Diploma in Medicine and Diploma in Surgery (DMDS) Course Profile:
Diploma in Medicine and Diploma in Surgery (DMDS) Course in Dhaka: Mobile No: 01797522136, 01987-073965. DMDS Course 4 Years: Diploma in Medicine & Surgery ( DMDS 4 Year). This course contains 30 subjects. The subjects are Human Anatomy & Physiology, Pharmacology-1, Practice of Medicine, Hematology, Pathology, Microbiology, Surgery, etc.

This course is divided into two semesters. The first semester contains 5 subjects and the second semester contains 5 subjects. The third semester contains 4 subjects and 4th semester contains 4 subjects. The 5th semester contains 3 subjects and the 6th semester contains 3 subjects. The 7th semester contains 3 subjects and the 8th semester contains 3 subjects. This Course is
Diploma in Medicine & Diploma in Surgery 4 Years (DMDS 4 Years) is Better than Others Diploma Medical Courses and Village Doctor Courses
DMDS 4 Years Course is better than Paramedical 1 Year, Paramedical 2 Years, Paramedical 3 Years, DMA 1 Years, DMA 2 Years, DMA 3 Years, DPM 2 Years, DPM 3 Years, DMS 1 Year, DMS 2 Years, DMS 3 Years Course, LMAF Courses, and RMP Courses.
After completing DMDS 4 Years, students can study Post Diploma Training Courses (PDT Courses). PDT Courses are PDT Medicine, PDT Cardiology, PDT Diabetology, PDT Dermatology, PDT Gastrology, PDT Gynecology, PDT Ophthalmology, PDT Ear Nose and Throat (PDT in ENT), PDT Pediatrics, PDT Orthopedics, PDT Skin and VD, PDT Hepatology, PDT Endocrinology, PDT Bronchology and Rhinology, PDT Neurology, PDT Psychiatry (For Managing and Counseling Psychiatric Patient).
Course Fee Summary for Diploma in Medine & Diploma in Surgery
The total course fee for this 4-year course is Tk 182500 only. Payment system: Admission fee Tk 30500, Monthly fee Tk 3000, and exam fee every six months.
Location for Diploma in Medine & Diploma in Surgery Course
Location for DMDS Course: Mobile Phone Number 01797522136, 01987073965. HRTD Medical Institute, Abdul Ali Madbor Mansion, Section-6, Block-Kha, Road-1, Plot-11, Metro Rail Piller Number 249, Mirpur-10 Golchattar, Dhaka-1216. This Institute is situated just by the West Side of Agrani Bank and the South Side of Islami Bank and Janata Bank Limited.
Higher Training Course opportunity after completing the DMDS Course
Higher Training Courses are PDT Courses. Mobile Phone 01797522136, 01987073965.PDT stands for Post Diploma Training. PDT Course in Medicine, PDT Course in Cardiology, PDT Course in Diabetology, PDT Course in Dermatology, PDT Course in Pediatrics, PDT Course in Gastrology, PDT Course in Geriatric Disease, PDT Course in International OTC Drugs, PDT Course in MCH, PDT Course in Gynecology, PDT Course in Orthopedics, PDT Course in Ear, Nose and Throat, PDT Course in Skin and VD, PDT Course in Ophthalmology.
Our Others Course:
Pharmacy Course, Dental Course, Nursing Course, Pathology Course, Homeopathy Course, Veterinary Course, Village Doctor Course, PDT( Post Diploma Training) Course, PPT, LMAF Training Course, LMAFP Course, Poultry Course, DMA ( Diploma Medical Assistant), Diploma in Medicine and Surgery (DMDS).
Job opportunities:
Jobs are available in Bangladesh and many other countries as dental assistants, dental technicians, or dental technologists. Each and every busy dental surgeon needs at least 2 to 3 dental technicians for the proper surgical treatment in his/her chamber or dental clinic.
Teachers for Diploma in Medine & Diploma in Surgery Courses
There are almost 50 Teachers at HRTD Medical Institute. All the teachers are MBBS doctors, FCPS doctors, BDS Doctors, DVM, MS Doctors, BHMS Doctors, BSc in Physiotherapy, and BSc in nursing, B-Pharm, They all are Members of BMDC, Veterinary Council, Nursing Council, and Pharmacy Council. Teachers are Dr. Suhana, MBBS, PGT, Dr. Anu, MBBS, PGT, Dr. Tisha, MBBS, PGT, Dr. Disha, MBBS, FCPS ( Part II), Dr. Benzir, MBBS, FCPS (Part II), Dr. Sakulur Rahman, MBBS, CCD (BIRDEM), Dr. Jannatul Aman, MBBS, PGT, Dr. Sanjana, BDS, Dental Surgeon, Dr. Juthi, BDS, Dental Surgeon, Dr. Danial Haque, MBBS, C-Card, Dr. Lamia, MBBS.
Subjects for Diploma in Medicine and Diploma in Surgery Course
Subjects for DMDS Course 4 Years:
1. Human Anatomy & Physiology-1, 2. General Chemistry & Pharmacology-1, 3. First Aid & Practice of Medicine-1, Study of OTC Drugs, Hematology-1 Pathology for Medical Practice, Cardiovascular Anatomy & Physiology, Medical Biochemistry, Surgery-1, Microbiology & Antimicrobial Drugs, Medical Diagnosis-1 & 2, Orthopedic Anatomy & Physiology, Microbiology and Pathology, Pharmacology-2, General Pathology, Anatomy & Physiology-2, Histology & Cytology, Practice of Medicine-2, Rhinology & Bronchology (Respiratory Disease & Treatment), Neuroanatomy & Physiology, Practice of Neuromedicine, Essential Drugs & Medicine, Gastro Anatomy & Physiology, Cardiovascular Drugs & Pharmacology, Gastrointestinal Drugs & Pharmacology, Cardiovascular Disease, Gynecological Disease, Dermatology, Diabetology, Urology, Hepatology.
Human Anatomy and Physiology for DMDS Course
The study of the Body Structure and its functions is Anatomy and Physiology. Here we discuss the systems of the Human Body and its Organs, Tissues, and Cells. The systems of the Human Body are the Digestive System, Respiratory System, Cardiovascular System, Skeletal System, Muscular System, Nervous System, Endocrine System, Immune System, Lymphatic System, Integumentary System, and Urinary System.
Pharmacology-1 for Diploma in Medicine & Diploma in Surgery Course
The study of Drugs and Medicine is called Pharmacology. Here we discuss group-wise drugs and their medicines in Pharmacology-1. Common Groups of Drugs are Pain Killer Drugs, Anti Ulcer Drugs, Anti Vomiting Drugs, Laxative Drugs, Motility Drugs, Antimotility Drugs, Bronchodilator Drugs, Antibiotic Drugs, Anti Fungal Drugs, Anti Protozoal Drugs, Anti Viral Drugs, Anthelmintic Drugs, Anti Hypertensive Drugs, Beta Blocker Drugs, Calcium Channel Blocker Drugs, ACE Inhibitor Drugs, Hemostatic Drugs, Analgesic Drugs, Antipyretic Drugs, Anti Thrombotic Drugs, etc.
First Aid for Diploma in Medicine & Diploma in Surgery Course
First Aid is an important subject for Medical Courses including Diplomas in Medicine& Surgery Course, RMP Courses, LMAF Courses, Paramedical Courses, DMA Courses, DMS Courses, Nursing Courses, Dental Courses, Pathology Courses, Physiotherapy Courses, Caregiver Courses, etc. Here we discuss Shock, Classification Shock, Causes of Shock, Stages of Shock, Clinical Features of Shock, Hypovolemic Shock, Cardiogenic Shock, Neurogenic Shock, Traumatic Shock, Burn Shock, Electric Shock, Psychogenic Shock, Anaphylactic Shock, First Aid of Shock, First Aid of Cut, First of Snake Bite, First Aid of Accidental Injury, etc.
Study of OTC Drugs for Diploma in Medicine & Diploma in Surgery Course
OTC Drugs are important for all Medical Assistant Courses, Diploma Medical Courses, LMAF Courses, and RMP Courses. It is also important for the Diploma in Medicine & Diploma in Surgery Course. These OTC Drugs can be sold or purchased without any prescription from Registered MBBS Doctors. These Drugs are Emergency and Safe for the patients. The study of OTC Drugs improves the quality of practice. Some OTC Drugs are Albendazole, Ascorbic Acid, Calcium, Multivitamins, Vitamin B Complex, Omeprazole, Oral Rehydration Salt, Salbutamol, etc.
Hematology and Pathology for Diploma in Medicine & Diploma in Surgery Course
The study of Blood and Blood Disease is called Hematology and the Study of Pathos and Process of Disease Creation and Diagnosis is called Pathology. In Hematology and Pathology, we discuss blood cells, their structure and functions, Blood Diseases, Common Pathos and their pathogenesis, Atrophy, Hypertrophy, Metaplasia, Gangrene, Pathological Tests like TC, DC, ESR, Hemoglobin Percentage, etc.
Microbiology and Antimicrobial Drugs for Diploma in Medicine and Diploma in Surgery Course
The Study of Microorganisms is called Microbiology. The Drugs that are used for the treatment of Infectious Diseases are Antimicrobial Drugs. Microorganisms are Bacteria, Protozoa, Fungus, and Virus. Antimicrobial Drugs are Antibiotic Drugs ( Antibacterial Drugs), Anti Protozoal Drugs, Anti Fungal Drugs, and Anti Viral Drugs. Antibacterial Drugs are Azithromycin, Erythromycin, Clarithromycin, Cefaclor, Cefixime, Cefuroxime, Ceftriaxone, Ciprofloxacin, Moxifloxacin, Doxicicline, Gentamycin, Neomycin, Flucloxacillin, Amoxicillin, Clindamycin, etc. Antiprotozoal Drugs are Metronidazole, Secnidazole, Tinidazole, Ornidazole, Nitazoxanide, etc. Antifungal Drugs are Fluconazole, Ketoconazole, Itraconazole, Econazole, Miconazole, Terbinafine, etc.
Cardiovascular Anatomy & Physiology for Diploma in Medine & Diploma in Surgery Course
Cardiovascular Anatomy is a branch of Anatomy, and Cardiovascular Physiology is a branch of Physiology. These two subjects are related to cardiology. Cardiovascular Anatomy and Physiology are being studied in a single subject for Diploma Medical Courses, Paramedical Courses, and All Short Medical Courses.
We discuss here the Anatomy of the Heart, Cardiac Chambers, Cardiac Valves, Cardiac Wall, Cardiac Septum, Right Heart, Left Heat, Function of Right Heat, Functions of Left Heart, Aorta, Venecava, Artery, Vein, Capillary, Pulmonary Blood Circulation, Cerebral Blood Circulation, Renal Blood Circulation, Hepatic Blood Circulation, Portal Vein and Portal Circulation, Heart Beat, Pulse, Pulse Rate, Tachycardia, Bradycardia, Blood Pressure, Normal Blood Pressure, Hypertension, Hypotension, Stroke Volume, Cardiac Output, Heart Failure, etc. This Subject is the most essential for the Diploma in Medicine and Diploma in Surgery Course.
Practice of Medicine for Diploma in Medicine & Diploma in Surgery Course
The study of Disease and Treatment is called the Practice of Medicine. This subject is important for a Diploma Medical Practitioner, Diploma Medical Assistant, and Rural Medical Practitioner. This subject discusses some common diseases. The discussion points for the Practice of Medicine are the Definition of Disease, Causes of Disease, Clinical Features of Disease ( Symptoms and Signs), Investigation of Disease, Treatment of Disease, Complication of Disease, and Advice for the Patients.
Dermatology for Diploma in Medicine & Diploma in Surgery Course
Dermatology. Mobile Phone Number 01797522136, 01987073965. The study of Skin Anatomy, Skin physiology, Skin Diseases, Diagnosis of Skin Diseases, Treatment of Skin Diseases, Complications of Skin Diseases, and Prevention of Skin Diseases is called Dermatology. Common Skin diseases and disorders are Tineasis, Candidiasis, Acne, Cold Sore, Blister, Hives, Actinic keratosis, Rosacea, Carbuncle, Latex allergy, Eczema, Psoriasis, Cellulitis, Measles, Basal cell carcinoma, Squamous cell carcinoma, Melanoma, Lupus, Contact dermatitis, Vitiligo, Warts, Chickenpox, Seborrheic eczema, Keratosis pilaris, Ringworm, Melasma, Impetigo, Temporary skin disorders, and Permanent Skin disorders. For more information, there are some courses at HRTD Medical Institute. These Courses are PDT Dermatology, PDT Skin VD, and PDT Medicine.
Practical Classes for Diploma in Medicine & Diploma in Surgery Course
Auscultation, Heart Beat, Heart Rate, Heart Sound, Pulse, Blood Pressure, Respiratory Rate, Inhaler, Rota Haler, Nebulizer, Blood Oxygen, Cyanosis, Blood Glucose (Diabetes), Body Temperature, Dehydration Test, Edema Test, Jaundice test, Anemia test, IM Injection, IV Injection, SC Injection, ID Injection, Saline Infusion, Cleaning, Dressing, Bandaging, Oxygen by Pulse Oximeter,
What are the branches of pathology?
Branches of Pathology
- General Pathology
- Systemic Pathology Or, Special Pathology
- Clinical Pathology
What do you know about Systemic Pathology?
Systemic Pathology is a branch of pathology that covers the morphologic features of various diseases. It mainly explains the etiology, pathogenesis, pathological changes, and clinicopathological relationship in combination with the cases.
Gynecological Disease for DMDS Course
Gynecological diseases are conditions that affect the female reproductive tract, including the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, and external genitalia. These can include infections, hormonal imbalances, benign or malignant tumors, menstrual disorders, and pregnancy-related conditions. Symptoms like abnormal bleeding, pelvic pain, and chronic conditions such as Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) are common. Early diagnosis and treatment by a gynecologist are crucial for managing these conditions and maintaining reproductive and overall health.
Common Gynecological Diseases
- Infections: Bacterial vaginosis, yeast infections, and sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are common causes of gynecological issues.
- Hormonal Imbalances: Conditions like PCOS, characterized by hormonal fluctuations and potential infertility, fall under this category.
- Benign Tumors: Uterine fibroids are non-cancerous growths that can cause heavy bleeding and pressure on other organs.
- Cancers: These include cervical cancer, ovarian cancer, and endometrial cancer, which can be serious public health challenges.
- Menstrual Disorders: Dysmenorrhea (painful periods) and heavy or abnormal bleeding can signal underlying issues and require investigation.
- Endometriosis: A condition where uterine-like tissue grows outside the uterus, leading to chronic pain.
- Pelvic Pain: Chronic pelvic pain (CPP) is persistent pain in the pelvic area unrelated to pregnancy and may indicate conditions like endometriosis or other issues.
Causes of Gynecological Diseases
- Hormonal Changes: Stress, anxiety, pregnancy, and menopause can disrupt hormone levels, increasing susceptibility to problems.
- Infections: Unprotected sexual activity and poor hygiene can introduce bacteria, viruses, or fungi, leading to infections.
- Genetic Factors: Family history of certain conditions, such as PCOS, can increase an individual’s risk.
- Lifestyle Factors: Poor hygiene, such as infrequent underwear changes or douching, can create an environment for infections to thrive.
Diagnosis and Treatment
- Diagnosis: Gynecological problems are diagnosed through methods like pelvic exams, Pap smears, colposcopy, biopsies, and ultrasounds.
- Treatment: Options range from monitoring and lifestyle changes to medication and, in some cases, surgery.
When to See a Doctor
Seek timely medical attention for symptoms such as abnormal vaginal bleeding, unusual discharge, chronic pelvic pain, or discomfort during intercourse, as early diagnosis is key to effective management.
Cardiovascular Disease for DMDS Course
cardiovascular disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is
a group of diseases affecting the heart and blood vessels. CVD is the leading cause of death globally, with the primary underlying cause in many cases being atherosclerosis, or the buildup of fatty plaques in the arteries.
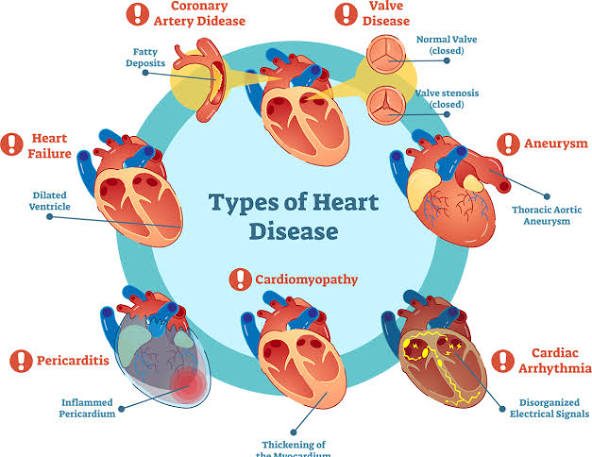
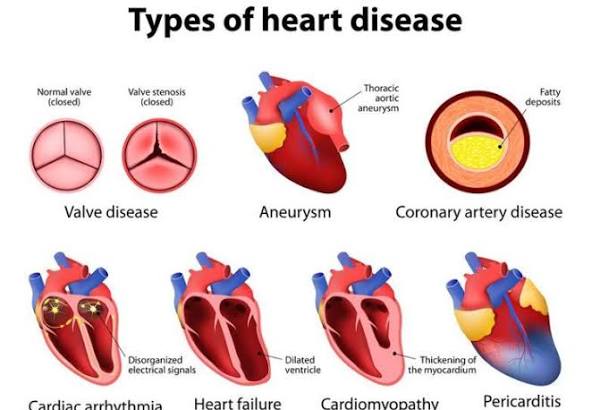
Types of cardiovascular disease
- Coronary Artery Disease (CAD): Also called coronary heart disease, this happens when plaque builds up in the arteries that supply blood to the heart. This can lead to angina (chest pain), heart attack, or heart failure.
- Cerebrovascular Disease: A disease of the blood vessels supplying the brain, which can cause a stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA).
- Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD): This involves blocked or narrowed arteries in the limbs, most commonly the legs and feet. It can cause cramping, numbness, or pain when walking.
- Heart Failure: Occurs when the heart cannot pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs. It can result from a heart attack, high blood pressure, or a weak heart muscle.
- Arrhythmia: An irregular heart rhythm, where the heart beats too fast, too slow, or erratically due to problems with its electrical system.
- Valvular Heart Disease: Affects the heart valves, which regulate blood flow between chambers. The valves may become narrowed (stenosis) or leaky (regurgitation).
- Aortic Disease: A problem with the body’s largest artery, the aorta. The most common condition is an aortic aneurysm, where the aorta bulges.
- Congenital Heart Disease: Heart defects that a person is born with, which affect the structure and function of the heart.
Common symptoms
Symptoms can vary depending on the specific condition but can include:
- Heart symptoms:
- Chest pain, pressure, heaviness, or discomfort (angina)
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue or exhaustion
- Dizziness or fainting
- Fluttering in the chest (palpitations)
- Symptoms of blockages in blood vessels:
- Pain, cramps, or sores in the legs
- Numbness or weakness in the face or limbs
- Trouble with speaking, seeing, or walking
Risk factors
Many factors can increase your risk of developing CVD, including:
- High blood pressure (hypertension)
- High cholesterol (hyperlipidemia)
- Tobacco use
- Diabetes
- Being overweight or obese
- Lack of physical activity
- Unhealthy diet
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Age and gender (risk increases with age and is generally higher in men)
- Family history
- Certain chronic conditions like kidney disease or autoimmune disorders
Treatment and prevention
Treatment for CVD depends on the specific condition and can range from lifestyle adjustments to surgical procedures.
Treatment options:
- Lifestyle changes: Making changes to diet, exercising regularly, and quitting smoking can help manage CVD.
- Medications: Doctors may prescribe medications to lower cholesterol (statins), manage blood pressure (beta-blockers), or prevent blood clots (antiplatelets).
- Procedures or surgery: For more advanced cases, options include angioplasty and stenting to clear blockages or coronary artery bypass surgery to restore blood flow.
- Cardiac rehabilitation: This is a supervised program of exercise and education to help strengthen the heart.
Prevention strategies:
- Avoid all tobacco products.
- Eat a heart-healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein, while limiting processed foods, saturated fats, sugar, and salt.
- Get at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week.
- Manage underlying health conditions like high blood pressure, cholesterol, and diabetes.
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Manage stress through relaxation techniques or other healthy coping mechanisms.
- Get regular health screenings to know your blood pressure, cholesterol, and blood sugar levels.
Diseases of Urinary System for DMDS Course
Diseases of the urinary system include common conditions such as urinary tract infections (UTIs), kidney stones, and urinary incontinence, as well as more serious issues like kidney failure, prostate problems in men, and various types of urinary tract cancers. These conditions affect the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra, and can be caused by infections, blockages, inflammation, or chronic health issues like diabetes. Symptoms vary but can include pain, changes in urination, and cloudy or bloody urine, while treatments range from antibiotics and self-care to medications and surgery, depending on the specific disorder.
Common Urinary System Diseases
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): Bacterial infections of any part of the urinary system, such as the bladder (cystitis) or kidneys (pyelonephritis).
- Kidney Stones: Hard deposits of mineral crystals that form in the kidneys and can block the flow of urine.
- Urinary Incontinence: The inability to control urine leakage from the urethra.
- Prostate Problems: Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) or prostate cancer in men can enlarge the prostate, obstructing the bladder and making urination difficult.
- Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD): A long-term condition where the kidneys are damaged and cannot filter blood properly.
Symptoms to Watch For
- Frequent, painful, or burning urination
- Cloudy, discolored (pink, red, or tea-colored), or strong-smelling urine
- Abdominal, pelvic, or back pain
- A frequent, urgent need to urinate
- Fever and chills, especially with a kidney infection
General Causes
- Bacterial infections: are a primary cause of UTIs.
- Blockages, such as enlarged prostate or kidney stones, impede urine flow.
- Inflammation: of the urinary tract, like interstitial cystitis, can cause chronic pain and discomfort.
- Chronic health conditions, such as diabetes, can lead to kidney damage.
- Cancer: affecting the urinary organs.
Orthopedic Anatomy for Diploma in Medicine and Diploma in Surgery Course
The main topics for orthopedic anatomy center on the comprehensive study of the musculoskeletal system (bones, muscles, joints, ligaments, tendons, and nerves) across various regions of the body. Key areas of study include regional anatomy, general principles of musculoskeletal health and injury, and specific pathologies and conditions.
I. Regional Anatomy
Orthopedic anatomy is often studied by body region, focusing on the specific bones, muscles, nerves, and vessels in each area and their surgical significance.
- Upper Limb: Shoulder, arm, elbow, forearm, wrist, and hand. This includes the study of the brachial plexus, major nerves (median, ulnar, radial), and common injuries like rotator cuff tears and carpal tunnel syndrome.
- Lower Limb: Hip, thigh, knee, leg, ankle, and foot. Key topics include the sciatic nerve, cruciate ligaments and meniscal injuries in the knee, and common fractures (femoral, ankle).
- Spine: The vertebral column and spinal cord, covering conditions like disc herniation, scoliosis, spinal stenosis, and traumatic injuries.
II. Foundational and General Principles
This area covers the basic science and general concepts that apply throughout the musculoskeletal system.
- Basic Sciences: Bone structure and function, function of joints, histology, embryology, and biomechanics.
- Imaging: Understanding and interpreting diagnostic modalities like X-rays, MRI, and CT scans.
- Fracture and Dislocation Management: General principles of injury, classification (e.g., Salter-Harris), healing processes, reduction, immobilization (casting, splinting), and internal/external fixation.
- Surgical Approaches: Knowledge of relevant anatomical landmarks and safe surgical techniques for specific regions.
III. Specific Diseases and Conditions
A major part of the subject involves the study of specific pathologies affecting the musculoskeletal system.
- Infections: Osteomyelitis and septic arthritis (e.g., Pott’s spine).
- Tumors: Diagnosis and management of benign and malignant bone tumors (e.g., osteosarcoma, giant cell tumor).
- Metabolic Diseases: Osteoporosis, rickets, osteomalacia, and Paget’s disease.
- Arthritis: Osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and gout.
- Pediatric Orthopedics: Congenital disorders such as clubfoot and developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH).
- Nerve Injuries: Traumatic and entrapment neuropathies like carpal tunnel syndrome and brachial plexus injuries.
- Sports Injuries: Common injuries to ligaments, tendons, and muscles.
For further information, resources are available from institutions such as the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS) or the National Institutes of Health (NIH) on Orthopedics.
Neuro Anatomy For Diploma in Medicine and Diploma in Surgery Course
Important topics in neuroanatomy include the central nervous system’s structure (cerebrum, brainstem, cerebellum, spinal cord), the cerebral cortex lobes, deep brain structures like the basal ganglia and thalamus, and the meninges and cerebrospinal fluid. Other crucial areas are the blood supply, cranial nerves, spinal tracts, and the limbic system, along with clinical correlations and the anatomy of injuries and diseases.
Brain structure and lobes
- Cerebrum: The largest part of the brain, divided into two hemispheres connected by the corpus callosum.
- Cerebral Lobes:
- Frontal Lobe: Responsible for motor function, problem-solving, memory, and language.
- Parietal Lobe: Processes sensory information.
- Temporal Lobe: Handles auditory information and memory.
- Occipital Lobe: The visual processing center.
- Brainstem: Connects the cerebrum to the spinal cord and includes the midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata.
- Cerebellum: Controls balance, coordination, and posture.
- Diencephalon: Includes the thalamus (relay center) and hypothalamus (homeostasis).
Other key structures and systems
- Basal Ganglia: Located deep in the brain, involved in motor control.
- Limbic System: A group of structures involved in emotion, memory, and motivation.
- Meninges and Ventricular System: The protective layers (dura mater, arachnoid mater, pia mater) and fluid-filled cavities within the brain.
- Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF): The fluid that circulates in and around the brain and spinal cord.
Functional pathways and nerves
- Spinal Cord Tracts: Ascending (sensory) and descending (motor) pathways that connect the brain and the rest of the body.
- Cranial Nerves: The 12 pairs of nerves that originate directly from the brain and control functions of the head and neck.
- Blood Supply: The arteries and veins that supply the brain, including the Circle of Willis.
Clinical and developmental topics
- Clinical Correlations: Understanding how specific anatomical structures relate to symptoms of neurological diseases and injuries is crucial.
- Neurodevelopment: The formation of the nervous system, including the neural tube, is a high-yield topic for understanding congenital conditions like spina bifida and anencephaly.
- Brain Hemorrhage: Types and locations of bleeding in the brain.
Histology & Cytology Diploma in Medicine and Diploma in Surgery Course
The most important topics in histology and cytology revolve around the structure, function, and organization of the four basic tissue types (epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous) and the cellular components and processes that form them. Understanding these is essential for diagnosing diseases.
Core Cytology Topics
Cytology focuses on the individual cell and its components.
- Cellular Organelles: Structure and function of the nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, ribosomes, lysosomes, peroxisomes, and the cell membrane.
- Cell Cycle and Division: The process of mitosis and cell renewal.
- Cellular Specializations: Surface modifications like microvilli, cilia, and flagella, and cell junctions (e.g., tight junctions).
- Transport Mechanisms: How substances move across the cell membrane (e.g., endocytosis and exocytosis).
- Cell Injury and Death: Understanding reversible and irreversible cell injury, necrosis, and apoptosis.
- Diagnostic Techniques: The use of fine needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) and Pap smears for disease screening, particularly cancer.
Core Histology Topics
Histology examines how cells organize into tissues and organs, focusing on microscopic anatomy.
The Four Primary Tissues
- Epithelial Tissue:
- Classification of lining epithelia (simple, stratified, squamous, cuboidal, columnar, transitional, pseudostratified).
- Structure and function of glandular epithelia (exocrine and endocrine glands).
- Connective Tissue:
- Components: Cells (fibroblasts, adipocytes, etc.) and extracellular matrix (fibers and ground substance).
- Types: Connective tissue proper (loose and dense), cartilage (hyaline, elastic, fibrous), bone tissue, blood, and lymph.
- Muscle Tissue:
- Types: Skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle.
- Structure of the myofibril and the mechanism of muscle contraction.
- Nervous Tissue:
- Components: Neurons and glial cells.
- Structure of nerve fibers, synapses, and impulse transmission.
Organ Systems Histology
Applying the basic tissue knowledge to understand the microscopic structure of major organs is critical:
- Cardiovascular system (heart, arteries, capillaries, veins)
- Respiratory system (trachea, lungs, alveoli)
- Digestive system (esophagus, stomach, intestines, liver, pancreas)
- Excretory/Urinary system (kidneys, ureters, bladder)
- Endocrine glands (thyroid, adrenal, etc.)
- Lymphoid organs (spleen, lymph nodes)
- Reproductive systems (testis, ovary, uterus)
- Integumentary system (skin)
Key Practical & Diagnostic Skills
- Microscopy: Proficiency in using optical and electron microscopes.
- Histological Techniques: Understanding tissue preparation, fixation, sectioning, and essential staining methods like Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E).
- Slide Identification: The ability to identify different tissues and their pathologies from prepared slides or images.
For further study resources, students can often find materials and even virtual slides on university websites (e.g., histology.be).
Rhinology & Bronchology For Diploma in Medicine and Diploma in Surgery Course
In Rhinology (the study of the nose and sinuses) and Bronchology (the study of the airways including the bronchi), the very important topics cover anatomy, pathophysiology, common diseases, diagnostic techniques, and advanced surgical procedures.
Rhinology (Nose and Sinuses)
Key topics in rhinology include:
- Anatomy and Physiology: Detailed understanding of the nasal cavity, paranasal sinuses, and the mechanics of nasal breathing and olfaction (sense of smell).
- Inflammatory Conditions:
- Allergic Rhinitis: A very common condition involving inflammation of the nasal cavity due to allergens.
- Chronic Rhinosinusitis (CRS): Persistent inflammation of the sinuses, with or without nasal polyps, which can be severe and intractable in cases of eosinophilic infiltration (ECRS).
- Structural Abnormalities:
- Nasal Septal Deviation: A common cause of nasal obstruction that often requires septoplasty.
- Turbinate Hypertrophy: Enlargement of the turbinates leading to airway obstruction.
- Epistaxis (Nosebleeds): Management, including laser applications for conditions like Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia (HHT).
- Surgical Techniques:
- Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery (FESS): A minimally invasive approach for treating sinus disorders.
- Image-Guided Surgery (IGS): Advanced technology used for precise sinus and skull base surgeries.
Bronchology (Airways and Lungs)
Key topics in bronchology primarily revolve around the diagnosis and management of airway diseases using specialized tools:
- Anatomy and Physiology: Understanding the larynx, trachea, bronchi, and lungs.
- Airway Obstruction: Management of central airway obstruction (CAO) due to both malignant and non-malignant causes.
- Diagnostic and Therapeutic Procedures:
- Bronchoscopy: An essential tool, often involving both flexible and rigid techniques.
- Foreign Body Removal: A critical application of rigid bronchoscopy, especially in children.
- Airway Stenting: Placement of silicone or other stents to maintain airway patency.
- Ablative Therapies: Techniques like laser, electrocautery, and cryotherapy used during bronchoscopy.
- Common Diseases:
- Bronchial Asthma: Chronic inflammatory disease of the airways.
- Bronchiectasis: Permanent enlargement of parts of the airways.
- Lung Cancer: Diagnosis and staging using bronchoscopic techniques.
Interdisciplinary Overlap
Both fields share an emphasis on airway management and often overlap in the management of systemic diseases with sinonasal or bronchial manifestations, such as cystic fibrosis (CF) or certain autoimmune conditions. The use of modern imaging (CT and MRI) and endoscopic techniques is vital in both subspecialties.
Medical Biochemistry For Diploma in Medicine and Diploma in Surgery Course
Key topics in medical biochemistry include metabolism (carbohydrates, lipids, amino acids), molecular biology (DNA replication, transcription, translation), and enzymology (kinetics, inhibition). Other important areas are bioenergetics, cell biology, genetic disorders, and clinical biochemistry, which involves understanding tests and metabolic diseases.
Metabolism
- Carbohydrates: Glycolysis, gluconeogenesis, citric acid cycle, pentose phosphate pathway, and glycogen metabolism.
- Lipids: Fatty acid oxidation, ketogenesis, cholesterol metabolism, and lipoprotein function.
- Amino Acids: Urea cycle, transamination, and major metabolic disorders like phenylketonuria (PKU) and Maple Syrup Urine Disease (MSUD).
Molecular Biology and Genetics
- DNA and RNA: Replication, transcription, translation, genetic code, and mutations.
- Gene Regulation: Operons, like the lac operon.
- Biotechnology: Recombinant DNA technology, PCR, and blotting techniques.
Enzymes and Bioenergetics
- Enzymes: Classification, kinetics, factors affecting enzyme activity (like pH), and inhibitors.
- Bioenergetics: Oxidative phosphorylation, electron transport chain (ETC), and ATP production.
Clinical and Other Topics
- Clinical Biochemistry: Liver function tests, kidney function tests, and acid-base balance.
- Inborn Errors of Metabolism: Understanding the metabolic basis of diseases and their associated biochemical pathways.
- Vitamins and Minerals: Functions, deficiency diseases, and their role as coenzymes.
General Pathology For Diploma in Medicine and Diploma in Surgery Course
Important topics in general pathology include cell injury, inflammation, neoplasia, and genetic diseases. Other key areas are healing and repair, hemodynamic disorders (like shock and edema), immunopathology, and infectious diseases. Understanding the fundamental concepts of disease, such as etiology, pathogenesis, and clinical significance, is crucial across all topics.
Fundamental disease processes
- Cell Injury: Covers reversible and irreversible injury, different types of cell death (necrosis and apoptosis), and their mechanisms.
- Inflammation: Includes the vascular and cellular responses, acute and chronic inflammation, and the types of cells involved.
- Healing and Repair: Focuses on the body’s response to injury, including tissue repair and regeneration.
- Hemodynamic Disorders: Explains conditions like edema, hemorrhage, embolism, and shock.
Diseases based on cause
- Genetic Diseases: Covers basic concepts of inheritance and chromosomal aberrations.
- Immunopathology: Studies the diseases related to the immune system, including hypersensitivity reactions.
- Infectious Diseases: Examines how microorganisms cause disease.
Neoplasia (Cancer)
- Benign vs. Malignant Tumors: Differentiates between the two types of tumors.
- Tumor Biology: Explains concepts like oncogenes, tumor suppressor genes, and the process of carcinogenesis.
- Diagnosis and Clinical Features: Covers how to diagnose cancer through lab tests and describes the clinical effects.
Other important topics
- Metabolic Diseases: Includes conditions like fatty liver.
- Tissue-Specific Pathology: While general pathology covers the basic principles, understanding how these principles apply to different organ systems like the heart, kidney, and liver is crucial for systemic pathology.
Practice of Neuromedicine For Diploma in Medicine and Diploma in Surgery Course
Key topics in the practice of neuromedicine (neurology) cover the diagnosis, management, and treatment of disorders affecting the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves. Important areas for study and practice include major disease categories, clinical methods, and diagnostic techniques.
Core Areas and Important Topics
The field of neuromedicine encompasses a wide range of conditions and functions:
- Vascular Neurology/Stroke: This is a critical area, covering ischemic stroke, intracerebral hemorrhage, subarachnoid hemorrhage, and transient ischemic attacks (TIAs). Key topics include risk factors, acute management (e.g., endovascular therapy), and rehabilitation.
- Epilepsy and Seizures: Topics involve the classification of seizures, management of epilepsy with anti-epileptic drugs, and the emergency management of status epilepticus.
- Movement Disorders: This includes conditions such as Parkinson’s disease, Huntington’s disease, and essential tremor, focusing on clinical features, underlying mechanisms (e.g., dopamine loss), and treatment strategies.
- Demyelinating Diseases: Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a primary focus, covering its inflammatory role, various treatment options, and long-term management.
- Neurodegenerative Disorders: Important topics include Alzheimer’s disease, various dementias, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), emphasizing early diagnosis and potential new therapies.
- Headache and Pain Management: Migraine and other headache disorders, as well as general neurological pain syndromes, are a significant part of practice.
- Infections and Immunologic Disorders: This includes conditions like meningitis (tubercular vs. pyogenic), encephalitis, and autoimmune neurological disorders.
- Neurotrauma: Management of traumatic brain and spinal cord injuries.
- Sleep Disorders: Diagnosis and management of conditions affecting sleep and circadian rhythms.
- Neuro-oncology: Diagnosis and treatment of brain and spinal cord tumors.
Essential Clinical Skills
A strong foundation in clinical methods remains paramount in neuromedicine practice.
- Neurological Examination: Meticulous examination of coordination, gait, mental status, reflexes, sensation, speech, strength, and vision is essential for accurate topographical diagnosis.
- History Taking: A thorough patient history remains the most important diagnostic tool for many conditions, such as headache and epilepsy.
- Diagnostic Interpretation: Neurologists must be proficient in requesting and analyzing results from neuroimaging (CT, MRI), electroencephalography (EEG), nerve conduction studies/electromyography (NCS/EMG), and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analysis.
Emerging and Trending Topics
The field is constantly evolving with advances in research and technology.
- Neuroplasticity and Rehabilitation: Understanding how the brain can rewire itself after injury (e.g., stroke) and the development of effective rehabilitation methods.
- Genomics and Biomarkers: The use of genetic testing and liquid biopsies for diagnosis and personalized treatment approaches.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Neurology: Application of AI in diagnosing conditions from scans, interpreting EEGs, and predicting disease progression.
- Preventive Neurology: A growing focus on brain health and preventive approaches to reduce the incidence of neurological disorders.
For more in-depth information, professional resources include the American Academy of Neurology (AAN) and the Royal College of Nursing Neuroscience nursing section.
Value of Diploma in Medicine and Diploma in Surgery Course
Diploma in Medicine and Diploma in Surgery courses can hold significant value in Bangladesh, given the country’s healthcare landscape and the increasing demand for skilled healthcare professionals. Diploma in Medicine and Diploma in Surgery courses and specialized training to individuals who work alongside doctors, nurses, and other medical professionals to support patient care and medical procedures. HRTD Medical Institute is a good DMDS located at Mirpur 10 Gol-Chattor, Dhaka, Bangladesh.
Here are several reasons why these courses can be valuable in Bangladesh:
বাংলাদেশে এই কোর্সগুলো মূল্যবান হওয়ার কয়েকটি কারণ এখানে রয়েছে:
Addressing Healthcare Workforce Shortages: Bangladesh, like many developing countries, faces shortages in its healthcare workforce. Diploma in Medicine and Diploma in Surgery courses can help bridge this gap by quickly training individuals in specific medical skills, allowing them to contribute to patient care without undergoing lengthy medical school education. HRTD Medical Institute is the best DMDS in Bangladesh. Online and offline DMDS are available here.
*Faster Entry into Healthcare: Medical school requires several years of education, whereas Diploma in Medicine and Diploma in Surgery courses can be completed in a shorter time frame. This enables individuals to enter the healthcare workforce more quickly, especially in roles such as medical technicians, radiology technicians, and laboratory assistants.
*Cost-Effectiveness: Traditional medical education can be expensive and time-consuming. Diploma in Medicine and Diploma in Surgery courses tend to be more affordable and can be completed without the need for extended periods of study, making them accessible to a wider range of individuals. HRTD Medical Institute is a good Diploma in Medicine and Diploma in Surgery courses where all paramedical and Diploma Medical Courses are available at reasonable prices.
*Focused Skill Development: DMDS courses are designed to provide specific skills and knowledge needed for particular roles within the healthcare sector. This focused training ensures that DMDS are well-equipped to handle the responsibilities of their chosen profession.
ফোকাসড স্কিল ডেভেলপমেন্ট: DMDS কোর্সগুলি স্বাস্থ্যসেবা সেক্টরের মধ্যে নির্দিষ্ট ভূমিকার জন্য প্রয়োজনীয় নির্দিষ্ট দক্ষতা এবং জ্ঞান প্রদানের জন্য ডিজাইন করা হয়েছে। এই কেন্দ্রীভূত প্রশিক্ষণ নিশ্চিত করে যে DMDS তাদের নির্বাচিত পেশার দায়িত্বগুলি পরিচালনা করার জন্য সুসজ্জিত।
*Diverse Career Opportunities: DMDS courses offer a range of career options, including medical laboratory technology, radiology technology, anesthesia technology, operation theater technology, and more. This diversity allows individuals to select a field that aligns with their interests and strengths. HRTD Medical Institute is the best Diploma in Medicine and Diploma in Surgery courses that offers some unique courses like DMSc ( Diploma in Medical Science). Students of this DMSc course can choose a career in First Aid DMDS Sector Dental Technology Sector Physiotherapy Technology Sector Nursing Technology Sectors etc.
*Contribution to Patient Care: Paramedical professionals play a crucial role in patient care by assisting doctors and nurses in various medical procedures, diagnostic tests, and treatments. Their presence helps alleviate the workload of other healthcare providers, leading to improved patient care.
*রোগীর যত্নে অবদান: প্যারামেডিক্যাল পেশাদাররা বিভিন্ন চিকিৎসা পদ্ধতি, ডায়াগনস্টিক পরীক্ষা এবং চিকিৎসায় ডাক্তার ও নার্সদের সহায়তা করে রোগীর যত্নে গুরুত্বপূর্ণ ভূমিকা পালন করে। তাদের উপস্থিতি অন্যান্য স্বাস্থ্যসেবা প্রদানকারীদের কাজের চাপ কমাতে সাহায্য করে, যা উন্নত রোগীর যত্নের দিকে পরিচালিত করে।
*Rising Demand: As healthcare services expand and modernize in Bangladesh, there’s a growing need for skilled paramedical professionals who can contribute to specialized areas of medical care. Diploma in Medicine and Diploma in Surgery DMDS Courses can help meet this demand.
*Flexibility: DMDS courses often offer flexible learning options, including part-time or online courses. This flexibility is especially beneficial for individuals who may need to balance their studies with work or other commitments.
* ক্রমবর্ধমান চাহিদা: বাংলাদেশে স্বাস্থ্যসেবা পরিষেবাগুলি প্রসারিত এবং আধুনিকীকরণের সাথে সাথে দক্ষ DMDS পেশাদারদের একটি ক্রমবর্ধমান প্রয়োজন যারা চিকিৎসা যত্নের বিশেষ ক্ষেত্রে অবদান রাখতে পারে। প্যারামেডিক্যাল কোর্স এই চাহিদা মেটাতে সাহায্য করতে পারে।
*Career Progression: Many DMDS courses provide a foundation for further career advancement. Post DMDS training and Post Diploma Training are available after completing DMDS Courses or Diploma Courses. These courses are post-paramedical training in cardiology, Post diploma training in cardiology, post-DMDS in gastrology, post-diploma training in gastrology, post-DMDS training in gynecology, post-diploma training in gynecology, post-DMDS training in dermatology, post diploma training in dermatology, post DMDS training ophthalmology, post diploma training in ophthalmology, post DMDS training in diabetology, post diploma training in diabetology.
In conclusion, paramedical short courses can hold significant value in Bangladesh by addressing healthcare workforce shortages, providing faster entry into the healthcare sector, offering cost-effective training, and contributing to patient care. These courses can play a vital role in strengthening the healthcare system and improving overall healthcare services in Bangladesh.
উপসংহারে, প্যারামেডিক্যাল শর্ট কোর্সগুলি স্বাস্থ্যসেবা কর্মশক্তির ঘাটতি মোকাবেলা করে, স্বাস্থ্যসেবা খাতে দ্রুত প্রবেশের ব্যবস্থা করে, সাশ্রয়ী মূল্যের প্রশিক্ষণ প্রদান করে এবং রোগীর যত্নে অবদান রাখার মাধ্যমে বাংলাদেশে উল্লেখযোগ্য মূল্য ধরে রাখতে পারে। এই কোর্সগুলো বাংলাদেশের স্বাস্থ্যসেবা ব্যবস্থাকে শক্তিশালী করতে এবং সামগ্রিক স্বাস্থ্যসেবা পরিষেবার উন্নতিতে গুরুত্বপূর্ণ ভূমিকা পালন করতে পারে।
Why DMDS Courses are important for a human being?
মহান আল্লাহ রাব্বুল আলআমিন মানুষকে যে জীবন দান করেছেন তার ধারক হিসেবে দিয়েছেন দেহকে । এই দেহকে ভালোভাবে জানতে পারা, এর পরিচর্যা করা, রক্ষনাবেক্ষন করতে পারা প্রত্যেকটি মানুষের জন্য ফরজ বলে আমি মনে করি । একজন ড্রাইভার যদি ড্রাইভিং এর পাশাপাশি তার গাড়ির প্রাথমিক পরিচর্যা, রক্ষনাবেক্ষন না করতে পারে তবে তাকে মাঝে মাঝে বড় ধরনের সমস্যায় পড়তেই হবে । আর যদি গাড়ির পরিচর্যা, প্রাথমিক মেকানিক, রক্ষনাবেক্ষন ইত্যাদি বিষয়ে জ্ঞান অর্জন করে, দক্ষতা এবং অভিজ্ঞতা অর্জন করে, তবে পথের মাঝে গাড়ি নষ্ট হলেও সে প্রাথমিক ভাবে সারিয়ে নিতে পারবে এবং পরবর্তিতে গাড়ি ড্রাইভ করে ভালো মানের ইন্জিনিয়ারিং সোপে নিয়ে গাড়ি ঠিক করে নিতে পারবে ।
একজন মানুষের ক্ষেত্রেও ঠিক তেমনি । দেহ সম্পকে জ্ঞান, দেহের প্রাথমিক পরিচর্যা, দেহের রক্ষনাবেক্ষন, দেহের প্রাথমিক চিকিৎসা ইত্যাদি বিষয়ে জ্ঞান, দক্ষতা এবং অভিজ্ঞতা অর্জন করলে সারাটা জীবন দেহটাকে সুন্দরভাবে পরিচালনা করা যায়, বেশি অসুস্থ্য হলে সঠিক সময়ে সঠিক ডাক্তারের কাছে গিয়ে সঠিক চিকিৎসা নেয়া যায় ।
Almighty Allah Rabbul Alamin has given the body as the container of the life He has given to man. I think it is a duty for every human being to know this body well, take care of it, and protect it. If a driver is not able to take basic care and maintenance of his car along with driving, then he has to face big problems at times. And if he acquires knowledge, skills and experience in car maintenance, basic mechanics, maintenance, etc., even if the car breaks down on the way, he can fix it initially and later drive the car and fix the car with good quality engineering soap.
The same is the case with a human being. If you acquire knowledge, skills and experience about the body, basic care of the body, maintenance of the body, basic treatment of the body, you can manage the body beautifully throughout your life, if you are very sick, you can go to the right doctor at the right time and get the right treatment.
Online DMDS Course in HRTD Paramedical Training Center
Online and Offline DMDS Training Center. Mobile Phone 01797522136, 01987073965. You can do DMDS course online or offline with us here. Weekly classes three days three hours. But for working people it is three hours in a day. Class days are Friday, Saturday and Monday. Morning batch from 9 am to 12 pm. Afternoon batch from 3 pm to 6 pm. Students who take online classes are given practical classes at their convenient time so that they don’t face any kind of problem.
Authority, DMDS Course Training Center, HRTD Limited, Mirpur-10 Gol-Chattar, Dhaka.
আপনি অনলাইনে বা অফলাইনে আমাদের এখানে DMDS কোর্স করতে পারবেন । সাপ্তাহিক ক্লাস তিন দিনে তিন ঘন্টা । তবে চাকরি জীবিদের জন্য একদিনেেই তিন ঘন্টা । ক্লাসের দিন গুলি হলো শুক্রবার, শনিবার এবং সোমবার । সকালের ব্যাচ ৯ টা থেকে ১২ টা । বিকেলের ব্যাচ ৩ টা থেকে ৬ টা । যে সকল ছাত্র ছাত্রী অনলাইনে ক্লাস করেন তাদের প্রাকটিকেল ক্লাস তাদের সবিধাজনক সময়ে দেওয়া হয় যাতে করে তারা কোন ধরনের সমস্যায় না পরেন ।
Offline DMDS Course in HRTD DMDS
Offline and Online DMDS Training Center. Mobile Phone 01797522136, 01987073965. You can do DMDS course online or offline with us here. Weekly classes three days three hours. But for working people it is three hours in a day. Class days are Friday, Saturday and Monday. Morning batch from 9 am to 12 pm. Afternoon batch from 3 pm to 6 pm. Students who take online classes are given practical classes at their convenient time so that they don’t face any kind of problem.
Authority, DMDS Course Training Center, HRTD Limited, Mirpur-10 Gol-Chattar, Dhaka.
আপনি অফলাইনে বা অনলাইনে আমাদের এখানে প্যারামেডিকেল কোর্স করতে পারবেন । সাপ্তাহিক ক্লাস তিন দিনে তিন ঘন্টা । তবে চাকরি জীবিদের জন্য একদিনেেই তিন ঘন্টা । ক্লাসের দিন গুলি হলো শুক্রবার, শনিবার এবং সোমবার । সকালের ব্যাচ ৯ টা থেকে ১২ টা । বিকেলের ব্যাচ ৩ টা থেকে ৬ টা । যে সকল ছাত্র ছাত্রী অনলাইনে ক্লাস করেন তাদের প্রাকটিকেল ক্লাস তাদের সবিধাজনক সময়ে দেওয়া হয় যাতে করে তারা কোন ধরনের সমস্যায় না পরেন ।
 HRTD Medical Institute
HRTD Medical Institute





