এর অংশ)
Functions (কার্য):
A. Sensory Function
| Structure | Nerve Branch | Dental/Clinical Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Upper teeth, upper gums | Maxillary (V2) | Upper toothache, dental anesthesia |
| Lower teeth, lower gums | Mandibular (V3) | Lower toothache, IAN block |
| Face, forehead, eye | Ophthalmic (V1) | Facial sensation, eye reflexes |
| Tongue (anterior 2/3) | Mandibular (V3 – Lingual nerve) | Tongue sensation, taste (with VII) |
| Oral mucosa | V2, V3 | Oral pain perception |
B. Motor Function
- Muscles of mastication (চিবানোর মাংসপেশি)
- Masseter
- Temporalis
- Medial pterygoid
- Lateral pterygoid
- Other small muscles: Tensor veli palatini, Tensor tympani
Dental Relevance:
- Chewing movement
- Bite force
- Jaw control during procedures
Branches of Trigeminal Nerve (V1, V2, V3)
| Branch | Name | Type | Area/Function | Dental Importance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V1 | Ophthalmic | Sensory | Forehead, eye, upper eyelid, nose bridge | Rarely dental, mostly face sensation |
| V2 | Maxillary | Sensory | Upper jaw, upper teeth, upper gums, maxillary sinus, upper lip | LA blocks, upper tooth procedures |
| V3 | Mandibular | Both | Lower jaw, lower teeth, lower gums, anterior tongue (sensation), mastication muscles | LA blocks, lower teeth procedures, mastication control |
Dental Local Anesthesia (LA) Related Nerves
- Inferior Alveolar Nerve (V3) → Lower teeth, mandibular block
- Mental Nerve (V3) → Lower anterior teeth & lip
- Lingual Nerve (V3) → Tongue anterior 2/3, floor of mouth
- Infraorbital Nerve (V2) → Upper teeth, upper lip, cheek
- Posterior Superior Alveolar Nerve (V2) → Upper molars
Clinical Relevance (Dental Focus)
- Toothache & pulpitis diagnosis
- Gum disease & oral pain pathways
- Nerve blocks for painless dental procedures
- Trigeminal neuralgia (severe facial pain)
- Surgical procedures: Tooth extraction, root canal, implants
Mnemonic for Trigeminal Nerve
“Three Big Branches Take Care of Face, Teeth & Chewing”
- V1 → Ophthalmic → Face
- V2 → Maxillary → Upper teeth
- V3 → Mandibular → Lower teeth + Chewing muscles
Quick Dental Chart – Trigeminal Nerve
| Branch | Teeth | Gum | Tongue | Muscles | LA Block |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V1 (Ophthalmic) | None | None | None | None | None |
| V2 (Maxillary) | Upper teeth | Upper gums | None | None | Infraorbital, PSA |
| V3 (Mandibular) | Lower teeth | Lower gums | Anterior 2/3 | Mastication | IAN, Mental, Lingual |
Dental Caries for Diploma Assistant (DDA) Course Fee
সংজ্ঞা (Definition):
Dental Caries হলো দাঁতের এনামেল, ডেন্টিন এবং কখনও কখনও পুলপকেও ক্ষয় করে এমন একটি সংক্রামক রোগ, যা মুখের ব্যাকটেরিয়ার দ্বারা তৈরি অ্যাসিডের কারণে হয়।
Etiology (কারণসমূহ)
A. ব্যাকটেরিয়া (Bacteria)
- Streptococcus mutans
- Lactobacillus species
B. খাদ্য (Diet)
- মিষ্টি ও কার্বোহাইড্রেটসমৃদ্ধ খাবার
- Cola, চিনি, চকোলেট
C. Saliva & Oral Hygiene
- কম লালা (Reduced saliva) → Acid clearance কমে
- Poor oral hygiene → Plaque জমে
D. Other Factors
- Tooth morphology (fissures, pits)
- Age (children & elderly more prone)
- Fluoride deficiency
Pathogenesis (উন্নয়ন প্রক্রিয়া)
- Plaque formation on tooth surface
- Bacteria metabolize sugar → Acid production
- Acid demineralizes enamel → White spot formation
- Enamel → Dentin → Pulp damage if untreated
Types of Dental Caries (Classification)
| Classification | Example/Explanation |
|---|---|
| Based on Location | Pit & fissure caries, Smooth surface caries, Root caries |
| Based on Progression | Acute caries (fast), Chronic caries (slow) |
| Based on Depth | Enamel caries, Dentin caries, Pulpal caries |
Clinical Features (Symptoms)
- Toothache (especially with sweets, cold, hot)
- Visible pit or hole on tooth
- Discoloration (white/brown/black spot)
- Sensitivity to cold, sweet, or hot food
- Bad breath (halitosis)
Diagnosis
- Clinical examination (mirror & probe)
- Radiographs (X-ray) – Bitewing, Periapical
- Laser fluorescence & dye tests (advanced)
Complications
- Pulpitis → Tooth pulp infection
- Abscess → Swelling & pain
- Tooth loss
- Spread of infection → Facial cellulitis
Prevention (নিয়ন্ত্রণ ও প্রতিরোধ)
- Proper brushing (2x/day)
- Fluoride toothpaste / fluoride varnish
- Reduce sugary food & drinks
- Dental sealants (especially molars)
- Regular dental check-up (every 6 months)
- Chewing sugar-free gum → Stimulates saliva
Treatment (চিকিৎসা)
| Stage | Treatment |
|---|---|
| Early enamel lesion | Fluoride treatment, remineralization |
| Dentin caries | Restoration (Filling – Amalgam/Composite) |
| Pulp involvement | Root canal treatment (RCT) |
| Severe destruction | Extraction |
Clinical Practice in Dental Surgery for Diploma Assistant (DDA) Course Fee
Dental surgery clinical practice হলো রোগীর দাঁত ও মুখগহ্বরের সমস্যার চিকিৎসা করার জন্য ডাক্তার দ্বারা পরিচালিত প্র্যাকটিক্যাল বা হ্যান্ডস-অন প্রক্রিয়া।
সংক্ষেপে:
“দাঁতের সার্জারি সংক্রান্ত রোগ নির্ণয় ও চিকিৎসার হ্যান্ডস-অন কাজ।”
Objectives (উদ্দেশ্য):
- রোগীর দাঁতের সমস্যা নির্ণয় করা
- Tooth extraction (দাঁত খোলা) শেখা ও পরিচালনা
- Minor oral surgical procedures করা
- Local anesthesia ব্যবহার শেখা
- Infection control ও sterilization প্র্যাকটিস করা
- Patient handling & safety শেখা
Clinical Practice Areas
A. History Taking & Examination
- Patient history: Pain, swelling, trauma, systemic diseases
- Intraoral examination: Tooth, gums, oral mucosa
- Extraoral examination: Face, lymph nodes, TMJ
- Radiographic evaluation: X-ray (Periapical, OPG)
Local Anesthesia (LA) Administration
- Types of LA: Lidocaine, Articaine, Mepivacaine
- Techniques:
- Inferior alveolar nerve block (IAN block)
- Mental nerve block
- Infraorbital nerve block
- Posterior superior alveolar (PSA) block
- Precautions: Allergy check, aspiration, dosage
Tooth Extraction (দাঁত তোলা)
Steps:
- Pre-operative assessment
- Aseptic preparation
- Administer LA
- Use proper instruments: Elevators, Forceps
- Extraction technique (simple vs surgical)
- Hemostasis & suturing if needed
- Post-operative instructions: Pain, swelling, diet, oral hygiene
Complications:
- Pain, swelling
- Bleeding
- Dry socket (Alveolar osteitis)
- Infection
- Nerve injury
D. Minor Oral Surgery Procedures
- Incision & drainage of abscess
- Removal of impacted teeth (surgical extraction)
- Frenectomy
- Biopsy
- Suturing techniques
E. Infection Control & Sterilization
- Hand hygiene, PPE (gloves, mask, apron)
- Instrument sterilization: Autoclave, Chemical disinfection
- Surface disinfection
- Safe disposal of sharps
F. Patient Communication & Post-Op Care
- Explain procedure & obtain consent
- Post-operative instructions:
- Pain management: Analgesics
- Swelling control: Ice packs
- Diet: Soft diet, avoid hot/spicy food
- Oral hygiene: Gentle brushing, antiseptic mouthwash
G. Record Keeping
- Patient details, diagnosis, procedure done
- LA dosage, materials used
- Follow-up notes
Oral Pathology For Dental Training Course In Bangladesh
অরাল প্যাথলজি (Oral Pathology) হলো মুখগহ্বরের রোগসমূহের কারণ, প্রকৃতি, গঠনগত পরিবর্তন এবং তার প্রভাব নিয়ে আলোচনা করে এমন একটি শাখা। এটি ডেন্টাল সায়েন্সের একটি গুরুত্বপূর্ণ অংশ।
What is Oral Pathology?
Oral Pathology is the branch of dental science that deals with the nature, identification, and management of diseases affecting the oral and maxillofacial regions. It combines clinical, radiographic, microscopic, and biochemical examinations to understand the causes and effects of diseases in the mouth.
অরাল প্যাথলজি কি?
অরাল প্যাথলজি হলো এমন একটি শাস্ত্র যা মুখগহ্বর, চোয়াল, দাঁত ও সংলগ্ন টিস্যুসমূহে দেখা দেওয়া রোগ এবং তাদের কারণ, গঠনগত পরিবর্তন ও কার্যপ্রক্রিয়া বিশ্লেষণ করে।
Common Oral Pathological Conditions
1. Dental Caries
- Decay of tooth structure due to bacterial activity
- Causes: Sugary diet, poor hygiene, acid production
2. Gingivitis
- Inflammation of the gums
- Symptoms: Redness, swelling, bleeding
3. Periodontitis
- Infection of the tissues around the teeth
- Can lead to tooth mobility and bone loss
4. Oral Ulcers
- Painful sores in the mouth
- Causes: Trauma, infections, nutritional deficiencies
5. Oral Candidiasis (Thrush)
- Fungal infection caused by Candida albicans
- Seen as white patches on the tongue or cheek
6. Leukoplakia
- White patches in the mouth that cannot be rubbed off
- Often linked to tobacco use
- Considered a premalignant condition
7. Oral Cancer
- Commonly affects the tongue, lips, and floor of the mouth
- Risk factors: Smoking, alcohol, HPV infection
8. Lichen Planus
- Chronic inflammatory condition
- May cause white striations, burning sensation
9. Ameloblastoma
- Benign but locally aggressive tumor of the jaw
- Often found in the mandible
মুখগহ্বরের সাধারণ প্যাথলজিক্যা ল রোগসমূহ:
১. ডেন্টাল ক্যারিজ (Dental Caries)
- দাঁতে ক্ষয় হওয়া বা গর্ত হওয়া
- ব্যাকটেরিয়া দ্বারা সৃষ্ট
- চিনি জাতীয় খাবারের সাথে সংযোগে আসে
২. জিনজিভাইটিস (Gingivitis)
- মাড়ির প্রদাহ
- রক্ত পড়া, ফুলে যাওয়া
- দন্ত ময়লা জমা হলে হয়
৩. পিরিওডোন্টাইটিস (Periodontitis)
- মাড়ি ও হাড়ের মধ্যে সংক্রমণ
- দাঁত আলগা হয়ে যেতে পারে
৪. অ্যারোশান এবং আলসার (Erosion & Ulcer)
- মুখে ক্ষত বা ঘা
- ভিটামিনের অভাব, ইনফেকশন বা ট্রমা
৫. অরাল ক্যান্সার (Oral Cancer)
- ঠোঁট, জিহ্বা, গাল বা মাড়িতে ক্যান্সার
- ধূমপান, পান খাওয়া এর প্রধান কারণ
৬. লিউকোপ্লাকিয়া (Leukoplakia)
- সাদা ছোপ যা ঘষে উঠানো যায় না
- প্রি-ক্যান্সারাস অবস্থা
৭. ক্যান্ডিডিয়াসিস (Candidiasis)
- মুখের ছত্রাকজনিত সংক্রমণ
- সাদা রঙের পাতলা আবরণ
অরাল প্যাথলজি কেন শেখা জরুরি?
- মুখের যেকোনো সমস্যা দ্রুত শনাক্ত করার জন্য
- ক্যান্সার বা গুরুতর রোগ আগেভাগে ধরার জন্য
- রোগের উপসর্গ বুঝে চিকিৎসা দিতে সহায়তা করে
ডায়াগনোসিসে যেসব পদ্ধতি ব্যবহৃত হয়:
- বায়োপসি (Biopsy)
- এক্স-রে (X-ray)
- মাইক্রোস্কোপিক পরীক্ষা
- ক্লিনিকাল অবজারভেশন
 HRTD Medical Institute
HRTD Medical Institute






Very shortly this site will be famous amid all blogging users, due to it’s good articles or reviews